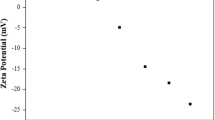Abstract
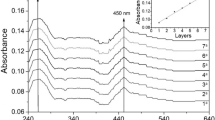
This work aimed to develop cantilever nanobiosensor functionalized with tyrosinase enzyme to detect 17β-estradiol and estrone hormones. In this system, the tyrosinase enzyme was covalently immobilized by self-assembled monolayer onto the cantilever sensor surface. It was possible to verify that the high hormone concentration investigated resulted in high voltage response. The nanobiosensor presented a distinction between the concentrations evaluated and was verified sensitivities of 0.497 and 0.101 V/μg, limit of detection of 0.1 and 0.4 ng/L for the hormones 17β-estradiol and estrone, respectively. The device showed good reversibility and during 30 days of storage maintained about 99% of the original signal. The cantilever nanobiosensor applied in different water samples (ultrapure, river, tap, and mineral) showed good performance, so could be readily extended toward the on-site monitoring of the other trace small molecular pollutants in environmental water matrices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, C., He, M., & Lin, Q. (2019). Selective detection of water pollutants using a differential aptamer-based graphene biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 126, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.047.
Kase, R., Javurkova, B., Simon, E., Swart, K., Buchinger, S., Könemann, S., et al. (2018). Screening and risk management solutions for steroidal estrogens in surface and wastewater. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 102, 343–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.02.013.
Vigneshvar, S., Sudhakumari, C. C., Senthilkumaran, B., & Prakash, H. (2016). Recent advances in biosensor technology for potential applications – an overview. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2016.00011.
Liu, S., Cheng, R., Chen, Y., Shi, H., & Zhao, G. (2018). A simple one-step pretreatment, highly sensitive and selective sensing of 17β-estradiol in environmental water samples using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 254, 1157–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.003.
Busayapongchai, P., & Siri, S. (2017). Sensitive detection of estradiol based on ligand binding domain of estrogen receptor and gold nanoparticles. Analytical Biochemistry, 518, 60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.11.003.
Alonso, J. M., Bielen, A. A. M., Olthuis, W., Kengen, S. W. M., Zuilhof, H., & Franssen, M. C. R. (2016). Self-assembled monolayers of 1-alkenes on oxidized platinum surfaces as platforms for immobilized enzymes for biosensing. Applied Surface Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.006.
Della Ventura, B., Iannaccone, M., Funari, R., Pica Ciamarra, M., Altucci, C., Capparelli, R., & Velotta, R. (2017). Effective antibodies immobilization and functionalized nanoparticles in a quartz-crystal microbalance-based immunosensor for the detection of parathion. PLoS One, 12(2), e0171754. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171754.
Sýs, M., & Vytřas, K. (2018). Tyrosinase electrochemical biosensors monitoring medicinally significant substances. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 25(33), 3988–4006. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170727121327.
El Harrad, L., Bourais, I., Mohammadi, H., & Amine, A. (2018). Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors based on enzyme inhibition for clinical and pharmaceutical applications. Sensors, 18(2), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010164.
Varmira, K., Mohammadi, G., Mahmoudi, M., Khodarahmi, R., Rashidi, K., Hedayati, M., & Jalalvand, A. R. (2018). Fabrication of a novel enzymatic electrochemical biosensor for determination of tyrosine in some food samples. Talanta, 183, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.053.
Camargo, J. R., Baccarin, M., Raymundo-Pereira, P. A., Campos, A. M., Oliveira, G. G., Fatibello-Filho, O., & Janegitz, B. C. (2018). Electrochemical biosensor made with tyrosinase immobilized in a matrix of nanodiamonds and potato starch for detecting phenolic compounds. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1034, 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.06.001.
Zaidi, K. U., Ali, A. S., Ali, S. A., & Naaz, I. (2014). Microbial tyrosinases: promising enzymes for pharmaceutical, food bioprocessing, and environmental industry. Biochemistry Research International, 2014, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/854687.
Marques De Oliveira, R., Ferreira, J., Santos, M. J. L., Faria, R. M., & Oliveira, O. N. (2011). Probing the functionalization of gold surfaces and protein adsorption by PM-IRRAS. ChemPhysChem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201100080.
Tagliazucchi, M., De Leo, L. P. M., Cadranel, A., Baraldo, L. M., Völker, E., Bonazzola, C., & Zamlynny, V. (2010). PM IRRAS spectroelectrochemistry of layer-by-layer self-assembled polyelectrolyte multilayers. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2010.02.013.
Muenchen, D. K., Martinazzo, J., Brezolin, A. N., de Cezaro, A. M., Rigo, A. A., Mezarroba, M. N., Manzoli, A., Steffens, J., & Steffens, C. (2018). Cantilever functionalization using peroxidase extract of low cost for glyphosate detection. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 186(4), 1061–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2799-y.
