Abstract
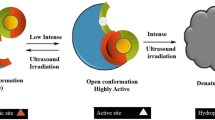
The enzyme under lower-intensity ultrasonic irradiation leads to favourable conformational changes, thereby enhancing its activity. The augmentation of activity of ultrasound-treated enzyme is strongly dependent on ultrasound intensity, duty cycle and exposure time, which was investigated for commercial lipases. Thermomyces lanuginosus (TL) lipase showed a 1.3-fold enhanced activity after irradiating at 22 kHz and 11.38 W cm−2 with 50 % duty cycle for 25-min ultrasonic treatment and 1.5-fold enhanced activity was observed for lipozyme (candida antarctica lipase B (CALB)) lipase, at 22 kHz and 15.48 W cm−2 with 66.67 % duty cycle for 20-min ultrasonic treatment. After sonication, thermodynamic parameters viz. E a, ΔH, ΔS and ΔG were evaluated and values were found to be significantly lower for both lipases. In addition, the changes in secondary structure due to sonication were investigated by using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), which revealed increase in a certain number of random coiled structure, loss of β-sheets, β-turns and α-helix content in TL lipase and CALB lipase. Also, fluorescence spectroscopy exhibited the increased number of tryptophan on surface of both lipases. Moreover, particle size distribution after sonication also helped to improve surface area and enhanced mass transfer, which contributed to improvement in lipase activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan, T., Lu, J., Nie, K., Deng, L., & Wang, F. (2010). Biodiesel production with immobilized lipase: a review. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 628–634.
Bajaj, A., Lohan, P., Jha, P. N., & Mehrotra, R. (2010). Biodiesel production through lipase catalyzed transesterification: an overview. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 62, 9–14.
Goswami, D., Basu, J. K., & De, D. (2013). Lipase applications in oil hydrolysis with a case study on castor oil: a review. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 33, 81–96.
Tomke, P. D., & Rathod, V. K. (2015). Ultrasound assisted lipase catalyzed synthesis of cinnamyl acetate via transesterification reaction in a solvent free medium. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 27, 241–251.
Khan, N. R., Jadhav, S. V., & Rathod, V. K. (2015). Lipase catalysed synthesis of cetyl oleate using ultrasound: optimisation and kinetic studies. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 27, 522–529.
Rodrigues, R. C., & Fernandez-Lafuente, R. (2010). Lipase from Rhizomucor miehei as a biocatalyst in fats and oils modification. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 66, 15–32.
Soumanou, M. M., Pérignon, M., & Villeneuve, P. (2013). Lipase-catalyzed interesterification reactions for human milk fat substitutes production: a review. Eur Lipid J Technol Sci., 115, 270–285.
Hasan, F., Shah, A. A., & Hameed, A. (2006). Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39, 235–251.
Cunha, A. G., Besteti, M. D., Manoel, E. A., da Silva, A. A. T., Almeida, R. V., Simas, A. B. C., Fernandez-Lafuente, R., Pinto, J. C., & Freire, D. M. G. (2014). Preparation of core–shell polymer supports to immobilize lipase B from Candida Antarctica effect of the support nature on catalytic. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 100, 59–67.
Manoel, E. A., Dos Santos, J. C. S., Freire, D. M. G., Rueda, N., & Fernandez-Lafuente, R. (2015). Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports involves the open form of the enzyme. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 71, 53–57.
Akoh, C. C., Lee, G., & Shaw, J. (2004). Protein engineering and applications of Candida rugosa lipase isoforms. Lipids, 39, 513–526.
Souza, M., Mezadri, E. T., Zimmerman, E., Leaes, E. X., Bassaco, M. M., Pra, V. D., Foletto, E., Cancellier, A., Terra, L. M., Jahn, S. L., & Mazutti, M. A. (2013). Evaluation of activity of a commercial amylase under ultrasound-assisted irradiation. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 89–94.
Gogate, P. R., & Kabadi, A. M. (2009). A review of applications of cavitation in biochemical engineering/biotechnology. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 44, 60–72.
Gogate, P. R. (2008). Cavitational reactors for process intensification of chemical processing applications: a critical review. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 47, 515–527.
O’Donnell, C. P., Tiwari, B. K., Bourke, P., & Cullen, P. J. (2010). Effect of ultrasonic processing on food enzymes of industrial importance. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2, 358–367.
Braginskaya, F. I., Zaitzeva, E. A., Zorina, O. M., Poltorak, O. M., Chukrai, E. S., & Dunn, F. (1990). Low intensity ultrasonic effects on yeast hexokinase. Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 29, 47–56.
Mawson, R., Gamage, M., Terefe, N. S., & Knoerzer, K. (2011). Ultrasound in enzyme activation and inactivation. Ultrasound Technologies for Food and Bioprocessing, 14, 369–404.
Subhedar, P. B., & Gogate, P. R. (2014). Enhancing the activity of cellulase enzyme using ultrasonic irradiations. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 101, 108–114.
Guiseppi-Elie, A., Choi, S. H., & Geckeler, K. E. (2009). Ultrasonic processing of enzymes: effect on enzymatic activity of glucose oxidase. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 58, 18–123.
Bashari, M., Eibaid, A., Wang, J., Tian, Y., Xu, X., & Jin, Z. (2013). Influence of low ultrasound intensity on the degradation of dextran catalyzed by dextranase. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 155–161.
