Abstract
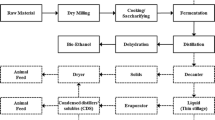
The major challenge associated with the rapid growth of the ethanol industry is the usage of the coproducts, i.e., condensed distillers solubles (CDS) and distillers dried grains, which are currently sold as animal feed supplements. As the growth of the livestock industries remains flat, alternative usage of these coproducts is urgently needed. CDS is obtained after the removal of ethanol by distillation from the yeast fermentation of a grain or a grain mixture by condensing the thin stillage fraction to semisolid. In this work, CDS was first characterized and yeast biomass was proven to be the major component of CDS. CDS contained 7.50% crude protein but with only 42% of that protein being water soluble. Then, CDS was applied as a nutrient supplement for simultaneous production of nisin and lactic acid by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (ATCC 11454). Although CDS was able to support bacteria growth and nisin production, a strong inhibition was observed when CDS was overdosed. This may be caused by the existence of the major ethanol fermentation byproducts, especially lactate and acetate, in CDS. In the final step, the CDS based medium composition for nisin and lactic acid production was optimized using response surface methodology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renewable Fuels Association (2006), http://www.ethanolrfa.org/industry/statistics/#A. Accessed February 13, 2007.
Wyman, C. E. (2001), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 91–93, 5–21.
Iowa Beef Center (2002), http://www.extension.iastate.edu/Publications/IBC18.pdf.
Hoffman, M. P. and Tsengeg, P. (2004), http://www.ag.iastate.edu/farms/04reports/w_/IncorporatingCondensed.pdf. Accessed February 13, 2007.
Parente, E. and Ricciardi, A. (1999), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 52, 628–638.
Food and Drug Administration (2001), GRAS Notice No. GRN 000065, Rockville, MD.
Cleveland, J., Thomas, J., Montville, J. T., Nes, F. I., and Chikindas, L. M. (2001), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 71, 1–20.
Sablon, E., Contreras, B., and Vandamme, E. (2000), Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 68, 21–59.
Jack, R. W., Tagg, J. R., and Ray, B. (1995), Microbiol. Rev. 59, 171–200.
Datta, R. and Tsai, S. P. (1997), In: Fuels and Chemicals from Biomass, ACS Symposium Series 666, Saha, W., Saha, B., and Woodward, J., eds. Oxford University Press, Oxford UK: pp. 224–236.
Liu, C., Liu, Y., Liao, W., Wen, Z., and Chen, S. (2004), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 114, 627–638.
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (1990), Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed. AOAC International, Gaithersburg, MD.
Ohnishi, S. T. and Barr, J. K. (1978), Anal. Biochem. 86, 193–200.
Liu, Y., Wei, L., Liu, C., and Chen, S., (2005), Eng. Life Sci. 5, 343–349.
Shimizu, H., Mizuguchi, T., Tanaka, E., and Shioya, S. (1999), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 3134–3141.
Kim, W. S., Hall, R. J., and Dunn, N. W. (1997), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48, 449–453.
Kim, W. S., Hall, R. J., and Dunn, N.W. (1998), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 50, 429–433.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Hu, B., Chen, S. et al. Utilization of condensed distillers solubles as nutrient supplement for production of nisin and lactic acid from whey. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137, 875–884 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9104-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9104-9