Abstract
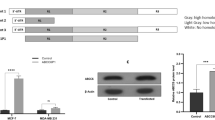
Arsenic is one of the most widespread global environmental toxicants associated with endemic poisoning. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins are transmembrane channels that transport and dispose of lipids and metabolic products across the plasma membrane. The majority of ABC family members (including ABCB1 and ABCC1) are reported to play a role in the development of arsenic and drug resistance in mammals. Previously, we established a human arsenic-resistant ECV-304 (AsRE) cell line and identified ABCA1 as a novel arsenic resistance gene. In the current study, we further investigated the potential contribution of ABCA1, ABCB1, and ABCC1 to arsenic resistance through measurement of survival rates and arsenic accumulation in AsRE cells with RNA interference. The arsenic resistance capacity of ABCC1 was the strongest among the three genes, while those of ABCA1 and ABCB1 were similar. Double or triple gene knockdown of ABCA1, ABCB1, and ABCC1 via RNA interference led to a decrease significant in arsenic resistance when ABCA1/ABCB1 or ABCB1/ABCC1 were simultaneously silenced. Interestingly, no differences were evident between cells with ABCA1/ABCC1 and ABCC1 only knockdown. Our findings suggest that ABCA1 and ABCB1 proteins display similar arsenic resistance capabilities and possibly coordinate to promote arsenic resistance in AsRE cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conde, P., Acosta-Saavedra, L. C., Goytia-Acevedo, R. C., & Calderon-Aranda, E. S. (2007). Sodium arsenite-induced inhibition of cell proliferation is related to inhibition of IL-2 mRNA expression in mouse activated T cells. Archives of Toxicology, 81(4), 251–259.
Kozul, C. D., Ely, K. H., Enelow, R. I., & Hamilton, J. W. (2009). Low-dose arsenic compromises the immune response to influenza A infection in vivo. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117(9), 1441–1447.
Jensen, T. J., Novak, P., Wnek, S. M., Gandolfi, A. J., & Futscher, B. W. (2009). Arsenicals produce stable progressive changes in DNA methylation patterns that are linked to malignant transformation of immortalized urothelial cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 241(2), 221–229.
Ettinger, A. S., Zota, A. R., Amarasiriwardena, C. J., Hopkins, M. R., Schwartz, J., Hu, H., & Wright, R. O. (2009). Maternal arsenic exposure and impaired glucose tolerance during pregnancy. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117(7), 1059–1064.
Frankel, S., Concannon, J., Brusky, K., Pietrowicz, E., Giorgianni, S., Thompson, W. D., & Currie, D. A. (2009). Arsenic exposure disrupts neurite growth and complexity in vitro. Neurotoxicology, 30(4), 529–537.
Gonsebatt, M. E., Del Razo, L. M., Cerbon, M. A., Zuniga, O., Sanchez-Pena, L. C., & Ramirez, P. (2007). Arsenite induced oxidative damage in mouse liver is associated with increased cytokeratin 18 expression. Archives of Toxicology, 81(9), 619–626.
Manna, P., Sinha, M., & Sil, P. C. (2008). Arsenic-induced oxidative myocardial injury: protective role of arjunolic acid. Archives of Toxicology, 82(3), 137–149.
Tseng, C. H., Tai, T. Y., Chong, C. K., Tseng, C. P., Lai, M. S., Lin, B. J., Chiou, H. Y., Hsueh, Y. M., Hsu, K. H., & Chen, C. J. (2000). Long-term arsenic exposure and incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a cohort study in arseniasis-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Environmental Health Perspectives, 108(9), 847–851.
Ferreccio, C., Gonzalez, C., Milosavjlevic, V., Marshall, G., Sancha, A. M., & Smith, A. H. (2000). Lung cancer and arsenic concentrations in drinking water in Chile. Epidemiology, 11(6), 673–679.
Hsueh, Y. M., Wu, W. L., Huang, Y. L., Chiou, H. Y., Tseng, C. H., & Chen, C. J. (1998). Low serum carotene level and increased risk of ischemic heart disease related to long-term arsenic exposure. Atherosclerosis, 141(2), 249–257.
Wang, L., Chen, S., Xiao, X., Huang, X., You, D., Zhou, X., & Deng, Z. (2006). arsRBOCT arsenic resistance system encoded by linear plasmid pHZ227 in Streptomyces sp. strain FR-008. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(5), 3738–3742.
