Abstract
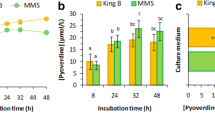
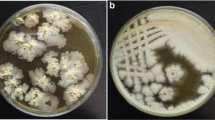
Siderophore production by Bacillus megaterium was detected, in an iron-deficient culture medium, during the exponential growth phase, prior to the sporulation, in the presence of glucose; these results suggested that the onset of siderophore production did not require glucose depletion and was not related with the sporulation. The siderophore production by B. megaterium was affected by the carbon source used. The growth on glycerol promoted the very high siderophore production (1,182 μmol g−1 dry weight biomass); the opposite effect was observed in the presence of mannose (251 μmol g−1 dry weight biomass). The growth in the presence of fructose, galactose, glucose, lactose, maltose or sucrose, originated similar concentrations of siderophore (546–842 μmol g−1 dry weight biomass). Aeration had a positive effect on the production of siderophore. Incubation of B. megaterium under static conditions delayed and reduced the growth and the production of siderophore, compared with the incubation in stirred conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt, C. K., Fleig, M., Sacher, F., & Brauch, H. E. (2004). Environmental Pollution, 131, 107–124.
Knepper, T. P. (2003). Trac-Trends Anal. Chemical, 22, 708–724.
Nowack, B. and VanBriesen, J.M. (2005) Biogeochemistry of chelating agents, vol. 910. Nowack, B. and VanBriesen, J.M., (eds.). Washington DC: American Chemical Society, pp. 1–18
Bucheli-Witschel, M., & Egli, T. (2001). FEMS Microbiol. Review, 25, 69–106.
Hider, R. C., & Kong, X. L. (2010). Natural Product Reports, 27, 637–657.
Budzikiewicz, H. (2010) Iron uptake and homeostasis in microorganisms. Cornelis, P. and Andrews, S.C., (eds.). Wymondham: Caister Academic Press, pp. 1–16
Carrano, C. J., Drechsel, H., Kaiser, D., Jung, G., Matzanke, B., Winkelmann, G., Rochel, N., & AlbrechtGary, A. M. (1996). Inorganic Chemistry, 35, 6429–6436.
von Wiren, N., Khodr, H., & Hider, R. C. (2000). Plant Physiology, 124, 1149–1157.
Martell, A.E. and Smith, R.M. (2004) Standard reference database 46 version 8.0. New York: National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), US Department of Commerce
Warren, R. A. J., & Neilands, J. B. (1965). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 240, 2055–2058.
Pierwola, A., Krupinski, T., Zalupski, P., Chiarelli, M., & Castignetti, D. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 831–836.
Winkelmann, G., Busch, B., Hartmann, A., Kirchhof, G., Sussmuth, R., & Jung, G. (1999). Biometals, 12, 255–264.
Yehuda, Z., Shenker, M., Hadar, Y., & Chen, Y. N. (2000). Journal of Plant Nutrition, 23, 1991–2006.
Das, A., Prasad, R., Srivastava, A., Giang, P.H., Bhatnagar, K. and Varma, A. (2007) Microbial siderophores. Varma, A. and Chincholkar, S.B. (eds.). Berlin: Springer, pp. 1–42
Nagoba, B., & Vedpathak, D. (2011). European of Journal General Medicine, 8, 229–235.
Miller, M. J. (1989). Chemical Reviews, 89, 1563–1579.
Shenker, M., & Chen, Y. (2005). Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 51, 1–17.
Lankford, C. E., Walker, J. R., Reeves, J. B., Nabbut, N. H., Byers, B. R., & Jones, R. J. (1966). Journal of Bacteriology, 91, 1070–1079.
Arceneaux, J., Davis, W. B., Downer, D. N., Haydon, A. H., & Byers, B. R. (1973). Journal of Bacteriology, 115, 919–927.
Arceneaux, J. E. L., & Byers, B. R. (1976). Journal of Bacteriology, 127, 1324–1330.
Arceneaux, J. E. L., & Byers, B. R. (1980). Journal of Bacteriology, 141, 715–721.
Hu, X. C., & Boyer, G. L. (1995). Biometals, 8, 357–364.
Mullis, K. B., Pollack, J. R., & Neilands, J. B. (1971). Biochemistry, 10, 4894–4898.
