Abstract
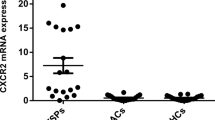
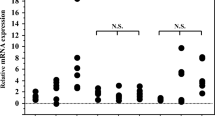
HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) is an aggressive neurological disease. The CD4+CD25+ T cell population plays pivotal roles in the maintenance of immunological tolerance and prevention of such autoimmune diseases. In the current study, proviral load (PVL), factor forkhead box p3 (Foxp3), and glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein (GITR) gene expression and regulatory T cells (Tregs) counts of 21 HAM/TSP patients and 16 HTLV-1 healthy carriers (ACs) were measured using real-time PCR, TaqMan method, and flow cytometry. The demographic, history of disease, and severity of myelopathy were assessed by a checklist and the Osame motor disability score (OMDS). The mean OMDS for HAM/TSP was 4.82 ± 2.37 which had no significant correlation with Treg count or the expression of Foxp3, GITR, and PVL. The CD4+CD25+ cell counts had no significant differences between HAM/TSP and ACs. Findings revealed a higher PVL in HAM/TSPs (313.36 copies/104) compared to ACs (144.93 copies/104, p = 0.035). The Foxp3 and GITR mRNA levels were lower in HAM/TSP patients (11.78 and 13.80, respectively) than those in healthy carriers (18.44 and 21.00, p = 0.041 and 0.03, respectively). There was a significant correlation between Treg frequency and Foxp3 gene expression (R = 0.67, p = 0.006) and GITR and Foxp3 (R = 0.84, p = 0.042) in HAM/TSP patients. Furthermore, the transcription factors have strong correlations with CD4+CD25+ T cell frequencies. These findings suggest that HTLV-1 infection can modify the expression of main functional transcription factors, FOXP3 and GITR, which may lead to immune response deterioration of Tregs and consequently HAM/TSP manifestation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor, J. M., & Nicot, C. (2008). HTLV-1 and apoptosis: role in cellular transformation and recent advances in therapeutic approaches. Apoptosis, 13, 733–747.
Ahmadi Ghezeldasht, S., Shirdel, A., Assarehzadegan, M. A., Hassannia, T., Rahimi, H., Miri, R., & Rezaee, S. A. (2013). Human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) oncogenesis: molecular aspects of virus and host interactions in pathogenesis of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL). Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Science, 16, 179–195.
Trevino, A., Aguilera, A., Caballero, E., Benito, R., Parra, P., Eiros, J. M., Hernandez, A., Calderon, E., Rodriguez, M., Torres, A., Garcia, J., Ramos, J. M., Roc, L., Marcaida, G., Rodriguez, C., Trigo, M., Gomez, C., de Lejarazu, R. O., de Mendoza, C., & Soriano, V. (2012). Trends in the prevalence and distribution of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 infections in Spain. Virology Journal, 9, 71.
Yamashiro, T., Kamiya, H., Miyara, T., Gibo, S., Ogawa, K., Akamine, T., Moromizato, H., Yara, S., & Murayama, S. (2012). CT scans of the chest in carriers of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1: presence of interstitial pneumonia. Academic Radiology, 19, 952–957.
Rafatpanah, H., Hedayati-Moghaddam, M. R., Fathimoghadam, F., Bidkhori, H. R., Shamsian, S. K., Ahmadi, S., Sohgandi, L., Azarpazhooh, M. R., Rezaee, S. A., Farid, R., & Bazarbachi, A. (2011). High prevalence of HTLV-I infection in Mashhad, Northeast Iran: a population-based seroepidemiology survey. Journal of Clinical Virology, 52, 172–176.
Naderi, M., Paryan, M., Azadmanesh, K., Rafatpanah, H., Rezvan, H., & Mirab, S. S. (2012). Design and development of a quantitative real time PCR assay for monitoring of HTLV-1 provirus in whole blood. Journal of Clinical Virology, 53, 302–307.
Hedayati-Moghaddam, M. R. F. F., Eftekharzadeh Mashhadi, I., Soghandi, L., & Bidkhori, H. R. (2011). Epidemiology of HTLV-1 in Neyshabour, northeast of Iran. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal, 13, 424–427.
Kalavi, K., Moradi, A., & Tabarraei, A. (2013). Population-based seroprevalence of HTLV-I infection in Golestan Province, south east of Caspian Sea, Iran. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Science, 16, 225–228.