Martinazzo, J., Muenchen, D. K., Brezolin, A. N., Cezaro, A. M., Rigo, A. A., Manzoli, A., et al. (2018). Cantilever nanobiosensor using tyrosinase to detect atrazine in liquid medium. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part B Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 53(4), 229–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2017.1421833.
Lu, L., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Huan, S., Shen, G., & Yu, R. (2010). A novel tyrosinase biosensor based on hydroxyapatite–chitosan nanocomposite for the detection of phenolic compounds. Analytica Chimica Acta, 665(2), 146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.03.033.
Lavrik, N. V., Sepaniak, M. J., & Datskos, P. G. (2004). Cantilever transducers as a platform for chemical and biological sensors. Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(7), 2229–2253. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1763252.
Datskos, P. G., & Sauers, I. (1999). Detection of 2-mercaptoethanol using gold-coated micromachined cantilevers. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 61(1–3), 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(99)00251-8.
CONAMA. (2005). Resolução n° 357, DE 17 DE MARÇO DE 2005.
European Commission. (2012). Directive of the European parliament and of the council amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy, COM (2011).
Daniel, M. D. S., & De Lima, E. C. (2014). Determinação simultânea de estriol, β-estradiol, 17α-etinilestradiol e estrona empregando-se extração em fase sólida (SPE) e cromatografia líquida de alta eficiência (HPLC). Ambiente e Agua - An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Science, 9(4). https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.1346.
Manickum, T., John, W., & Mlambo, Z. D. (2016). Development and validation of a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry test method for screening and quantitation of steroid estrogens (endocrine disruptor compounds) in water and wastewater using large volume injection. Annals of Chromatography and Separation Techniques, 2(2473–0696).
Sodré, F. F., Locatelli, M. A. F., & Jardim, W. F. (2010). Occurrence of emerging contaminants in Brazilian drinking waters: a sewage-to-tap issue. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 206(1–4), 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0086-9.
Moreira, M., Aquino, S., Coutrim, M., Silva, J., & Afonso, R. (2011). Determination of endocrine-disrupting compounds in waters from Rio das Velhas, Brazil, by liquid chromatography/high resolution mass spectrometry (ESI-LC-IT-TOF/MS). Environmental Technology, 32(12), 1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2010.537829.
Torres, N. H., Aguiar, M. M., Ferreira, L. F. R., Américo, J. H. P., Machado, Â. M., Cavalcanti, E. B., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2015). Detection of hormones in surface and drinking water in Brazil by LC-ESI-MS/MS and ecotoxicological assessment with Daphnia magna. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(6), 379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4626-z.
Stredansky, M. (2017). Multienzyme amperometric gluconic acid biosensor based on nanocomposite planar electrodes for analysis in musts and wines. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 1183–1192. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.02.31.
Welch, C. M., & Compton, R. G. (2006). The use of nanoparticles in electroanalysis: a review. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 384(3), 601–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0230-3.
Yogeswaran, U., & Chen, S.-M. (2008). A review on the electrochemical sensors and biosensors composed of nanowires as sensing material. Sensors, 8(1), 290–313. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8010290.
Sassolas, A., Blum, L. J., & Leca-Bouvier, B. D. (2012). Immobilization strategies to develop enzymatic biosensors. Biotechnology Advances, 30(3), 489–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.09.003.
Silvério, M. D. O., Castro, C. F. S., & Miranda, A. R. (2013). Avaliação da atividade antioxidante e inibitÃ\textthreesuperiorria da tirosinase das folhas de Dipteryx alata Vogel (Baru). Revista Brasileira de Plantas Medicinais, 15, 59–65 Retrieved from http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-05722013000100008&nrm=iso.
Zolghadri, S., Bahrami, A., Hassan Khan, M. T., Munoz-Munoz, J., Garcia-Molina, F., Garcia-Canovas, F., & Saboury, A. A. (2019). A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2018.1545767.
Lee, K. E., Bharadwaj, S., Yadava, U., & Kang, S. G. (2019). Evaluation of caffeine as inhibitor against collagenase, elastase and tyrosinase using in silico and in vitro approach. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 34(1), 927–936. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2019.1596904.
Liu, X., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Feng, H., Liu, X., & Wong, D. K. Y. (2012). Detection of estradiol at an electrochemical immunosensor with a Cu UPD|DTBP–Protein G scaffold. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 35(1), 56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.02.002.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank URI Erechim for the infrastructure.
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 00,1, Cnpq, Fapergs, and Finep.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Cezaro, A.M., Rigo, A.A., Martinazzo, J. et al. Cantilever Nanobiosensor Functionalized with Tyrosinase for Detection of Estrone and β-estradiol in Water. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 190, 1512–1524 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03195-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03195-8