Abstract
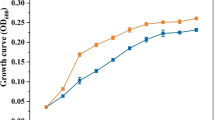
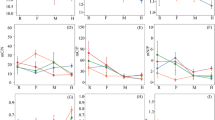
Biofertilizers have been widely used in many countries for their benefit to soil biological and physicochemical properties. A new microbial biofertilizer containing Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Bacillus thuringiensis was prepared to decrease nicotine content in tobacco leaves by regulating soil nitrogen supply. Soil NO3 −-N, NH4 +-N, nitrogen supply-related enzyme activities, and nitrogen accumulation in plant leaves throughout the growing period were investigated to explore the mechanism of nicotine reduction. The experimental results indicated that biofertilizer can reduce the nicotine content in tobacco leaves, with a maximum decrement of 16–18 % in mature upper leaves. In the meantime, the total nitrogen in mature lower and middle leaves increased with the application of biofertilizer, while an opposite result was observed in upper leaves. Protein concentration in leaves had similar fluctuation to that of total nitrogen in response to biofertilizer. NO3 −-N content and nitrate reductase activity in biofertilizer-amended soil increased by 92.3 and 42.2 %, respectively, compared to those in the control, whereas the NH4 +-N and urease activity decreased by 37.8 and 29.3 %, respectively. Nitrogen uptake was improved in the early growing stage, but this phenomenon was not observed during the late growth period. Nicotine decrease is attributing to the adjustment of biofertilizer in soil nitrogen supply and its uptake in tobacco, which result in changes of nitrogen content as well as its distribution in tobacco leaves. The application of biofertilizer containing P. chrysosporium and B. thuringiensis can reduce the nicotine content and improve tobacco quality, which may provide some useful information for tobacco cultivation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atafar, Z., Mesdaghinia, A., Nouri, J., Homaee, M., Yunesian, M., Ahmadimoghaddam, M., & Mahvi, A. H. (2010). Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 83–89.
Jafarnejadi, A. R., Sayyad, G., Homaee, M., & Davamei, A. H. (2013). Spatial variability of soil total and DTPA-extractable cadmium caused by long-term application of phosphate fertilizers, crop rotation, and soil characteristics. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 4087–4096.
Nacke, H., Gonçalves Jr, A. C., Schwantes, D., Nava, I. A., Strey, L., & Coelho, G. F. (2013). Availability of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, and Cr) in agriculture from commercial fertilizers. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 537–544.
Singh, A., & Mishra, A. K. (2015). Influence of various levels of iron and other abiotic factors on siderophorogenesis in paddy field cyanobacterium Anabaena oryzae. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176(2), 372–386.
Jain, R., Gary, V., & Saxena, J. (2015). Effect of an organophosphate pesticide, monocrotophos, on phosphate-solubilizing efficiency of soil fungal isolates. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175(2), 813–824.
Yu, Q., Ma, J., Zou, P., Lin, H., Sun, W., Yin, J., & Fu, J. (2015). Effects of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers plus nitrification inhibitor DMPP on nitrogen runoff loss in vegetable soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 472–481.
Zanetti, F., Giacomello, M., Donati, Y., Carnesecchi, S., Frieden, M., & Barazzone-Argiroffo, C. (2014). Nicotine mediates oxidative stress and apoptosis through cross talk between NOX1 and Bcl-2 in lung epithelial cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 76, 173–184.
Kaiser, D. R., Reinert, D. J., Reichert, J. M., Streck, C. A., & Pellegrini, A. (2010). Nitrate and ammonium in soil solution in tobacco management systems. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 34, 379–388.
Walch-Liu, P., Neumann, G., Bangerth, F., & Engels, C. (2000). Rapid effects of nitrogen form on leaf morphogenesis in tobacco. Journal of Experimental Botany, 51, 227–237.
Wyland, L. J., Jackson, L. E., Chaney, W. E., Klonsky, K., Koike, S. T., & Kimple, B. (1996). Winter cover crops in a vegetable cropping system: impacts on nitrate leaching, soil water, crop yield, pests and management costs. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 59, 1–17.
Bastida, F., Pérez-de-Mora, A., Babic, K., Hai, B., Hernández, T., García, C., & Schloter, M. (2009). Role of amendments on N cycling in Mediterranean abandoned semiarid soils. Applied Soil Ecology, 41, 195–205.
