Abstract.
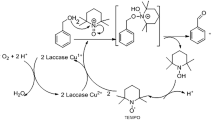
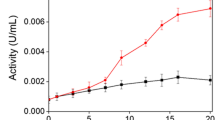
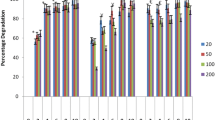
White-rot fungi were studied for the decolorization of 23 industrial dyes. Laccase, manganese peroxidase, lignin peroxidase, and aryl alcohol oxidase activities were determined in crude extracts from solid-state cultures of 16 different fungal strains grown on whole oats. All Pleurotus ostreatus strains exhibited high laccase and manganese peroxidase activity, but highest laccase volumetric activity was found in Trametes hispida. Solid-state culture on whole oats showed higher laccase and manganese peroxidase activities compared with growth in a complex liquid medium. Only laccase activity correlated with the decolorization activity of the crude extracts. Two laccase isoenzymes from Trametes hispida were purified, and their decolorization activity was characterized.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 May 1998 / Accepted: 7 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, E., Pickard, M. & Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Industrial Dye Decolorization by Laccases from Ligninolytic Fungi. Curr Microbiol 38, 27–32 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006767
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006767