Abstract
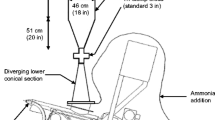
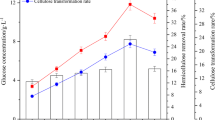
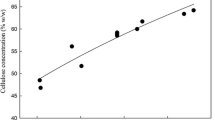
The production of ethanol and methane from corn stover (CS) was investigated in a biorefinery process. Initially, a novel soaking pretreatment (NaOH and aqueous-ammonia) for CS was developed to remove lignin, swell the biomass, and improve enzymatic digestibility. Based on the sugar yield during enzymatic hydrolysis, the optimal pretreatment conditions were 1 % NaOH + 8 % NH4OH, 50°C, 48 h, with a solid-to-liquid ratio 1:10. The results demonstrated that soaking pretreatment removed 63.6 % lignin while reserving most of the carbohydrates. After enzymatic hydrolysis, the yields of glucose and xylose were 78.5 % and 69.3 %, respectively. The simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of pretreated CS using Pichia stipitis resulted in an ethanol concentration of 36.1 g/L, corresponding only to 63.3 % of the theoretical maximum. In order to simplify the process and reduce the capital cost, the liquid fraction of the pretreatment was used to re-soak new CS. For methane production, the re-soaked CS and the residues of SSF were anaerobically digested for 120 days. Fifteen grams CS were converted to 1.9 g of ethanol and 1337.3 mL of methane in the entire process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo, L., Van der Voet, E., & Huppes, G. (2009). An energy analysis of ethanol from cellulosic feedstock—corn stover. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 13, 2003–2011.
Converti, A., Oliveira, R. P. S., Torres, B. R., Lodi, A., & Zilli, M. (2009). Biogas production and valorization by means of a two-step biological process. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5771–5776.
Chen, M., Zhao, J., & Xia, L. M. (2009). Comparison of four different chemical pretreatments of corn stover for enhancing enzymatic digestibility. Biomass and Bioenergy, 33, 1381–1385.
Pang, Y. Z., Liu, Y. P., Li, X. J., Wang, K. S., & Yuan, H. R. (2008). Improving biodegradability and biogas production of corn stover through sodium hydroxide solid state pretreatment. Energy & Fuels, 22, 2761–2766.
Thomsen, M. H. (2005). Complex media from processing of agricultural crops for microbial fermentation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68, 598–606.
Fan, Y. T., Zhang, Y. H., Zhang, S. F., Hou, H. W., & Ren, B. Z. (2006). Efficient conversion of wheat straw wastes into biohydrogen gas by cow dung compost. Bioresource Technology, 97, 500–505.
Kim, T. H., & Lee, Y. Y. (2005). Pretreatment and fractionation of corn stover by ammonia recycle percolation process. Bioresource Technology, 96, 2007–2013.
Teymouri, F., Laureano-Perez, L., Alizadeh, H., & Dale, B. E. (2005). Optimization of the ammonia fiber explosion (AFEX) treatment parameters for enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover. Bioresource Technology, 96, 2014–2018.
Kim, S., & Holtzapple, M. T. (2005). Lime pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover. Bioresource Technology, 96, 1994–2006.
Li, X., & Kim, T. H. (2011). Low-liquid pretreatment of corn stover with aqueous ammonia. Bioresource Technology, 102, 4779–4786.
Kim, T. H., & Lee, Y. Y. (2005). Pretreatment of corn stover by soaking in aqueous ammonia. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 124, 1119–1131.
Xu, J. L., & Cheng, J. J. (2011). Pretreatment of switchgrass for sugar production with the combination of sodium hydroxide and lime. Bioresource Technology, 102, 3861–3868.
Saha, B. C., & Cotta, M. A. (2007). Enzymatic saccharification and fermentation of alkaline peroxide pretreated rice hulls to ethanol. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 41, 528–532.
Hendriks, A. T. W. M., & Zeeman, G. (2009). Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresource Technology, 100, 10–18.
Wyman, C. E., Dale, B. E., Elander, R. T., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M. R., & Lee, Y. Y. (2005). Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresource Technology, 96, 1959–1966.
Sierra, R., Granda, C., & Holtzapple, M. T. (2009). Short-term lime pretreatment of poplar wood. Biotechnology Progress, 25, 323–332.
Gupta, R., Kim, T. H., & Lee, Y. Y. (2008). Substrate dependency and effect of xylanase supplementation on enzymatic hydrolysis of ammonia-treated biomass. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 148, 59–70.
Gregg, D., & Saddler, J. N. (1996). A techno-economic assessment of the pretreatment and fractionation steps of a biomass-to-ethanol process. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 57, 711–727.
Paoli, F. D., Bauer, A., Leonhartsberger, C., Amon, B., & Amon, T. (2011). Utilization of by-products from ethanol production as substrate for biogas production. Bioresource Technology, 102, 6621–6624.