Lindomar, A. L., Raquel, A. L., Daniela, R., Mara, C. Z., Manuela, B., Vendelino, O. N., Jorge, L. N., Cla’udia, M., Vladimir, O., & de De’bora, O. (2014). A review on lipase-catalyzed reactions in ultrasound-assisted systems. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 37, 2381–2394.
Dey, S., & Rathod, V. K. (2013). Ultrasound assisted extraction of b-carotene from Spirulina platensis. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 271–276.
Palacios, D., Busto, M. D., & Ortega, N. (2014). Study of a new spectrophotometric end-point assay for lipase activity determination in aqueous media. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 55, 536–542.
Talekar, S., Nadar, S., Joshi, A., & Joshi, G. (2014). Pectin cross-linked enzyme aggregates (pectin-CLEAs) of glucoamylase. RSC Advances, 4, 59444–59453.
Sojitra, U. V., Nadar, S. S., & Rathod, V. K. (2016). Immobilization of pectinase onto chitosan magnetic nanoparticles by macromolecular cross-linker. Carbohydrate Polymers. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.018.
Yu, Z., Zeng, W., Zhang, W., Liao, X., & Shi, B. (2014). Effect of ultrasound on the activity and conformation of α-amylase, papain and pepsin. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 21, 930–936.
Maa, H., Huang, L., Jia, J., He, R., Luo, L., & Zhu, W. (2011). Effect of energy-gathered ultrasound on alcalase. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 18, 419–424.
Rokhina, E. V., Lens, P., & Virkutyte, J. (2009). Low-frequency ultrasound in biotechnology: state of the art. Trends in Biotechnology, 27, 298–306.
Gebicka, L., & Gekicki, J. L. (1997). The effect of ultrasound on heme enzymes in aqueous solution. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 12, 133–141.
Basto, C., Silva, C. J., Gubitz, G., & Cavaco-Paulo, A. (2007). Stability and decolourization ability of Trametes villosa laccase in liquid ultrasonic fields. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 14, 355–362.
Szabo, O. E., & Csiszar, E. (2013). The effect of low-frequency ultrasound on the activity and efficiency of a commercial cellulase enzyme. Carbohydrate Polymers, 98, 1483–1489.
Bhasarkar, J., Arup, J. B., Goswami, P., & Moholkar, V. S. (2015). Mechanistic analysis of ultrasound assisted enzymatic desulfurization of liquid fuels using horseradish peroxidase. Bioresource Techn., 196, 88–98.
Kadkhodaee, R., & Malcolm, J. W. (2008). Ultrasonic inactivation of Bacillus a-amylase. I. Effect of gas content and emitting face of probe. Ultrasonics Sonochem., 15, 133–142.
Khanna, S., Goyal, A., & Moholkar, V. S. (2013). Mechanistic investigation of ultrasonic enhancement of glycerol bioconversion by immobilized Clostridium pasteurianum on silica support. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 110, 1637–1645.
Malani, R. S., Khanna, S., Chakma, S., & Moholkar, V. S. (2014). Mechanistic insight into sono-enzymatic degradation of organic pollutants with kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 21, 1400–1406.
Qu, W., Maa, H., Liu, B., He, R., & Pan, Z. (2013). Enzymolysis reaction kinetics and thermodynamics of defatted wheat germ protein with ultrasonic pretreatment. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 1408–1413.
Jadhav, S. H., & Gogate, P. R. (2014). Intensification in the activity of lipase enzyme using ultrasonic irradiation and stability studies. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53, 1377–1385.
Knorr, D., Zenker, M., Heinz, V., & Lee, D. U. (2004). Applications and potential of ultrasonics in food processing. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 15, 261–266.
Sulaiman, A. Z., Ajit, A., & Chisti, Y. (2013). Ultrasound mediated enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose. Biotechnology Progress, 29, 1–10.
Yu, Z., Zeng, W., & Lu, X. (2013). Influence of ultrasound to the activity of tyrosinase. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 805–809.
Nadar, S., Gawas, S., & Rathod, V. K. (2016). Self-assembled organic-inorganic hybrid glucoamylase nanoflowers with enhanced activity and stability. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.071.
Nadar, S., Muley, A., Ladole, M., & Joshi, P. (2016). Macromolecular cross-linked enzyme aggregates (M-CLEAs) of α-amylase. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 84, 69–78.
Gulseren, I., Güzey, D., Bruce, B. D., & Weiss, J. (2007). Structural and functional changes in ultrasonicated bovine serum albumin solutions. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 14, 173–183.
Wang, Z., Lin, X., Li, P., Zhang, J., Wanga, S., & Ma, H. (2012). Effects of low intensity ultrasound on cellulase pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 117, 222–227.
Jambrak, A. R., Mason, T. J., Lelas, V., Paniwnyk, L., & Herceg, Z. (2014). Effect of ultrasound treatment on particle size and molecular weight of whey proteins. Journal of Food Engineering, 121, 5–23.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the University Grants Commission (UGC) of India for financially supporting the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadar, S.S., Rathod, V.K. Sonochemical Effect on Activity and Conformation of Commercial Lipases. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 181, 1435–1453 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2294-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2294-2