Abstract
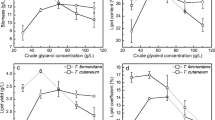
In the present study, acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) fermentation wastewater with high chemical oxygen demand (COD) value (about 18,000 mg/L) was biologically treated by oleaginous yeast Trichosporon cutaneum without any pretreatment. During fermentation, most COD degradation was finished within 48 h and finally, a maximum COD degradation of 68 % was obtained. The highest biomass and lipid content was 4.9 g/L and 14.7 %, respectively. Various materials including sugars (glucose and xylose), organic acids (acetic acid and butyric acid), and alcohol compounds (ethanol and butanol) could be utilized as carbon sources by T. cutaneum simultaneously; thus, it has a broad carbon source spectrum and is a potential microorganism for biological treatment for various wastewaters. Overall, the lipid composition of microbial oils produced by this bioconversion is similar to that of vegetable oils, and thus, it could be used for biodiesel production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia, V., Pakkila, J., Ojamo, H., Muurinen, E., & Keiski, R. L. (2011). Challenges in biobutanol production: how to improve the efficiency? Renewable Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15, 964–980.
Qureshi, N., & Ezeji, T. C. (2008). Butanol, ‘a superior biofuel’ production from agricultural residues (renewable biomass): recent progress in technology. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2, 319–330.
Lu, C., Zhao, J., Yang, S. T., & Wei, D. (2011). Fed-batch fermentation for n-butanol production from cassava bagasse hydrolysate in a fibrous bed bioreactor with continuous gas stripping. Bioresource Technology, 104, 380–387.
Chen, X. F., Huang, C., Xiong, L., Chen, X. D., & Ma, L. L. (2012). Oil production on wastewaters after butanol fermentation by oleaginous yeast Trichosporon coremiiforme. Bioresource Technology, 118, 594–597.
Peng, W. F., Huang, C., Chen, X. F., Xiong, L., Chen, X. D., Chen, Y., & Ma, L. L. (2013). Microbial conversion of wastewater from butanol fermentation to microbial oil by oleaginous yeast Trichosporon dermatis. Renewable Energy, 55, 31–34.
Colussi, I., Cortesi, A., Vedova, L. D., Gallo, V., & Robles, F. (2009). Start-up procedures and analysis of heavy metals inhibition on methanogenic activity in EGSB reactor. Bioresource Technology, 100, 6290–6294.
Wei, C., Zhang, T., Feng, C., Wu, H., Deng, Z., Wu, C., & Lu, B. (2011). Treatment of food processing wastewater in a full-scale jet biogas internal loop anaerobic fluidized bed reactor. Biodegradation, 22, 347–357.
Yousuf, A., Sannino, F., Addorisio, V., & Pirozzi, D. (2010). Microbial conversion of olive oil mill wastewaters into lipids suitable for biodiesel production. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 8630–8635.
Chen, X. F., Huang, C., Xiong, L., Chen, X. D., & Ma, L. L. (2012). Microbial oil production from corncob acid hydrolysate by Trichosporon cutaneum. Biotechnology Letters, 34, 1025–1028.
Hu, C., Wu, S., Wang, Q., Jin, G., Shen, H., & Zhao, Z. K. (2011). Simultaneous utilization of glucose and xylose for lipid production by Trichosporon cutaneum. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 4, 25.
Huang, X., Wang, Y., Liu, W., & Bao, J. (2011). Biological removal of inhibitors leads to the improved lipid production in the lipid fermentation of corn stover hydrolysate by Trichosporon cutaneum. Bioresource Technology, 102, 9705–9709.
Chen, X. F., Huang, C., Yang, X. Y., Xiong, L., Chen, X. D., & Ma, L. L. (2013). Evaluating the effect of medium composition and fermentation condition on the microbial oil production by Trichosporon cutaneum on corncob acid hydrolysate. Bioresource Technology, 143, 18–24.
Xue, F. Y., Miao, J. X., Zhang, X., Luo, H., & Tan, T. W. (2008). Studies on lipid production by Rhodotorula glutinis fermentation using monosodium glutamate wastewater as culture medium. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5923–5927.
Folch, J., Lees, M., & Sloane-Stanley, G. (1957). A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 226, 497–509.
Zhu, S. L., Huang, W., Xu, J., Wang, Z., Xu, J., & Yuan, Z. H. (2014). Metabolic changes of starch and lipid triggered by nitrogen starvation in the microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Bioresource Technology, 152, 292–298.
Huang, C., Zong, M. H., Wu, H., & Liu, Q. P. (2009). Microbial oil production from rice straw hydrolysate by Trichosporon fermentans. Bioresource Technology, 100, 4535–4538.
Papanikolaou, S., & Aggelis, G. (2003). Modeling lipid accumulation and degradation in Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on industrial fats. Current Microbiology, 46, 398–402.
Bajpai, D., & Tyagi, V. (2006). Biodiesel: source, production, composition, properties and its benefits. Journal of Oleo Science, 55, 487–502.
Zhou, W., Wang, W., Li, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides Y2 in bioethanol wastewater and evaluation of biomass energetic yield. Bioresource Technology, 127, 435–440.
Venkata Subhash, G., & Venkata Mohan, S. (2011). Biodiesel production from isolated oleaginous fungi Aspergillus niger IICTGSVML1 using corncob waste liquor as a substrate. Bioresource Technology, 102, 9286–9290.
Chi, Z., Zheng, Y., Jiang, A., & Chen, S. L. (2011). Lipid production by culturing oleaginous yeast and algae with food waste and municipal wastewater in an integrated process. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 165, 442–453.
Schneider, T., Graeff-Honninger, S., French, W., Hernandez, R., Merkt, N., Claupein, W., Hetrick, M., & Pham, P. (2013). Lipid and carotenoid production by oleaginous red yeast Rhodotorula glutinis cultivated on brewery effluents. Energy, 61, 34–43.
Dynowska, M., Biedunkiewicz, A., Ejdys, E., Sucharzewska, E., & Roslan, M. (2011). Fungi of the genus Trichosporon isolated from the skin in hospitalized patients. Acta Mycologica, 48, 147–153.
Aleksieva, Z., Ivanova, D., Godjevargova, T., & Atanasov, B. (2002). Degradation of some phenol derivatives by Trichosporon cutaneum R57. Process Biochemistry, 37, 1215–1219.
Yinbo, Q., Hongzhang, C., & Peiji, G. (1992). SCP production from steam exploded hemicellulose autohydrolysate by Trichosporon cutaneum. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 73, 386–389.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2013B010404036), project of Guangzhou Science and Technology (2013 J4300031), the Support Plan Project of National Science and Technology (2012BAD32B07), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51378486, U1261116), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2012040007546), the Project of Jiangsu Province Science and Technology (BE2013083), the Foundation of Xuyi Center of Attapulgite Applied Technology Research Development and Industrialization, Chinese Academy of Sciences (20121004), and Foundation of Director of Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences (y407r41001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, L., Huang, C., Li, XM. et al. Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol (ABE) Fermentation Wastewater Treatment by Oleaginous Yeast Trichosporon cutaneum . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 563–571 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1595-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1595-1