Abstract
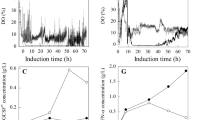
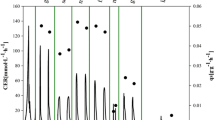
Various induction strategies were investigated for effective porcine interferon-α (pIFN-α) production by Pichia pastoris in a 10 L fermenter. We found that pIFN-α concentration could be significantly improved with the strategies of low-temperature induction or methanol/sorbitol co-feeding. On this basis, a combinational strategy of induction at lower temperature (20 °C) with methanol/sorbitol co-feeding has been proposed for improvement of pIFN-α production. The results reveal that maximal pIFN-α concentration and antiviral activity reach the highest level of 2.7 g/L and 1.8 × 107 IU/mg with the proposed induction strategy, about 1.3–2.1 folds higher than those obtained with other sub-optimal induction strategies. Metabolic analysis and online multi-variable measurement results indicate that energy metabolic enrichment is responsible for the performance enhancement of pIFN-α production, as a large amount of ATP could be simultaneously produced from both formaldehyde oxidation pathway in methanol metabolism and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in sorbitol metabolism. In addition, the proposed combinational induction strategy enables P. pastoris to be resistant to high methanol concentration (42 g/L), which conceivably occur associating with the error-prone methanol over-feeding. As a result, the proposed combinational induction strategy simultaneously increased the targeted protein concentration and operational stability leading to significant improvement of pIFN-α production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cereghino, J. L., & Cregg, J. M. (2000). Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 24, 45–66.
Macauley-Patrick, S., Fazenda, M. L., McNeil, B., & Harvey, L. M. (2005). Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast, 22, 249–270.
Chinsangaram, J., Moraes, M. P., Koster, M., & Grubman, M. J. (2003). Novel viral disease control strategy: adenovirus expressing alpha interferon rapidly protects swine from foot-and-mouth disease. Joural of Virolory, 77, 1621–1625.
Chang, H. W., Jeng, C. R., Liu, J. J., Lin, T. L., Chang, C. C., Chia, M. Y., Tsai, Y. C., & Pang, V. F. (2005). Reduction of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infection in swine alveolar macrophages by porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2)-induced interferon-alpha. Veterinary Microbiology, 108, 167–177.
Cereghino, G. P., Cereghino, J. L., Ilgen, C., & Cregg, J. M. (2002). Production of recombinant proteins in fermenter cultures of the yeast Pichia pastoris. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13, 329–332.
Ohya, T., Ohyama, M., & Kobayashi, K. (2006). Optimization of human serum albumin production in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris by repeated fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 90, 876–887.
Khatri, N. K., & Hoffmann, F. (2006). Impact of methanol concentration on secreted protein production in oxygen-limited cultures of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 93, 871–879.
Gao, M. J., Zhan, X. B., Zheng, Z. Y., Wu, J. R., Dong, S. J., Li, Z., Shi, Z. P., & Lin, C. C. (2013). Enhancing pIFN-α production and process stability in fed-batch culture of Pichia pastoris by controlling the methanol concentration and monitoring the responses of OUR/DO levels. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 171, 1262–1275.
Yu, R. S., Dong, S. J., Zhu, Y. M., Jin, H., Gao, M. J., Duan, Z. Y., Zheng, Z. Y., Shi, Z. P., & Li, Z. (2010). Effective and stable porcine interferon-α production by Pichia pastoris fed-batch cultivation with multi-variables clustering and analysis. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 33, 473–483.
Jahic, M., Wallberg, F., Bollok, M., Garcia, P., & Enfors, S. (2003). Temperature limited fed-batch technique for control of proteolysis in Pichia pastoris bioreactor cultures. Microbial Cell Factories, 2(1), 6.
Jin, H., Liu, G. Q., Ye, X. F., Duan, Z. Y., Li, Z., & Shi, Z. P. (2010). Enhanced porcine interferon-α production by recombinant Pichia pastoris with a combinational control strategy of low induction temperature and high dissolved oxygen concentration. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 52, 91–98.
Dragosits, M., Stadlmann, J., Albiol, J., Baumann, K., Maurer, M., Gasser, B., Sauer, M., Altmann, F., Ferrer, P., & Mattanovich, D. (2009). The effect of temperature on the proteome of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 1380–1392.
Wang, Y., Wang, Z. H., Xu, Q. L., Du, G. C., Hua, Z. Z., Liu, L. M., Li, J. H., & Chen, J. (2009). Lowering induction temperature for enhanced production of polygalacturonate lyase in recombinant Pichia pastoris. Process Biochemistry, 44, 949–954.
Choi, D. B., & Park, E. Y. (2006). Enhanced production of mouse α-amylase by feeding combined nitrogen and carbon sources in fed-batch culture of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Process Biochemistry, 41, 390–397.