Boostani, R., Mellat Ardakani, A., & Ashrafi, H. (2011). Khorasan disease: prevalence of HTLV-I associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) in West Azarbaijan from 2004 to 2007. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal, 13, 428–430.
Fazly Bazzaz, B., & Rezaee, S. A. (2013). The significance of HTLV-I in molecular oncology. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Science, 16, 178.
Furukawa, Y., Saito, M., Matsumoto, W., Usuku, K., Tanaka, Y., Izumo, S., & Osame, M. (2003). Different cytokine production in tax-expressing cells between patients with human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I)-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis and asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 187, 1116–1125.
Bangham, C. (2009). CTL quality and the control of human retroviral infections. European Journal of Immunology, 39, 1700–1712.
Nagai, M., Kubota, R., Greten, T. F., Schneck, J. P., Leist, T. P., & Jacobson, S. (2001). Increased activated human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) Tax11-19-specific memory and effector CD8+ cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: correlation with HTLV-I provirus load. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 183, 197–205.
Yamano, Y., Nagai, M., Brennan, M., Mora, C. A., Soldan, S. S., Tomaru, U., Takenouchi, N., Izumo, S., Osame, M., & Jacobson, S. (2002). Correlation of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) mRNA with proviral DNA load, virus-specific CD8(+) T cells, and disease severity in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Blood, 99, 88–94.
Izumo, S., Umehara, F., Kashio, N., Kubota, R., Sato, E., & Osame, M. (1997). Neuropathology of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Leukemia, 11(Suppl 3), 82–84.
Osame, M. (2002). Pathological mechanisms of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Journal of Neurovirology, 8, 359–364.
Gessain, A., & Mahieux, R. (2012). Tropical spastic paraparesis and HTLV-1 associated myelopathy: clinical, epidemiological, virological and therapeutic aspects. Revue Neurologique (Paris), 168, 257–269.
Irish, B. P., Khan, Z. K., Jain, P., Nonnemacher, M. R., Pirrone, V., Rahman, S., Rajagopalan, N., Suchitra, J. B., Mostoller, K., & Wigdahl, B. (2009). Molecular mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases induced by human retroviruses: a review. American Journal of Infectious Diseases, 5, 231–258.
Rafatpanah, H., Farid Hosseini, R., & Pourseyed, S. H. (2013). The impact of immune response on HTLV-I in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Science, 16, 235–241.
Sakaguchi, S., Sakaguchi, N., Shimizu, J., Yamazaki, S., Sakihama, T., Itoh, M., Kuniyasu, Y., Nomura, T., Toda, M., & Takahashi, T. (2001). Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and transplantation tolerance. Immunological Reviews, 182, 18–32.
Shevach, E. (2002). CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2, 389–400.
Zhang, L., & Zhao, Y. (2007). The regulation of Foxp3 expression in regulatory CD4+ CD25+ T cells: multiple pathways on the road. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 211, 590–597.
Rafatpanah, H., Rezaee, A., Etemadi, M. M., Hosseini, R. F., Khorram, B., Afsahr, L., Taylor, G., Mokhber, N., Mahmoudi, M., Abbaszadegan, M. R., Foroghipor, M., Hashemi, P., Amiri, A., Tehrani, M., Azarpazhooh, A., & Azarpazhooh, M. R. (2012). The impact of interferon-alpha treatment on clinical and immunovirological aspects of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy in northeast of Iran. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 250, 87–93.
Ronchetti, S., Zollo, O., Bruscoli, S., Agostini, M., & Bianchini, R. (2004). GITR, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, is costimulatory to mouse T lymphocyte subpopulations. European Journal of Immunology, 34, 613–622.
Hori, S., Nomura, T., & Sakaguchi, S. (2003). Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science, 299, 1057–1061.
Fontenot, J. D., Gavin, M. A., & Rudensky, A. Y. (2003). Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nature Immunology, 4, 330–336.
Bal, H. P., Cheng, J., Murakami, A., Tallarico, A. S., Wang, W., Zhou, D., Vasicek, T. J., & Marasco, W. A. (2005). GITR overexpression on CD4+ CD25+ HTLV-1 transformed cells: detection by massively parallel signature sequencing. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 332, 569–584.
Kovacs, E., Szilagyi, L., Koncz, G., Lanyi, S., & Abraham, B. (2013). Enhanced in vitro refolding of soluble human glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor-related ligand. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 170, 819–830.