Yang, N., Wang, Z., Gao, Y., Zhao, H., Li, K., Li, F., & Malhi, S. S. (2014). Effects of planting soybean in summer fallow on wheat grain yield, total N and Zn in grain and available N and Zn in soil on the Loess Plateau of China. European Journal of Agronomy, 58, 63–72.
Hatch, D. J., Goodlass, G., Joynes, A., & Shepherd, M. A. (2007). The effect of cutting, mulching and applications of farm yard manure on nitrogen fixation in a red clover grass sward. Bioresource Technology, 98(17), 3243–3248.
Mohammadi, K., & Rokhzadi, A. (2012). An integrated fertilization system of canola (Brassica napus L.) production under different crop rotations. Industrial Crops and Products, 37, 264–269.
Gharib, F. A., Moussa, L. A., & Massoud, O. N. (2008). Effect of compost and bio-fertilizers on growth, yield and essential oil of sweet marjoram (Majorana hortensis) plant. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 10, 381–387.
Herrmann, L., & Lesueur, D. (2013). Challenges of formulation and quality of biofertilizers for successful inoculation. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 8859–8873.
Parra-Cota, F. I., Peña-Cabriales, J. J., de los Santos-Villalobos, S., Martínez-Gallardo, N. A., & Délano-Frier, J. P. (2014). Burkholderia ambifaria and B. caribensis promote growth and increase yield in grain amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus and A. hypochondriacus) by improving plant nitrogen uptake. PloS One, 9(2), e88094.
Singh, S., & Datta, P. (2007). Outdoor evaluation of herbicide resistant strains of Anabaena variabilis as biofertilizer for rice plants. Plant and Soil, 296, 95–102.
Innok, S., Chunleuchanon, S., Boonkerd, N., & Teaumroong, N. (2009). Cyanobacterial akinete induction and its application as biofertilizer for rice cultivation. Journal of Applied Phycology, 21, 737–744.
Gamal-Eldin, H., & Elbanna, K. (2011). Field evidence for the potential of Rhodobacter capsulatus as biofertilizer for flooded rice. Current Microbiology, 62, 391–395.
Zhu, H. J., Sun, L. F., Zhang, Y. F., Zhang, X. L., & Qiao, J. J. (2012). Conversion of spent mushroom substrate to biofertilizer using a stress-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing Pichia farinose FL7. Bioresource Technology, 111, 410–416.
Yu, Z., Zeng, G. M., Chen, Y. N., Zhang, J. C., Yu, Y., Li, H., Liu, Z. F., & Tang, L. (2011). Effects of inoculation with Phanerochaete chrysosporium on remediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soil waste by composting. Process Biochemistry, 46, 1285–1291.
Zhang, J., Zeng, G., Chen, Y., Liang, J., Zhang, C., Huang, B., Sun, W., Chen, M., Yu, M., Huang, H., & Zhu, Y. (2014). Phanerochaete chrysosporium inoculation shapes the indigenous fungal communities during agricultural waste composting. Biodegradation, 25, 669–680.
Chen, A., Zeng, G., Chen, G., Liu, L., Shang, C., Hu, X., Lu, L., Chen, M., Zhou, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2014). Plasma membrane behavior, oxidative damage, and defense mechanism in Phanerochaete chrysosporium under cadmium stress. Process Biochemistry, 49, 589–598.
Huang, Z., Chen, G., Zeng, G., Chen, A., Zuo, Y., Guo, Z., Tan, Q., Song, Z., & Niu, Q. (2015). Polyvinyl alcohol-immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium and its application in the bioremediation of composite-polluted wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 289, 174–183.
Pan, Z., Xu, L., Zhu, Y., Shi, H., Chen, Z., Chen, M., Chen, Q., & Liu, B. (2014). Characterization of a new cry2Ab gene of Bacillus thuringiensis with high insecticidal activity against Plutella xylostella L. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 2655–2662.
Guan, P., Dai, X., Zhu, J., Li, Q., Li, S., Wang, S., Li, P., & Zheng, A. (2014). Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. sichuansis strain MC28 produces a novel crystal protein with activity against Culex quinquefasciatus larvae. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 1417–1421.
Hamadou-Charfi, D. B., Sauer, A. J., Abdelkafi-Mesrati, L., Jaoua, S., & Stephan, D. (2015). Production of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against the Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3Aa16. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175(5), 2357–2365.
Kamoun, F., Fguira, I. B., Hassen, N. B. B., Mejdoub, H., Lereclus, D., & Jaoua, S. (2011). Purification and characterization of a new Bacillus thuringiensis bacteriocin active against Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus cereus and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 165(1), 300–314.