Horstkotte, B., Arnau, C., Valero, F., Elsholz, O., & Cerdà, V. (2008). Monitoring of sorbitol in Pichia pastoris cultivation applying sequential injection analysis. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 42, 77–83.
Çelik, E., Çalık, P., & Oliver, S. G. (2009). Fed-batch methanol feeding strategy for recombinant protein production by Pichia pastoris in the presence of co-substrate sorbitol. Yeast, 26, 473–484.
Jungo, C., Schenk, J., Pasquier, M. M., Marison, I. W., & von Stockar, U. (2007). A quantitative analysis of the benefits of mixed feeds of sorbitol and methanol for production of recombinant avidin with Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biotechnology, 131, 57–66.
Ramón, R., Ferrer, P., & Valero, F. (2007). Sorbitol co-feeding reduces metabolic burden caused by the overexpression of a Rhizopus oryzae lipase in Pichia pastoris. Journal Biotechnology, 130, 39–46.
Gao, M. J., Li, Z., Yu, R. S., Wu, J. R., Zheng, Z. Y., Shi, Z. P., Zhan, X. B., & Lin, C. C. (2012). Methanol/sorbitol co-feeding induction enhanced porcine interferon-α production by P. pastoris associated with energy metabolism shift. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 35, 1125–1136.
Zhu, T. C., You, L. J., Gong, F. Y., Xie, M. F., Xue, Y. F., Li, Y., & Ma, Y. Y. (2011). Combinatorial strategy of sorbitol feeding and low-temperature induction leads to high-level production of alkaline β-mannanase in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 49, 407–412.
Tian, M. Y., Huitema, E., Da Cunha, L., Torto-Alalibo, T., & Kamoun, S. (2004). A Kazal-like extracellular serine protease inhibitor from Phytophthora infestans targets the tomato pathogenesis-related protease P69B. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 26370–26377.
Suye, S., Ogawa, A., Yokoyama, S., & Obayashi, A. (1990). Screening and identification of Candida methanosorbosa as alcohol oxidase-producing methanol using yeast. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 54, 1297–1298.
Schütte, H., Flossdorf, J., Sahm, H., & Kula, M. R. (1976). Purification and properties of formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii. European Journal of Biochemistry, 62, 151–160.
Gao, M. J., Zheng, Z. Y., Wu, J. R., Dong, S. J., Li, Z., Jin, H., Zhan, X. B., & Lin, C. C. (2012). Improvement of specific growth rate of Pichia pastoris for effective porcine interferon-α production with an on-line model based glycerol feeding strategy. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1437–1445.
Jungo, C., Marison, I., & Von Stockar, U. (2007). Regulation of alcohol oxidase of a recombinant Pichia pastoris Mut+ strain in transient continuous cultures. Journal of Biotechnology, 130, 236–246.
Trinh, L. B., Phue, J. N., & Shiloach, J. (2003). Effect of methanol feeding strategies on production and yield of recombinant mouse endostatin from Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 82, 438–444.
Lim, H. K., Choi, S. J., Kim, K. Y., & Jung, K. H. (2003). Dissolved-oxygen-stat controlling two variables for methanol induction of rGuamerin in Pichia pastoris and its application to repeated fed-batch. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 62, 342–348.
Khatri, N. K., & Hoffmann, F. (2006). Oxygen-limited control of methanol uptake for improved production of a single-chain antibody fragment with recombinant Pichia pastoris. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72, 492–498.
Çelik, E., & Çalık, P. (2012). Production of recombinant proteins by yeast cells. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 1108–1118.
Lüers, G. H., Advani, R., Wenzel, T., & Subramani, S. (1998). The Pichia pastoris dihydroxyacetone kinase is a PTS1-containing, but cytosolic, protein that is essential for growth on methanol. Yeast, 14, 759–771.
Van der Klei, I. J., Yurimoto, H., Sakai, Y., & Veenhuis, M. (2006). The significance of peroxisomes in methanol metabolism in methylotrophic yeast. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 12, 1453–1462.
Krainer, F. W., Dietzsch, C., Hajek, T., Herwig, C., Spadiut, O., & Glieder, A. (2012). Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris strains with an engineered methanol utilization pathway. Microbial Cell Factories, 11, 22.
Schroer, K., Peter, L. K., Hartner, F. S., Glieder, A., & Pscheidt, B. (2010). Engineering the Pichia pastoris methanol oxidation pathway for improved NADH regeneration during whole-cell biotransformation. Metabolic Engineering, 12, 8–17.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial supports from National Natural Science Foundation of China (#31301408), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (#BK20130122), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (#2014 M551501), a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions,the 111 Project (No. 111-2-06),and the Jiangsu province “Collaborative Innovation Center for Advanced Industrial Fermentation” industry development program.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, MJ., Zhan, XB., Gao, P. et al. Improving Performance and Operational Stability of Porcine Interferon-α Production by Pichia pastoris with Combinational Induction Strategy of Low Temperature and Methanol/Sorbitol Co-feeding. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 493–504 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1590-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1590-6