Abstract
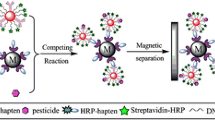
In the present work, a simple, fast, and highly sensitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for 17β-estradiol (E2) in environmental water samples was developed, using magnetic particles (MPs) labeled with secondary antibody as both the immobilization matrix and the separation tools. The specific anti-E2 polyclonal antibody (PcAb) was produced against a conjugate of estradiol–bovine serum albumin. The specificity of the anti-E2 antibody was studied. The results showed that the antibody did not cross-react with the structurally related endocrine-disrupting compounds, including estrone, ethinyl E2, estriol, E2-17-glucuronide, E2-3-sulfate-17-glucuronide, androstenedione, and dihydrotestosterone. The water samples were pretreated with solid-phase extraction using C18 cartridges for the removal of matrix effects. Several physicochemical parameters including the dilution ratios of E2-6–horseradish peroxidase conjugate and anti-E2 PcAb, immunoreaction time, volume of chemiluminescent substrate and MPs, chemiluminescence reaction time, and pH of assay solution were studied and optimized. At optimal experimental conditions, it was found that the proposed method exhibited high performance with detection limit of 2.0 pg/mL, linear range of 20–1,200 pg/mL, and total assay time of 45 min. Both inter- and intra-assay coefficient of variation were less than 10%. The average recoveries of three different spiked concentration samples ranged from 86.3% to 108%. The method was successfully applied to the determination of E2 in river, waste, and tap water, and showed a good correlation with the commercially available radioimmunoassay kit.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingrand, V., Herry, G., Beausse, J., & Roubin, M.-R. (2003). Journal of Chromatography. A, 1020, 99–104. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00770-2.
Kavlock, R. J., Daston, G. P., DeRosa, C., Fenner-Crisp, P., Gray, L. E., & Kaattari, S. (1996). Environmental Health Perspectives, 104(Suppl. 4), 715–740. doi:10.2307/3432708.
Rose, J., Holbech, H., Lindholst, C., Norum, U., Povlsen, A., & Korsgaard, B. (2002). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 131, 531–539.
Jensen, T. K., Toppari, J., Keiding, N., & Skakkebaek, N. E. (1995). Clinical Chemistry, 41, 1896–1901.
Krambovitis, E., Hatzidakis, G., Hatzoglous, A., Romain, S., Durand, A., & Stefanakis, A. (1995). Clinical Chemistry, 41, 48–53.
Kanagaraj, P., Vijayababu, M. R., Ilangovan, R., Senthilkumar, K., Venkataraman, P., & Aruldhas, M. M. (2007). Clinica Chimica Acta, 377, 70–78. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2006.07.030.
Ying, G. G., Kookana, R. S., & Ru, Y. J. (2002). Environment International, 28, 545–551. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00075-2.
Hintemann, T., Schneider, C., Schöler, H. F., & Schneider, R. J. (2006). Water Research, 40, 2287–2294. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.028.
Ternes, T. A., Andersen, H., Daniel, G., & Bonerz, M. (2002). Analytical Chemistry, 74, 3498–3504. doi:10.1021/ac015717z.
Farré, M., Kuster, M., Brix, R., Rubio, F., Alda, M.-J. L., & Barceló, D. (2007). Journal of Chromatography. A, 1160, 166–175. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.05.032.
Snyder, S. A., Keith, T. L., Verbrugge, D. A., Snyder, E. M., Gross, T. S., & Kannan, K. (1999). Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 2814–2820. doi:10.1021/es981294f.
Colli, I., Reder, S., Bucher, S., & Gauglitz, G. (2002). Biomolecular Engineering, 18, 273–280. doi:10.1016/S1389-0344(01)00111-3.
Zhao, L. X., & Lin, J.-M. (2005). Journal of Biotechnology, 118, 177–186. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.02.023.
Zhu, D. B., Tang, Y. B., Xing, D., & Chen, W. R. (2008). Analytical Chemistry, 80, 3566–3571. doi:10.1021/ac0713306.
Zhu, D. B., Xing, D., Shen, X. Y., & Liu, J. F. (2004). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 324, 964–969. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.121.
Zhu, D. B., Xing, D., Shen, X. Y., Liu, J. F., & Chen, Q. (2004). Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 20, 448–453. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2004.02.029.
Zhou, X. M., Xing, D., Zhu, D. B., & Jia, Li. (2008). Electrochemistry Communications, 10, 564–567. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2008.01.039.
Yan, G. H., Xing, D., Tan, S. C., & Chen, Q. (2004). Journal of Immunological Methods, 288, 47–54. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2004.02.006.
Majima, K., Fukui, T., Yuan, J., Wang, G., & Matsumoto, K. (2002). Analytical Sciences, 18, 869–874. doi:10.2116/analsci.18.869.
Li, Z. L., Wang, S., Lee, N. A., Allan, R. D., & Kennedy, I. R. (2004). Analytica Chimica Acta, 503, 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2003.10.026.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2007CB714507) and National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 20728505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, TB., Wang, X., Jin, H. et al. Development of Magnetic Particle-based Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay for the Detection of 17β-estradiol in Environmental Water. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158, 582–594 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8356-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8356-3