Abstract
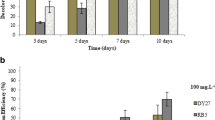
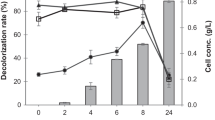
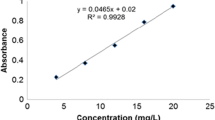
This study presents the biodecolorization potential of basidiomycete fungi Trametes hirsuta, Pycnoporus sp., and Irpex sp. for different reactive dyes viz. Reactive Red 120, Remazol Brilliant Blue R (RBBR), Reactive Orange G, and Reactive Orange 16 under static and shaking conditions. The screening trials revealed that T. hirsuta exhibited maximum potential (83.75 %) for biodecolorization of RBBR dye under static conditions after the fifth day of incubation. However, the rate of biodecolorization of RBBR dye by Pycnoporus sp. was much slow and reached maximum (81.25 %) after 15 days of incubation under shaking conditions. By process optimization, enhanced decolorization (91.2 %) of RBBR by T. hirsuta was achieved at pH 5.5 within 24 h using a defined salt medium amended with p-coumaric acid under static conditions. pH was found to be an important parameter for the enzymatic system involved in RBBR dye decolorization by T. hirsuta and Pycnoporus sp. Biodecolorization of RBBR dye was determined by a reduction in optical density at the wavelength of maximum absorbance (λ, 578 nm) by UV–vis spectrophotometer. The shift in maximum wavelength toward shorter/longer wavelength in UV–vis scanning spectrum revealed the degradation of RBBR dye into different transformation products.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiou, M. S., & Li, H. Y. (2002). Equilibrium and kinetic modeling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan beads. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 93, 233–248.
Lachheb, H., Puzenat, E., Houas, A., Ksibi, M., Elaloui, E., Guillard, C., et al. (2002). Photocatalytic degradation of various types of dyes (Alizarin S, Crocein Orange G, Methyl Red, Congo Red, Methylene Blue) in water by UV-irradiated titania. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 39, 75–90.
Morikawa, Y., Shiomi, K., Ishihara, Y., & Matsuura, N. (1997). Triple primary cancers involving kidney, urinary bladder and liver in a dye workers. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 31, 44–49.
Ghoreishi, S. M., & Haghighi, R. (2003). Chemical catalytic reaction and biological oxidation for 229 treatments of non-biodegradable textile-effluents. Chemical Engineering Journal, 95, 163–169.
Kashinath, A., Novotny, C. K., Kamalesh, K. S., Patel, C., & Vaclava, A. (2003). Decolourization of synthetic dyes by Irpex lacteus in liquid culture and packed bed bioreactor. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 32, 167–173.
Ramsay, J. A., & Goode, C. (2004). Decoloration of a carpet dye effluent using Trametes versicolor. Biotechnology Letters, 26, 197–201.
Wang, X., Cheng, X., & Sun, S. (2008). Autocatalysis in Reactive Black 5 biodecolorization by Rhodopseudomonas palustris W1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 907–915.
Asgher, M., Azim, N., & Bhatti, H. N. (2009). Decolorization of practical textile industry effluents by white rot fungus Coriolus versicolor IBL-04. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 47, 61–65.
Bibi, I., Bhatti, H. N., & Asgher, M. (2011). Comparative study of natural and synthetic phenolic compounds as efficient laccase mediators for the transformation of cationic dye. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 56, 225–231.
Asgher, M., Kausar, S., Bhatti, H. N., Shah, S. A. H., & Ali, M. (2008). Optimization of medium for decolorization of Solar golden yellow R direct textile dye by Shizophyllum commune IBL-06. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 61, 189–193.
Miyazaki, Y., & Nakamura, M. (2005). Molecular cloning of developmentally specific genes by representational difference analysis during the fruiting body formation in the basidiomycete Lentintula edodes. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 42, 493–505.
Bhatti, H. N., Rashid, M. H., Nawaz, R., Asgher, M., Perveen, R., & Jabbar, A. (2007). Optimization of media for enhanced glucoamylase production in solid state fermentation by Fusarium solani. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 45, 51–56.
Fortnagel, P., Harm, H., Wittich, R. M., Krohn, S., Meyer, H., Sinnwell, V., et al. (1990). Metabolism of dibenzofuran by Pseudomonas sp. strain HH69 and the mixed culture HH27. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56, 1148–1156.
