Abstract
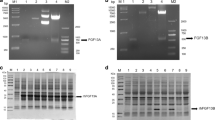
Fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) is considered as a crucial gene for tumorigenesis in humans and the development of mammalian embryos. The secreted, mature form of human FGF4 is thought to be comprised of 175 amino acid residues (proline32 to leucine206, Pro32-Leu206). Here, we found that bacterially expressed, 6× histidine (His)-tagged human FGF4 (Pro32-Leu206) protein, referred to as HishFGF4, was unstable such as in phosphate-buffered saline. In these conditions, site-specific cleavage, including between Ser54 and Leu55, in HishFGF4 was identified. In order to generate stable human FGF4 derivatives, a 6× His-tagged human FGF4 (Leu55-Leu206), termed HishFGF4L, was expressed in Escherichia coli. HishFGF4L could be purified from the supernatant of cell lysates by heparin column chromatography. In phosphate-buffered saline, HishFGF4L was considered as sufficiently stable. HishFGF4L exerted significant mitogenic activities in mouse embryonic fibroblast Balb/c 3T3 cells. In the presence of PD173074, an FGF receptor inhibitor, the growth-stimulating activity of HishFGF4L disappeared. Taken together, we suggest that HishFGF4L is capable of promoting cell growth via an authentic FGF signaling pathway. Our study provides a simple method for the production of a bioactive human FGF4 derivative in E. coli.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itoh, N., & Ornitz, D. M. (2011). Journal of Biochemistry, 149(2), 121–130.
Sakamoto, H., Mori, M., Taira, M., et al. (1986). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 83(11), 3997–4001.
Niswander, L., & Martin, G. R. (1992). Development, 114(3), 755–768.
Rappolee, D. A., Basilico, C., Patel, Y., et al. (1994). Development, 120(8), 2259–2269.
Feldman, B., Poueymirou, W., Papaioannou, V. E., et al. (1995). Science, 267(5195), 246–249.
Arman, E., Haffner-Krausz, R., Chen, Y., et al. (1998). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(9), 5082–5087.
Tanaka, S., Kunath, T., Hadjantonakis, A., et al. (1998). Science, 282, 2072–2075.
Delli-Bovi, P., Curatola, A. M., Newman, K. M., et al. (1988). Molecular and Cellular Biology, 8(7), 2933–2941.
Kuroda, S., Kasugai, S., Oida, S., et al. (1999). Bone, 25(4), 431–437.
Hosoi, Y., Ando, Y., Arakawa, M., et al. (2011). Journal of Reproduction and Development, 57(5), 650–654.
Sugawara, S., Ito, T., Suzuki, H., et al. (2013). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 77(1), 173–177.
Sugawara, S., Ito, T., Sato, S., et al. (2013). Animal Science Journal, 84(3), 275–280.
Saito, K., Ogawa, A., Toyofuku, K., et al. (2011). Reproduction, 141(2), 259–268.
Iha, M., Watanabe, M., Kihara, Y., et al. (2012). Reproduction, 143, 477–489.
Bellosta, P., Talarico, D., Rogers, D., et al. (1993). Journal of Cell Biology, 121(3), 705–713.
Fuller-Pace, F., Peters, G., & Dickson, C. (1991). Journal of Cell Biology, 115(2), 547–555.
Miyagawa, K., Kimura, S., Yoshida, T., et al. (1991). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 174(1), 404–410.
Skaper, S. D., Kee, W. J., Facci, L., et al. (2000). Journal of Neurochemistry, 75(4), 1520–1527.
Pardo, O. E., Latigo, J., Jeffery, R. E., et al. (2009). Cancer Research, 69(22), 8645–8651.
Yang, Q. E., Fields, S. D., Zhang, K., et al. (2011). Biology of Reproduction, 85(5), 946–953.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS KAKENHI No. 24580413) and the Akita Prefectural University President’s Research Project (H24Kendai-chi No. 44 and H25Kendai-chi No. 79) to M. K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugawara, S., Ito, T., Sato, S. et al. Identification of Site-Specific Degradation in Bacterially Expressed Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 4 and Generation of an Aminoterminally Truncated, Stable Form. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 206–215 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0544-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0544-0