Gaballa, A. and Helmann, J.D. (2010) Iron uptake and homeostasis in microorganisms. Cornelis, P. and Andrews, S.C., (eds.). Wymondham: Caister Academic Press, pp. 229–246.
Hu, X. C., & Boyer, G. L. (1996). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 4044–4048.
Davis, W. B., McCauley, M. J., & Byers, B. R. (1971). Journal of Bacteriology, 105, 589–594.
Byers, B. R., Powell, M. V., & Lankford, C. E. (1967). Journal of Bacteriology, 93, 286–294.
Storey, E. P., Boghozian, R., Little, J. L., Lowman, D. W., & Chakraborty, R. (2006). Biometals, 19, 637–649.
Nicolaisen, K., Moslavac, S., Samborski, A., Valdebenito, M., Hantke, K., Maldener, I., Muro-Pastor, A. M., Flores, E., & Schleiff, E. (2008). Journal of Bacteriology, 190, 7500–7507.
Sonier, M. B., Contreras, D. A., Treble, R. G., & Weger, H. G. (2012). Botany-Botanique, 90, 181–190.
Alexander, D. B., & Zuberer, D. A. (1991). Biology and Fertility of Soils, 12, 39–45.
Schwyn, B., & Neilands, J. B. (1987). Analytical Biochemistry, 160, 47–56.
Chaplin, M.F. (1986) Carbohydrate analysis—a practical approach. Chaplin, M.F. and Kennedy, J.F. (eds.). Washington DC: IRL Press. pp. 1–36
Schalk, I. J., Hannauer, M., & Braud, A. (2011). Environmental Microbiology, 13, 2844–2854.
Villegas, M.E.D. (2007) Microbial siderophores, vol. 12. Varma, A. and Chincholkar, S.B. (eds.). Berlin: Springer. pp. 219–231
Vary, P. S., Biedendieck, R., Fuerch, T., Meinhardt, F., Rohde, M., Deckwer, W. D., & Jahn, D. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 76, 957–967.
Schaeffer, P. (1969). Bacteriological Reviews, 33, 48–71.
Schallmey, M., Singh, A., & Ward, O. P. (2004). Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 50, 1–17.
Martin, J. F., & Demain, A. L. (1980). Microbiological Reviews, 44, 230–251.
Ruiz, B., Chavez, A., Forero, A., Garcia-Huante, Y., Romero, A., Sanchez, M., Rocha, D., Sanchez, B., Rodriguez-Sanoja, R., Sanchez, S., & Langley, E. (2010). Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 36, 146–167.
Tschierske, M., Drechsel, H., Jung, G., & Zahner, H. (1996). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 45, 664–670.
Wilson, M. K., Abergel, R. J., Arceneaux, J. E. L., Raymond, K. N., & Byers, B. R. (2010). Biometals, 23, 129–134.
Chincholkar, S.B., Chaudhari, B.L. and Rane, M.R. (2007) Microbial siderophores, vol. 12. Varma, A. and Chincholkar, S.B. (eds.). Berlin: Springer, pp. 233–242
Duffy, B. K., & Defago, G. (1999). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 2429–2438.
Stulke, J., & Hillen, W. (2000). Annual Review of Microbiology, 54, 849–880.
Gupta, N., Mehra, G., & Gupta, R. (2004). Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 50, 361–368.
Ayoub, M., & Abdullah, A. Z. (2012). Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16, 2671–2686.
Guimaraes, P. M. R., Teixeira, J. A., & Domingues, L. (2010). Biotechnology Advances, 28, 375–384.
Chisti, Y. and Moo-Young, M. (2001) Basic biotechnology: 2nd ed. Ratledge, C. and Kristiansen, B. (eds.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 151–171
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Porto University/Totta Bank for their financial support through the project “Microbiological production of chelating agents” (Ref: 180). The authors also thank the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) through the Portuguese Government for their financial support of this work through the grants Strategic project-LA23/2013-2014 (IBB) and PEST-C/EQB/LA0006/2011 (REQUIMTE). Manuela D. Machado gratefully acknowledges the postdoctoral (SFRH/BPD/72816/2010) grant from FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, S., Neto, I.F.F., Machado, M.D. et al. Siderophore Production by Bacillus megaterium: Effect of Growth Phase and Cultural Conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 549–560 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0562-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0562-y