Hafiz, I., Asgher, M., & Bhatti, H. N. (2008). Optimization of Cibacron Turquoise P-GR decolorization by Ganoderma lucidum-IBL-05. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 17, 1987–1993.
Wariishi, H., Valli, K., & Gold, M. H. (1992). Manganese (II) oxidation by manganese peroxidase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium, kinetic mechanism and role of chelators. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 23688–23695.
Tien, M., & Kirk, T. K. (1988). Lignin peroxidases of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Methods in Enzymology, 161, 238–249.
Shin, K. S., & Lee, Y. J. (2000). Purification and characterization of new member of laccase family from white-rot basiodiomycete Coriolus hirsutus. Archives of Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 384, 109–115.
Rodriguez, E., Pickard, M. A., & Vazquez-Duhalt, R. (1999). Industrial dye decolorization by laccase from ligninolytic fungi. Current Microbiology, 38, 27–32.
Boer, C. G., Obici, L., Souza, C. G., & Peralta, R. M. (2004). Decolourization of synthetic dyes by solid state cultures of Lentinula (Lentinus) edodes producing manganese peroxidase as the main ligninolytic enzyme. Bioresource Technology, 94, 107–112.
Kariminiaae-Hamedaani, H. R., Sakuraia, K., & Sakakibara, M. (2007). Decolorization of synthetic dyes by a new manganese peroxidase-producing white rot fungus. Dyes and Pigments, 72, 157–162.
Reddy, A. (1995). The potential for white rot fungi in the treatment of pollutants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 6, 320–328.
Chander, M., Arora, D. S., & Bath, H. K. (2004). Biodecolorization of some industrial dyes by white-rot fungi. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31, 94–97.
Eichlerova, I., Homolka, L., & Nerud, F. (2006). Ability of industrial dyes decolorization and ligninolytic enzymes production by different Pleurotus species with special attention on Pleurotus calyptratus, strain CCBAS 461. Process Biochemistry, 41, 941–946.
Nagai, M., Sato, T., Watanabe, H., Saito, K., Kawata, M., & Enei, H. (2002). Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes and decolorization of chemically different dyes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 60, 327–335.
Mazmanci, M. A., & Unyayar, A. (2005). Decolorization of reactive black 5 by Funalia trogii immobilized on Luffa clyndried sponge. Process Biochemistry, 40, 337–342.
Zhang, F., Knapp, J. S., & Tapley, K. N. (1999). Decolorization of cotton bleaching effluent with wood rotting fungus. Water Research, 33, 919–928.
Kapdan, I. K., Kargi, F., McMullan, G., & Marchant, R. (2000). Effect of environmental conditions on biological decolorization of textile dyestuff by Coriolus versicolor. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 26, 381–387.
Tavares, A. P. M., Coelho, M. A. Z., Agapito, M. S. M., Coutinho, J. A. P., & Xavier, A. M. R. B. (2006). Optimization and modeling of laccase production by Trametes versicolor in a bioreactor. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 134, 233–248.
Murugesan, K., Nam, I. H., Kim, Y. M., & Chang, Y. S. (2007). Decolorization of reactive dyes by a thermostable laccase produced by Ganoderma lucidum in solid state culture. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 1662–1672.
Claus, H., Faber, G., & Konig, H. (2002). Redox-mediated decolorization of synthetic dyes by fungal laccases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 59, 672–678.
Call, H. P., & Mucke, I. J. (1997). History, overview and applications of mediated ligninolytic systems, especially laccase-mediator-systems (lignozyme process). Biotechnology, 53, 163–202.
Have, T. R., & Teunissen, P. J. M. (2001). Oxidative mechanisms involved in lignin degradation by white-rot fungi. Chemical Reviews, 101, 3397–3413.
Nilsson, I., Mollar, A., Mattiason, B., Rubindamayugi, M. S. T., & Welander, U. (2005). Decolorization of synthetic and real textile wastewater by use of white rot fungi. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 38, 94–100.
Young, L., & Yu, J. (1996). Ligninase-catalysed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Water Research, 31, 1187–1193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bibi, I., Bhatti, H.N. Enhanced Biodecolorization of Reactive Dyes by Basidiomycetes Under Static Conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 2078–2090 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9635-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9635-6