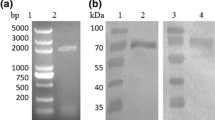
Abstract
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is attracting increasing interest on account of its prominent benefits in type 2 diabetes. However, its clinical application is limited because of short biological half-life. This study was designed to produce a C-terminal site-specific PEGylated analog of cysteine-mutated GLP-1 (cGLP-1) to prolong its action. The gene of cGLP-1 was inserted into pET32a to construct a thioredoxinA fusion protein. After expression in BL21 (DE3) strain, the fusion protein was purified with Ni-affinity chromatography and then was PEGylated with methoxy-polyethylene glycol-maleimide (mPEG10K-MAL). The PEGylated fusion protein was purified with anion exchange chromatography and then was cleaved by enterokinase. The digested product was further purified with reverse-phase chromatography. Finally, 8.7 mg mPEG10K–cGLP-1 with a purity of up to 98% was obtained from the original 500 ml culture. The circular dichroism spectra indicated that mPEG10K–cGLP-1 maintained the secondary structure of native GLP-1. As compared with that of native GLP-1, the plasma glucose lowering activity of mPEG10K–cGLP-1 was significantly extended. These results suggest that our method will be useful in obtaining a large quantity of mPEG10K–cGLP-1 for further study and mPEG10K–cGLP-1 might find a role in the therapy of type 2 diabetes through C-terminal site-specific PEGylation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drucker, D. J. (1998). Diabetes, 47, 159–169.
Qualmann, C., Nauck, M. A., Holst, J. J., et al. (1995). Acta Diabetologica, 32, 13–16.
Turton, M. D., O'shea, D., Gunn, I., et al. (1996). Nature, 379, 69–72.
Flint, A., Raben, A., Astrup, A., et al. (1998). Journal of Clinical Investigation, 101, 515–520.
Nauck, M. A., & Meier, J. J. (2005). Regulatory Peptides, 128, 135–148.
Pauly, R. P., Rosche, F., Wermann, M., et al. (1996). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 23222–23229.
Vilsboll, T., Agerso, H., Krarup, T., et al. (2003). Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 88, 220–224.
Dou, W. F., Lei, J. Y., Zhang, L. F., et al. (2008). Protein Expression and Purification, 61, 45–49.
Lee, S. H., Lee, S., Youn, Y. S., et al. (2005). Bioconjugate Chemistry, 16, 377–382.
Siegel, E. G., Gallwitz, B., Scharf, G., et al. (1999). Regulatory Peptide, 79, 93–102.
Zhang, Z. Z., Yang, S. S., Dou, H., et al. (2004). Protein Expression and Purification, 36, 292–299.
Mitsuda, Y., Takimoto, A., Kamitani, S., et al. (2002). Protein Expression and Purification, 25, 448–455.
Kingsley, G. R., & Getchell, G. (1960). Clinical Chemistry, 6, 466–475.
Burcelin, R., Dolci, W., & Thorens, B. (1999). Metabolism, 48, 252–258.
Deacon, C. F., Knudsen, L. B., Madsen, K., et al. (1998). Diabetologia, 41, 271–278.
Zhou, L., Zhao, Z., Li, B., et al. (2008). Protein Expression and Purification, 64, 225–230.
Mehrnejad, F., Naderi-Manesh, H., Ranjbar, B., et al. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 149, 109–118.
Wang, J. H., Tam, S. C., Huang, H., et al. (2004). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 317, 965–971.
Long, D. L., Doherty, D. H., Eisenberg, S. P., et al. (2006). Experimental Hematology, 34, 697–704.
Veronese, F. M., Mero, A., Caboi, F., et al. (2007). Bioconjugate Chemistry, 18, 1824–1830.
Yamamoto, Y., Tsutsumi, Y., Yoshioka, Y., et al. (2003). Nature Biotechnology, 21, 546–552.
Sato, H. (2002). Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 54, 487–504.
Deiters, A., Cropp, T. A., Summerer, D., et al. (2004). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 14, 5743–5745.
Adelhorst, K., Hedegaard, B. B., Knudsen, L. B., et al. (1994). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 6275–6278.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China National Nature Science Foundation (30772679) and Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China-863 Program (2007AA02Z101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mingming Gao and Hong Tian contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Tian, H., Ma, C. et al. Expression, Purification, and C-terminal Site-Specific PEGylation of Cysteine-Mutated Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162, 155–165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8725-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8725-6