Abstract
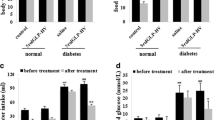
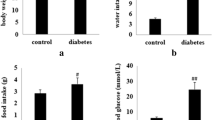
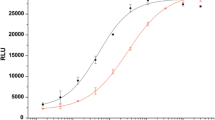
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), is currently used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus and hirudin (HV), plays an important role in controlling thrombosis and cardiovascular diseases. This investigation aimed to develop a fusion peptide 5rolGLP-HV which combined functions of rolGLP-1 and rHV to treat diabetes and thrombosis. In this study, we constructed a fusion gene including five copies of rolGLP-1 and one copy of rHV (5rolGLP-HV). The optimum expression conditions of 5rolGLP-HV in a soluble form were 0.8 mM IPTG induction when OD600 reached 0.6–0.8 and further growing at 25 °C for 9 h. Isolated rolGLP-1 and rHV were acquired by trypsin digestion in vitro, and the concentration of them was determined by HPLC in vivo. Oral administration of 5rolGLP-HV significantly decreased the levels of blood glucose, GHbA1C, TC, and TG in diabetic mice at the time of 3 weeks compared to the saline-treated group (p < 0.05), while the insulin level was reversed significantly (p < 0.05). 5rolGLP-HV treatment significantly shortened the length of thrombus in thrombosis mice compared to the saline-treated group (p < 0.01). These results indicated that 5rolGLP-HV had dual-function in treating diabetes and preventing thrombosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- DPP-IV:
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV
- rolGLP-1:
-
Recombinant oral long-acting GLP-1
- HV:
-
Hirudin
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- OD:
-
Optical density
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- GHbA1C:
-
Glycosylated hemoglobin A1c
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- FBG:
-
Fasting blood-glucose
- ATU:
-
Antithrombin units
References
Ferroni, P., Basili, S., Falco, A., & Davi, G. (2004). Platelet activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2(8), 1282–1291.
Ajjan, R., & Grant, P. J. (2006). Coagulation and atherothrombotic disease. Atherosclerosis, 186(2), 240–259.
Ajjan, R. A., & Ariens, R. A. (2009). Cardiovascular disease and heritability of the prothrombotic state. Blood Reviews, 23(2), 67–78.
Lennox, R., Porter, D.W., Flatt, P.R., Holscher, C., Irwin, N., Gault, V.A. (2014). Comparison of the independent and combined effects of sub-chronic therapy with metformin and a stable GLP-1 receptor agonist on cognitive function, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and metabolic control in high-fat fed mice. Neuropharmacology, 8622–8630.
Dailey, M. J., & Moran, T. H. (2013). Glucagon-like peptide 1 and appetite. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 24(2), 85–91.
Samson, S. L., Sathyanarayana, P., Jogi, M., Gonzalez, E. V., Gutierrez, A., Krishnamurthy, R., Muthupillai, R., Chan, L., & Bajaj, M. (2011). Exenatide decreases hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a mouse model of obesity and in a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia, 54(12), 3093–3100.
Mack, C. M., Moore, C. X., Jodka, C. M., Bhavsar, S., Wilson, J. K., Hoyt, J. A., Roan, J. L., Vu, C., Laugero, K. D., Parkes, D. G., et al. (2006). Antiobesity action of peripheral exenatide (exendin-4) in rodents: effects on food intake, body weight, metabolic status and side-effect measures. International Journal of Obesity, 30(9), 1332–1340.
Parlevliet, E. T., de Leeuw van Weenen, J. E., Romijn, J. A., & Pijl, H. (2010). GLP-1 treatment reduces endogenous insulin resistance via activation of central GLP-1 receptors in mice fed a high-fat diet. American Journal of Physiology, Endocrinology and Metabolism, 299(2), E318–E324.
Parlevliet, E. T., Wang, Y., Geerling, J. J., Schroder-Van der Elst, J. P., Picha, K., O’Neil, K., Stojanovic-Susulic, V., Ort, T., Havekes, L. M., Romijn, J. A., et al. (2012). GLP-1 receptor activation inhibits VLDL production and reverses hepatic steatosis by decreasing hepatic lipogenesis in high-fat-fed APOE*3-Leiden mice. PLoS ONE, 7(11), e49152.
Gao, M., Tian, H., Ma, C., Gao, X., Guo, W., & Yao, W. (2010). Expression, purification, and C-terminal site-specific PEGylation of cysteine-mutated glucagon-like peptide-1. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162(1), 155–165.
Tahrani, A. A., Piya, M. K., Kennedy, A., & Barnett, A. H. (2010). Glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: targets and new therapies. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 125(2), 328–361.
Green, B. D., Liu, H. K., McCluskey, J. T., Duffy, N. A., O’Harte, F. P., McClenaghan, N. H., & Flatt, P. R. (2005). Function of a long-term, GLP-1-treated, insulin-secreting cell line is improved by preventing DPP IV-mediated degradation of GLP-1. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism, 7(5), 563–569.
Reimann, F., & Gribble, F. M. (2002). Glucose-sensing in glucagon-like peptide-1-secreting cells. Diabetes, 51(9), 2757–2763.
Drucker, D. J., & Nauck, M. A. (2006). The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet, 368(9548), 1696–1705.
Holst, J. J. (2007). The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiological Reviews, 87(4), 1409–1439.
Baggio, L. L., & Drucker, D. J. (2007). Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology, 132(6), 2131–2157.
Ben-Shlomo, S., Zvibel, I., Shnell, M., Shlomai, A., Chepurko, E., Halpern, Z., Barzilai, N., Oren, R., & Fishman, S. (2011). Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces hepatic lipogenesis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Journal of Hepatology, 54(6), 1214–1223.