Kirk, T. K., Schultz, E., Connors, W. J., Lorenz, L. F., & Zeikus, J. G. (1978). Influence of culture parameters on lignin metabolism by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Archives of Microbiology, 117, 277–285.
Singh, D. K., & Kumar, S. (2008). Nitrate reductase, arginine deaminase, urease and dehydrogenase activities in natural soil (ridges with forest) and in cotton soil after acetamiprid treatments. Chemosphere, 71, 412–418.
Huang, Y. F., Ye, Y. L., & Yang, S. Q. (2009). Feasibility of NO3 −-N determination by dual wavelength spectrophotometric method. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 25, 43–45.
Çakir, R., & Çebi, U. (2010). The effect of irrigation scheduling and water stress on the maturity and chemical composition of Virginia tobacco leaf. Field Crops Research, 119, 269–276.
Goenage, R. J., Volk, R. J., & Long, R. C. (1989). Uptake of nitrogen by flue-cured tobacco during maturation and senescence. Plant and Soil, 120, 133–139.
Jiang, F., Li, C. J., Jeschke, W. D., & Zhang, F. S. (2001). Effect of top excision and replacement by 1-naphthylacetic acid on partition and flow of potassium in tobacco plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 52, 2143–2150.
Shi, Q. M., Li, C. J., & Zhang, F. S. (2006). Nicotine synthesis in Nicotiana tabacum L. induced by mechanical wounding is regulated by auxin. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 2899–2907.
Xi, X. Y., Li, C. J., & Zhang, F. S. (2005). Nitrogen supply after removing the shoot apex increases the nicotine concentration and nitrogen content of tobacco plants. Annals of Botany, 96, 793–797.
Liu, W. Q., Guo, H. X., & Li, H. (2008). Proteomics identification of differentially expressed proteins relevant for nicotine synthesis in flue-cured tobacco roots before and after decapitation. Agricultural Sciences in China., 7, 1084–1090.
Karaivazoglou, N. A., Papakosta, D. K., & Divanidis, S. (2005). Effect of chloride in irrigation water and form of nitrogen fertilizer on Virginia (flue-cured) tobacco. Field Crops Research, 92, 61–74.
Richards, I. R., Wallace, P. A., & Paulson, G. A. (1996). Effects of applied nitrogen on soil nitrate-nitrogen content after harvest of winter barley. Fertilizer Research, 45, 61–67.
Zhang, J., Zeng, G., Chen, Y., Yu, M., Huang, H., Fan, C., Zhu, Y., Li, H., Liu, Z., Chen, M., & Jiang, M. (2013). Impact of Phanerochaete chrysosporium inoculation on indigenous bacterial communities during agricultural waste composting. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 3159–3169.
Yu, M., Zeng, G., Chen, Y., Yu, H., Huang, D., & Tang, L. (2009). Influence of Phanerochaete chrysosporium on microbial communities and lignocellulose degradation during solid-state fermentation of rice straw. Process Biochemistry, 44, 17–22.
Mekki, A., Dhouib, A., & Sayadi, S. (2006). Changes in microbial and soil properties following amendment with treated and untreated olive mill wastewater. Microbiological Research, 161, 93–101.
Hasan, H. A., Abdullah, S. R. S., Kofli, N. T., & Kamarudin, S. K. (2012). Effective microbes for simultaneous bio-oxidation of ammonia and manganese in biological aerated filter system. Bioresource Technology, 124, 355–363.
Myrold, D. D., & Posavatz, N. R. (2007). Potential importance of bacteria and fungi in nitrate assimilation in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 1737–1743.
Qin, S. P., Hu, C. S., & Dong, W. X. (2010). Nitrification results in underestimation of soil urease activity as determined by ammonium production rate. Pedobiologia, 53, 401–404.
Ali, T. A., & Wainwright, M. (1995). Effect of Phanerochaete chrysosporium on transformations of urea, sulphur-coated urea and peptone in soil. Bioresource Technology, 53, 91–93.
Acknowledgments
This research was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51508186, 51579099), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2016JJ3076), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department, China (15C0654), the Scientific Research Staring Foundation for the introduced talents of Hunan Agricultural University (14YJ07), and the Youth Foundation of Hunan Agricultural University (15QN32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, C., Chen, A., Chen, G. et al. Microbial Biofertilizer Decreases Nicotine Content by Improving Soil Nitrogen Supply. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 181, 1–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2195-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2195-4