Abstract
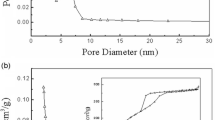
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles were synthesized by using tannic acid as a pore-forming agent, which is an environmentally friendly, cheap, and non-surfactant template. SEM and TEM images indicated that the tannic acid-templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles (TA-MSNs) are monodisperse spherical-like particles with an average diameter of 195 ± 16 nm. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) results showed that the TA-MSNs had a relatively high surface area (447 m2/g) and large pore volume (0.91 cm3/g), and the mean pore size was ca. 10.1 nm. Burkholderia cepacia lipase was immobilized on the TA-MSNs by physical adsorption for the first time, and the properties of immobilized lipase (BCL@TA-MSNs) were investigated. The BCL@TA-MSNs exhibited satisfactory thermal stability; strong tolerance to organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, isooctane, n-hexane, and tetrahydrofuran; and high operational reusability when BCL@TA-MSNs were applied in esterification and transesterification reactions. After recycling 15 times in the transesterification reaction for biodiesel production, over 85 % of biodiesel yield can be maintained. With these desired characteristics, the TA-MSNs may provide excellent candidates for enzyme immobilization.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, P., Gai, S., & Lin, J. (2012). Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chemical Society Reviews, 41, 3679–3698.
Perego, C., & Millini, R. (2013). Porous materials in catalysis: challenges for mesoporous materials. Chemical Society Reviews, 42, 3956–3976.
Popat, A., Hartono, S. B., Stahr, F., Liu, J., Qiao, S. Z., & Qing Lu, G. (2011). Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bioadsorption, enzyme immobilisation, and delivery carriers. Nanoscale, 3, 2801–2818.
Tao, Z. (2014). Mesoporous silica-based nanodevices for biological applications. RSC Advances, 4, 18961–18980.
Popat, A., Ross, B. P., Liu, J., Jambhrunkar, S., Kleitz, F., & Qiao, S. Z. (2012). Enzyme-responsive controlled release of covalently bound prodrug from functional mesoporous silica nanospheres. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 51, 12486–12489.
Hoffmann, F., Cornelius, M., Morell, J., & Fröba, M. (2006). Silica-based mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 45, 3216–3251.
Wan, Y., & Zhao, D. (2007). On the controllable soft-templating approach to mesoporous silicates. Chemical Reviews, 107, 2821–2860.
Gao, Z., & Zharov, I. (2014). Large pore mesoporous silica nanoparticles by templating with a nonsurfactant molecule, tannic acid. Chemistry of Materials, 26, 2030–2037.
Wei, Y., Jin, D., Ding, T., Shih, W. H., Liu, X., Cheng, S. Z., & Fu, Q. (1998). A non-surfactant templating route to mesoporous silica materials. Advanced Materials, 10, 313–316.
Wu, S.-H., Mou, C.-Y., & Lin, H.-P. (2013). Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chemical Society Reviews, 42, 3862–3875.
Yagüe, C., Moros, M., Grazu, V., Arruebo, M., & Santamaria, J. (2008). Synthesis and stealthing study of bare and PEGylated silica micro-and nanoparticles as potential drug-delivery vectors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 137, 45–53.
Wei, Y., Xu, J., Dong, H., Dong, J. H., Qiu, K., & Jansen-Varnum, S. A. (1999). Preparation and physisorption characterization of D-glucose-templated mesoporous silica sol-gel materials. Chemistry of Materials, 11, 2023–2029.
Yanagisawa, T., Shimizu, T., Kuroda, K., & Kato, C. (1990). The preparation of alkyltriinethylaininonium–kaneinite complexes and their conversion to microporous materials. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 63, 988–992.
Bau, L., Bartova, B., Arduini, M. and Mancin, F. (2009) Surfactant-free synthesis of mesoporous and hollow silica nanoparticles with an inorganic template. Chemical Communication. 7584–7586.
Hasan, F., Shah, A. A., & Hameed, A. (2006). Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39, 235–251.
Mohammadi, M., Habibi, Z., Dezvarei, S., Yousefi, M., & Ashjari, M. (2015). Selective enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids by hydrolysis of fish oil using immobilized and stabilized Rhizomucor miehei lipase preparations. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 94, 414–421.