Izumo, S., Goto, I., Itoyama, Y., Okajima, T., Watanabe, S., Kuroda, Y., Araki, S., Mori, M., Nagataki, S., Matsukura, S., Akamine, T., Nakagawa, M., Yamamoto, I., & Osame, M. (1996). Interferon-alpha is effective in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Neurology, 46, 1016–1021.
Vakili, R., Sabet, F., Aahmadi, S., Boostani, R., Rafatpanah, H., Shamsian, A., & Rezaee, S. A. (2013). Human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral load and clinical features in Iranian HAM/TSP patients: comparison of HTLV-I proviral load in HAM/TSP patients. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Science, 16, 268–272.
Richardson, J. H. E. A., Cruickshank, J. K., Rudge, P., & Dalgleish, A. G. (1990). In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Journal of Virology, 64, 5682–5687.
Hanon, E., Hall, S., Taylor, G. P., Saito, M., Davis, R., Tanaka, Y., Usuku, K., Osame, M., Weber, J. N., & Bangham, C. R. (2000). Abundant tax protein expression in CD4+ T cells infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) is prevented by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood, 95, 1386–1392.
Umehara, F., Izumo, S., Ronquillo, A. T., Matsumuro, K., Sato, E., & Osame, M. (1994). Cytokine expression in the spinal cord lesions in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology, 53, 72–77.
Kuroda, Y., & Matsui, M. (1993). Cerebrospinal fluid interferon-gamma is increased in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 42, 223–226.
Nakamura, S., Nagano, I., Yoshioka, M., Shimazaki, S., Onodera, J., & Kogure, K. (1993). Detection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-positive cells in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 42, 127–130.
Oh, U., Grant, C., Griffith, C., Fugo, K., Takenouchi, N., & Jacobson, S. (2006). Reduced Foxp3 protein expression is associated with inflammatory disease during human t lymphotropic virus type 1 infection. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 193, 1557–1566.
Hayashi, D., Kubota, R., Takenouchi, N., Tanaka, Y., Hirano, R., Takashima, H., Osame, M., Izumo, S., & Arimura, K. (2008). Reduced Foxp3 expression with increased cytomegalovirus-specific CTL in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 200, 115–124.
Toulza, F., Heaps, A., Tanaka, Y., Taylor, G. P., & Bangham, C. R. (2008). High frequency of CD4+ FoxP3+ cells in HTLV-1 infection: inverse correlation with HTLV-1-specific CTL response. Blood, 111, 5047–5053.
Best, I., Lopez, G., Verdonck, K., Gonzalez, E., Tipismana, M., Gotuzzo, E., Vanham, G., & Clark, D. (2009). IFN-gamma production in response to tax 161-233, and frequency of CD4+ Foxp3+ and Lin HLA-DRhigh CD123+ cells, discriminate HAM/TSP patients from asymptomatic HTLV-1-carriers in a Peruvian population. Immunology, 128, e777–e786.
Saito, M., & Bangham, C. R. (2012). Immunopathogenesis of human T-cell leukemia virus type-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: recent perspectives. Leukemia Research and Treatment, 2012, 1–12.
Takenouchi, N., Yamano, Y., Usuku, K., Osame, M., & Izumo, S. (2003). Usefulness of proviral load measurement for monitoring of disease activity in individual patients with human T-lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Journal of Neurovirology, 9, 29–35.
Satou, Y., Utsunomiya, A., Tanabe, J., Nakagawa, M., Nosaka, K., & Matsuoka, M. (2012). HTLV-1 modulates the frequency and phenotype of FoxP3+ CD4+ T cells in virus-infected individuals. Retrovirology, 9, 46.
Acknowledgements
The authors do appreciate the great help of the Neurology Department of Ghaem Hospital and the support of the Iranian Academic Center for Education, Culture & Research (ACECR), Mashhad, Iran. This study was a subject of a thesis for a MD, pathology student and granted by the vice chancellor for Research, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran. We specially thank for the valuable help of Dr. Arman Mosavat. This manuscript is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Ali Sadeghian as a friend, mentor, and colleague.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (No 88134).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghezeldasht, S.A., Sadeghian, H., Azarpazhooh, M.R. et al. Evaluation of T Regulatory Lymphocytes Transcription Factors in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis (HAM/TSP) Patients. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 182, 1403–1414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2406-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2406-7