Madonna, R., & De Caterina, R. (2011). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of vascular injury in diabetes—part I: pathways of vascular disease in diabetes. Vascular Pharmacology, 54(3-6), 68–74.
Honardoost, M., Sarookhani, M. R., Arefian, E., & Soleimani, M. (2014). Insulin resistance associated genes and miRNAs. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174(1), 63–80.
Standl, E., Muller, M., & Schnell, O. (2009). The impact of glucose-lowering therapy on cardiovascular outcomes. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 23(3), 401–411.
Markwardt, F. (1985). Pharmacology of hirudin: one hundred years after the first report of the anticoagulant agent in medicinal leeches. Biomedica Biochimica Acta, 44(7-8), 1007–1013.
Donella-Deana, A., Varro, A., Dockray, G. J., & Pinna, L. A. (1991). Substitution of phosphotyrosine for sulphotyrosine in biologically active peptides. Enzymatic phosphorylation of a progastrin peptide confers immunoreactivity reminiscent of the sulphated derivative. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1095(1), 75–77.
Lombardi, A., De Simone, G., Galdiero, S., Staiano, N., Nastri, F., & Pavone, V. (1999). From natural to synthetic multisite thrombin inhibitors. Biopolymers, 51(1), 19–39.
Nowak, G., & Markwardt, F. (1991). Hirudin in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Haemostasis, 21(Suppl), 1142–1148.
Jiang, W., Li, W., Hong, Y., Wang, S., Fang, B. (2015). Cloning, expression, mutagenesis library construction of glycerol dehydratase, and binding mode simulation of its reactivase with ligands. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.
Zafar, A., Aftab, M.N., Ud Din, Z., Aftab, S., Iqbal, I., Ul Haq, I. (2015). Cloning, purification and characterization of a highly thermostable amylase gene of thermotoga petrophila into Escherichia coli. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.
Zhang, Y. F., Wei, Y. M., Ma, B. C., Qiao, K. Y., Ma, Z. H., Li, C., Ma, C., Ji, Y. L., Dong, Z., Hao, J. F., et al. (2013). Expression of rolGLP-HV in E-coli and its dual-function for the treatment of diabetes and thrombosis. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics, 19(3), 257–263.
Zeng, X.Y., Dong, S., He, N.N., Jiang, C.J., Dai, Y., Xia, Y.F. (2015). Comparative pharmacokinetics of arctigenin in normal and type 2 diabetic rats after oral and intravenous administration. Fitoterapia, 105119–105126.
Rouse, R., Xu, L., Stewart, S., & Zhang, J. (2014). High fat diet and GLP-1 drugs induce pancreatic injury in mice. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 276(2), 104–114.
Shrivastava, A., Chaturvedi, U., Sonkar, R., Khanna, A. K., Saxena, J. K., & Bhatia, G. (2012). Antioxidant effect of Azadirachta indica on high fat diet induced diabetic Charles Foster rats. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 167(2), 229–236.
Morsy, M.A., Heeba, G.H., Mahmoud, M.E. (2015). Ameliorative effect of eprosartan on high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced early diabetic nephropathy in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 75090–75097.
Liu, C., Hu, M. Y., Zhang, M., Li, F., Li, J., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Guo, H. F., Xu, P., Liu, L., et al. (2014). Association of GLP-1 secretion with anti-hyperlipidemic effect of ginsenosides in high-fat diet fed rats. Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental, 63(10), 1342–1351.
Shi, B. X., Li, J. C., Yu, A. P., Yuan, B., & Wu, C. S. (2006). Two-step ion-exchange chromatographic purification of recombinant hirudin-II and its C-terminal-truncated derivatives expressed in Pichia pastoris. Process Biochemistry, 41(12), 2446–2451.
Ma, B., Tu, P., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Ma, C., Ji, Y., Li, X., Abbas, S. A., & Li, M. (2013). Expression and purification of optimized rolGLP-1, a novel GLP-1 analog, in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) and its good glucoregulatory effect on type 2 diabetic mice. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 14(11), 985–994.
Hou, J., Yan, R., Yang, L., Wu, Z., Wang, C., Ding, D., Li, N., Ma, C., & Li, M. (2007). High-level expression of fusion protein containing 10 tandem repeated GLP-1 analogs in yeast Pichia pastoris and its biological activity in a diabetic rat model. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 71(6), 1462–1469.
Hou, J., Yan, R., Ding, D., Yang, L., Wang, C., Wu, Z., Yu, X., Li, W., & Li, M. (2007). Oral administration of a fusion protein containing eight GLP-1 analogues produced in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biotechnology Letters, 29(10), 1439–1446.
Cen, X., Ni, J., Tan, T., Liu, X., Li, C., Chen, J., Huang, Y., Zhu, S., & Bi, Q. (2006). Investigation on recombinant hirudin via oral route. Peptides, 27(4), 836–840.
Fujita, M., Ito, Y., Hong, K., & Nishimuro, S. (1995). Characterization of nattokinase-degraded products from human fibrinogen or cross-linked fibrin. Fibrinolysis, 9(3), 157–164.
Billings, P. C., St Clair, W. H., Maki, P. A., & Kennedy, A. R. (1992). Distribution of the Bowman Birk protease inhibitor in mice following oral administration. Cancer Letters, 62(3), 191–197.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Key Technologies R&D Program of Tianjin (14ZCZDSY00013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, H. et al. Construction of a Fusion Peptide 5rolGLP-HV and Analysis of its Therapeutic Effect on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Thrombosis in Mice. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179, 59–74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-1979-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-1979-x