Mohammadi, M., Habibi, Z., Dezvarei, S., Yousefi, M., Samadi, S., & Ashjari, M. (2014). Improvement of the stability and selectivity of Rhizomucor miehei lipase immobilized on silica nanoparticles: selective hydrolysis of fish oil using immobilized preparations. Process Biochemistry, 49, 1314–1323.
Adlercreutz, P. (2013). Immobilisation and application of lipases in organic media. Chemical Society Reviews, 42, 6406–6436.
Mateo, C., Palomo, J. M., Fernandez-Lorente, G., Guisan, J. M., & Fernandez-Lafuente, R. (2007). Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 1451–1463.
Marciello, M., Filice, M., & Palomo, J. M. (2012). Different strategies to enhance the activity of lipase catalysts. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2, 1531–1543.
Ansorge-Schumacher, M. B., & Thum, O. (2013). Immobilised lipases in the cosmetics industry. Chemical Society Reviews, 42, 6475–6490.
Kapoor, M., & Gupta, M. N. (2012). Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Process Biochemistry, 47, 555–569.
Pan, S., Liu, X., Xie, Y., Yi, Y., Li, C., Yan, Y., & Liu, Y. (2010). Esterification activity and conformation studies of Burkholderia cepacia lipase in conventional organic solvents, ionic liquids and their co-solvent mixture media. Bioresource Technology, 101, 9822–9824.
Salum, T., Baron, A., Zago, E., Turra, V., Baratti, J., Mitchell, D., & Krieger, N. (2008). An efficient system for catalyzing ester synthesis using a lipase from a newly isolated Burkholderia cepacia strain. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 26, 197–203.
Liu, T., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Li, Q., Wang, J., & Yan, Y. (2011). Improving catalytic performance of Burkholderia cepacia lipase immobilized on macroporous resin NKA. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 71, 45–50.
Mohammadi, M., Ashjari, M., Dezvarei, S., Yousefi, M., Babaki, M., & Mohammadi, J. (2015). Rapid and high-density covalent immobilization of Rhizomucor miehei lipase using a multi component reaction: application in biodiesel production. RSC Advances, 5, 32698–32705.
Liu, J., Li, C., Yang, Q., Yang, J., & Li, C. (2007). Morphological and structural evolution of mesoporous silicas in a mild buffer solution and lysozyme adsorption. Langmuir, 23, 7255–7262.
Hudson, S., Cooney, J., & Magner, E. (2008). Proteins in mesoporous silicates. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 47, 8582–8594.
Hartmann, M. (2005). Ordered mesoporous materials for bioadsorption and biocatalysis. Chemistry of Materials, 17, 4577–4593.
Takahashi, H., Li, B., Sasaki, T., Miyazaki, C., Kajino, T., & Inagaki, S. (2000). Catalytic activity in organic solvents and stability of immobilized enzymes depend on the pore size and surface characteristics of mesoporous silica. Chemistry of Materials, 12, 3301–3305.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Ejima, H., Richardson, J. J., Liang, K., Best, J. P., van Koeverden, M. P., Such, G. K., Cui, J., & Caruso, F. (2013). One-step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science, 341, 154–157.
Wei, L., Gao, Z., Jing, Y., & Wang, Y. (2013). Adsorption of CO2 from simulated flue gas on pentaethylenehexamine-loaded mesoporous silica support adsorbent. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 14965–14974.
Bootz, A., Vogel, V., Schubert, D., & Kreuter, J. (2004). Comparison of scanning electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering and analytical ultracentrifugation for the sizing of poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 57, 369–375.
Yamada, H., Urata, C., Higashitamori, S., Aoyama, Y., Yamauchi, Y., & Kuroda, K. (2014). Critical roles of cationic surfactants in the preparation of colloidal mesostructured silica nanoparticles: control of mesostructure, particle size, and dispersion. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6, 3491–3500.
Yamamoto, E., Kitahara, M., Tsumura, T., & Kuroda, K. (2014). Preparation of size-controlled monodisperse colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles and fabrication of colloidal crystals. Chemistry of Materials, 26, 2927–2933.
Fu, W. H., Guan, Y., Wang, Y. M., & He, M.-Y. (2016). A facile synthesis of monodispersed mesoporous silica nanospheres with Pm3n structure. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 220, 168–174.
Kruk, M., & Jaroniec, M. (2001). Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic-inorganic nanocomposite materials. Chemistry of Materials, 13, 3169–3183.