Tan, X., Yang, L., Xian, L., Huang, J., Di, C., Gu, W., Guo, S., & Yang, L. (2014). ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) promotes arsenic tolerance in human cells by reducing cellular arsenic accumulation. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology, 41(4), 287–294.
Kaminski, W. E., Orso, E., Diederich, W., Klucken, J., Drobnik, W., & Schmitz, G. (2000). Identification of a novel human sterol-sensitive ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA7). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 273(2), 532–538.
von Eckardstein, A., Nofer, J. R., & Assmann, G. (2001). High density lipoproteins and arteriosclerosis. Role of cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 21(1), 13–27.
Bodzioch, M., Orso, E., Klucken, J., Langmann, T., Bottcher, A., Diederich, W., Drobnik, W., Barlage, S., Buchler, C., Porsch-Ozcurumez, M., Kaminski, W. E., Hahmann, H. W., Oette, K., Rothe, G., Aslanidis, C., Lackner, K. J., & Schmitz, G. (1999). The gene encoding ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 is mutated in Tangier disease. Nature Genetics, 22(4), 347–351.
Brooks-Wilson, A., Marcil, M., Clee, S. M., Zhang, L. H., Roomp, K., van Dam, M., Yu, L., Brewer, C., Collins, J. A., Molhuizen, H. O., Loubser, O., Ouelette, B. F., Fichter, K., Ashbourne-Excoffon, K. J., Sensen, C. W., Scherer, S., Mott, S., Denis, M., Martindale, D., Frohlich, J., Morgan, K., Koop, B., Pimstone, S., Kastelein, J. J., Genest Jr., J., & Hayden, M. R. (1999). Mutations in ABC1 in Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Nature Genetics, 22(4), 336–345.
Nofer, J. R., & Remaley, A. T. (2005). Tangier disease: still more questions than answers. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 62(19-20), 2150–2160.
Cwiklinska, A., Strzelecki, A., Kortas-Stempak, B., Zdrojewski, Z., & Wroblewska, M. (2015). ApoE-containing HDL and the development of atherosclerosis. Postȩpy Higieny i Medycyny Doświadczalnej (Online), 69, 1–9.
Glavinas, H., Krajcsi, P., Cserepes, J., & Sarkadi, B. (2004). The role of ABC transporters in drug resistance, metabolism and toxicity. Current Drug Delivery, 1(1), 27–42.
Hung, T. H., Hsu, S. C., Cheng, C. Y., Choo, K. B., Tseng, C. P., Chen, T. C., Lan, Y. W., Huang, T. T., Lai, H. C., Chen, C. M., & Chong, K. Y. (2014). Wnt5A regulates ABCB1 expression in multidrug-resistant cancer cells through activation of the non-canonical PKA/beta-catenin pathway. Oncotarget, 5(23), 12273–12290.
Gao, F., Liu, J., Dong, W. W., Wang, W., Wang, Y., Cai, D., Zheng, Z., & Sun, K. (2014). Investigation of the mechanism involved in the As2O3-regulated decrease in MDR1 expression in leukemia cells. Oncology Reports, 31(2), 926–932.
Recio-Vega, R., Dena-Cazares, J. A., Ramirez-de la Pena, J. L., Jacobo-Avila, A., Portales-Castanedo, A., Gallegos-Arreola, M. P., Ocampo-Gomez, G., & Michel-Ramirez, G. (2015). MRP1 expression in bronchoalveolar lavage cells in subjects with lung cancer who were chronically exposed to arsenic. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 56(9), 759–766.
Konecny, G. E. (2013). Are ABCB1 (P-glycoprotein) polymorphisms clinically relevant in ovarian cancer?—finally an answer. Gynecologic Oncology, 131(1), 1–2.
Tabe, Y., Konopleva, M., Contractor, R., Munsell, M., Schober, W. D., Jin, L., Tsutsumi-Ishii, Y., Nagaoka, I., Igari, J., & Andreeff, M. (2006). Up-regulation of MDR1 and induction of doxorubicin resistance by histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide (FK228) and ATRA in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood, 107(4), 1546–1554.
Shi, B., Xiang, X., Ke, Y., Zhou, L., & Ke, C. (2015). Abcb1 gene expression pattern and function of copper detoxification in Fujian oyster, Crassostrea angulata. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B, Biochemistry Molecular Biology, 190, 8–15.