Petersson, A., Thomsen, M. H., Hauggaard-Nielsen, H., & Thomsen, A. B. (2007). Potential bioethanol and biogas production using lignocellulosic biomass from winter rye, oilseed rape and faba bean. Biomass and Bioenergy, 31, 812–819.
Oleskowicz-Popiel, P., Kádár, Z., Heiske, S., Klein-Marcuschamer, D., Simmons, B. A., Blanch, H. W., et al. (2012). Co-production of ethanol, biogas, protein fodder and natural fertilizer in organic farming—evaluation of a concept for a farm-scale biorefinery. Bioresource Technology, 104, 440–446.
Sluiter, A., Hames, B., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., Templeton, D., & Crocker, D. (2008). Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP), Golden, Co: NREL.
Adney, B. & Baker, J. (1996). Measurement of cellulase activities. Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP), Golden, Co: NREL.
Chen, Z. B., Tian, S., Li, J., Li, Y., & Yang, X. S. (2010). Screening of microbial community degrading cornstalk. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 31, 933–936 (In Chinese).
Lu, Y., Lai, Q. H., Zhang, C., Zhao, H. X., Ma, K., Zhao, X. B., et al. (2009). Characteristics of hydrogen and methane production from cornstalks by an augmented two- or three-stage anaerobic fermentation process. Bioresource Technology, 100, 2889–2895.
Shi, J. C., Liao, X. D., Wu, Y. B., & Liang, J. B. (2011). Effect of antibiotics on methane arising from anaerobic digestion of pig manure. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 166, 457–463.
Lin, Y. Q., Wang, D. H., Wu, S. Q., & Wang, C. M. (2009). Alkali pretreatment enhances biogas production in the anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper sludge. Journal of Hazardous Material, 170, 366–373.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Zhang, Y. H. P., Berson, E., Sarkanen, S., & Dale, B. E. (2009). Sessions 3 and 8: pretreatment and biomass recalcitrance: fundamentals and progress. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 153, 80–83.
NREL. (National Renewable Energy Laboratory) in Golden, CO. (2001) “SSF Experimental Protocols—Lignocellulosic Biomass Hydrolysis and Fermentation” in the LAP (Laboratory Analytical Procedure).
McIntosh, S., & Vancov, T. (2010). Enhanced enzyme saccharification of Sorghum bicolor straw using dilute alkali pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6718–6727.
Han, Y. W., Catalano, E. A., & Ciegler, A. (1983). Treatments to improve the digestibility of crop residues. In E. J. Soltes (Ed.), Wood and agricultural residues—research on use for feed, fuels and chemicals (pp. 217–238). New York: Academic Press.
Ko, J. K., Bak, J. S., Jung, M. W., Lee, H. J., Choi, I. G., Kim, T. H., et al. (2009). Ethanol production from rice straw using optimized aqueous-ammonia soaking pretreatment and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation processes. Bioresource Technology, 100, 4374–4380.
Tomás-Pejó, E., Oliva, J. M., Ballesteros, M., & Olsson, L. (2008). Comparison of SHF and SSF processes from steam-exploded wheat straw for ethanol production by xylose-fermenting and robust glucose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 100, 1122–1131.
Cheng, K. K., Zhang, J. A., Ping, W. X., Ge, J. P., Zhou, Y. J., Ling, H. Z., et al. (2008). Sugarcane bagasse mild alkaline/oxidative pretreatment for ethanol production by alkaline recycle process. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 151, 43–50.
Zhao, J., & Xia, L. M. (2009). Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of alkaline-pretreated corn stover to ethanol using a recombinant yeast strain. Fuel Processing Technology, 90, 1193–1197.
Faga, B. A., Wilkins, M. R., & Banat, I. M. (2010). Ethanol production through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of switchgrass using Saccharomyces cerevisiae D5A and thermotolerant Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB strains. Bioresource Technology, 101, 2273–2279.
Öhgren, K., Vehmaanperä, J., Siika-Aho, M., Galbe, M., Viikari, L., & Zacchi, G. (2007). High temperature enzymatic prehydrolysis prior to simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of steam pretreated corn stover for ethanol production. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 607–613.
Öhgren, K., Bengtsson, O., Gorwa-Grauslund, M. F., Galbe, M., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., & Zacchi, G. (2006). Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of glucose and xylose in steam-pretreated corn stover at high fiber content with Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB3400. Journal of Biotechnology, 126, 488–498.
ORNL (2006). Bioenergy Conversion Factors, Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Available from: http://bioenergy.ornl.gov. Accessed 2 December 2011.
Kaparaju, P., Serrano, M., Thomsen, A. B., Kongjan, P., & Angelidaki, I. (2009). Bioethanol, biohydrogen and biogas production from wheat straw in a biorefinery concept. Bioresource Technology, 100, 2562–2568.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support received from the Key Projects of the National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2008BADC4B13; 2008BADC4B16; 2011BAD22B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, Z., Tian, S., Chen, Z. et al. Soaking Pretreatment of Corn Stover for Bioethanol Production Followed by Anaerobic Digestion Process. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 2088–2102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9751-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9751-3