Xia, L. Y., Zhang, M. Q., Yuan, C. e., & Rong, M. Z. (2011). A facile heteroaggregate-template route to hollow magnetic mesoporous spheres with tunable shell structures. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21, 9020–9026.
Li, Y., Zhou, G., Li, C., Qin, D., Qiao, W., & Chu, B. (2009). Adsorption and catalytic activity of porcine pancreatic lipase on rod-like SBA-15 mesoporous material. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 341, 79–85.
Yang, J., Zhang, J., Zhu, L., Chen, S., Zhang, Y., Tang, Y., Zhu, Y., & Li, Y. (2006). Synthesis of nano titania particles embedded in mesoporous SBA-15: characterization and photocatalytic activity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 952–958.
Zhao, H., Yu, N., Ding, Y., Tan, R., Liu, C., Yin, D., Qiu, H., & Yin, D. (2010). Task-specific basic ionic liquid immobilized on mesoporous silicas: efficient and reusable catalysts for Knoevenagel condensation in aqueous media. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 136, 10–17.
Zhou, Z., Inayat, A., Schwieger, W., & Hartmann, M. (2012). Improved activity and stability of lipase immobilized in cage-like large pore mesoporous organosilicas. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 154, 133–141.
Salis, A., Svensson, I., Monduzzi, M., Solinas, V., & Adlercreutz, P. (2003). The atypical lipase B from Candida antarctica is better adapted for organic media than the typical lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosa. Biochimica Biophys Acta (BBA) - Proteins Proteomics, 1646, 145–151.
Gomes, F. M., Pereira, E. B., & de Castro, H. F. (2004). Immobilization of lipase on chitin and its use in nonconventional biocatalysis. Biomacromolecules, 5, 17–23.
Chao, C., Liu, J., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., Zhang, Y., Xiang, X., & Chen, R. (2013). Surface modification of halloysite nanotubes with dopamine for enzyme immobilization. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5, 10559–10564.
Liu, Y., Zeng, Z., Zeng, G., Tang, L., Pang, Y., Li, Z., Liu, C., Lei, X., Wu, M., & Ren, P. (2012). Immobilization of laccase on magnetic bimodal mesoporous carbon and the application in the removal of phenolic compounds. Bioresource Technology, 115, 21–26.
Altstein, M., Segev, G., Aharonson, N., Ben-Aziz, O., Turniansky, A., & Avnir, D. (1998). Sol-gel-entrapped cholinesterases: a microtiter plate method for monitoring anti-cholinesterase compounds. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 46, 3318–3324.
Chen, J.-P., & Lin, W.-S. (2003). Sol-gel powders and supported sol-gel polymers for immobilization of lipase in ester synthesis. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 32, 801–811.
Zhao, Z. Y., Liu, J., Hahn, M., Qiao, S., Middelberg, A. P., & He, L. (2013). Encapsulation of lipase in mesoporous silica yolk–shell spheres with enhanced enzyme stability. RSC Advances, 3, 22008–22013.
Zhou, Z., & Hartmann, M. (2013). Progress in enzyme immobilization in ordered mesoporous materials and related applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 42, 3894–3912.
Secundo, F. (2013). Conformational changes of enzymes upon immobilisation. Chemical Society Reviews, 42, 6250–6261.
Ren, G., & Yu, H. (2011). Oriented adsorptive immobilization of esterase BioH based on protein structure analysis. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 53, 286–291.
Sereti, V., Zoumpanioti, M., Papadimitriou, V., Pispas, S., & Xenakis, A. (2014). Biocolloids based on amphiphilic block copolymers as a medium for enzyme encapsulation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 118, 9808–9816.
Kalantari, M., Kazemeini, M., Tabandeh, F., & Arpanaei, A. (2012). Lipase immobilisation on magnetic silica nanocomposite particles: effects of the silica structure on properties of the immobilised enzyme. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22, 8385–8393.
Jaeger, K.-E., & Eggert, T. (2002). Lipases for biotechnology. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13, 390–397.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21276060, 21276062, and 21306039), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (13JCYBJC18500), the Science and Technology Research Key Project of Higher School in Hebei Province (YQ2013025), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2015202082), Project of Science and Technology of Hebei Province (13273607 and 13274314), and Tianjin City High School Science & Technology Fund Planning Project (20140513).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 694 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Sun, W., Zhou, L. et al. Improved Performance of Lipase Immobilized on Tannic Acid-Templated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179, 1155–1169 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2056-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2056-1