Illmer, T., Schaich, M., Platzbecker, U., Freiberg-Richter, J., Oelschlagel, U., von Bonin, M., Pursche, S., Bergemann, T., Ehninger, G., & Schleyer, E. (2004). P-Glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux is a resistance mechanism of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to treatment with imatinib mesylate. Leukemia, 18(3), 401–408.
Wu, R. W., Chu, E. S., Huang, Z., Xu, C. S., Ip, C. W., & Yow, C. M. (2015). Effect of FosPeg(R) mediated photoactivation on P-gp/ABCB1 protein expression in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. B, 148, 82–87.
Xiang, C., Wang, J., Kou, X., Chen, X., Qin, Z., Jiang, Y., Sun, C., Xu, J., Tan, W., Jin, L., Lin, D., He, F., & Wang, H. (2015). Pulmonary expression of CYP2A13 and ABCB1 is regulated by FOXA2, and their genetic interaction is associated with lung cancer. The FASEB Journal, 29(5), 1986–1998.
Chong, K. Y., Hsu, C. J., Hung, T. H., Hu, H. S., Huang, T. T., Wang, T. H., Wang, C., Chen, C. M., Choo, K. B., & Tseng, C. P. (2015). Wnt pathway activation and ABCB1 expression account for attenuation of proteasome inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 16(1), 149–159.
Carew, M. W., Naranmandura, H., Shukalek, C. B., Le, X. C., & Leslie, E. M. (2011). Monomethylarsenic diglutathione transport by the human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1). Drug Metabolism and Disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals, 39(12), 2298–2304.
Hong, G. L., Liu, J. M., Zhao, G. J., Tan, J. P., Wu, B., Li, M. F., Liang, G., Qiu, Q. M., & Lu, Z. Q. (2016). Cycloartenyl Ferulate inhibits Paraquat-induced apoptosis in HK-2 cells with the involvement of ABCC1. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 117(4), 872–880.
Leslie, E. M., Haimeur, A., & Waalkes, M. P. (2004). Arsenic transport by the human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1). Evidence that a tri-glutathione conjugate is required. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(31), 32700–32708.
Mann, K. K., Colombo, M., & Miller Jr., W. H. (2008). Arsenic trioxide decreases AKT protein in a caspase-dependent manner. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 7(6), 1680–1687.
Lindahl, M., Petrlova, J., Dalla-Riva, J., Wasserstrom, S., Rippe, C., Domingo-Espin, J., Kotowska, D., Krupinska, E., Berggreen, C., Jones, H. A., Sward, K., Lagerstedt, J. O., Goransson, O., & Stenkula, K. G. (2015). ApoA-I Milano stimulates lipolysis in adipose cells independently of cAMP/PKA activation. Journal of Lipid Research, 56(12), 2248–2259.
Chen, Z., Wang, Z. Y., & Chen, S. J. (1997). Acute promyelocytic leukemia: cellular and molecular basis of differentiation and apoptosis. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 76(1-3), 141–149.
Pettersson, H. M., Karlsson, J., Pietras, A., Ora, I., & Pahlman, S. (2007). Arsenic trioxide and neuroblastoma cytotoxicity. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 39(1), 35–41.
Bonati, A., Rizzoli, V., & Lunghi, P. (2006). Arsenic trioxide in hematological malignancies: the new discovery of an ancient drug. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 7(6), 397–405.
Cheng, H. C., Liu, S. W., Li, W., Zhao, X. F., Zhao, X., Cheng, M., Qiu, L., & Ma, J. (2015). Arsenic trioxide regulates adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow MSCs of aplastic anemia patients through BMP4 gene. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 47(9), 673–679.
Funding
This work is supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (30560129) to L.Y., National Natural Science Foundation of China (31400630 and 31570738) to X.L.X., and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772168) to X.H.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.Y. and X.H.T. conceived and designed the experiments; T.Z. and W.Q.N. performed the experiments; Z.Y. and S.L.G. analyzed the data; C.H.D. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; X.L.X. wrote the paper. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 318 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, T., Niu, W., Yuan, Z. et al. ABCA1 Is Coordinated with ABCB1 in the Arsenic-Resistance of Human Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187, 365–377 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2800-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2800-9