Abstract
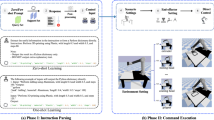
This work considers path-planning processes for manipulation tasks such as assembly, maintenance or disassembly in a virtual reality (VR) context. The approach consists in providing a collaborative system associating a user immersed in VR and an automatic path planning process. It is based on semantic, topological and geometric representations of the environment and the planning process is split in two phases: coarse and fine planning. The automatic planner suggests a path to the user and guides him trough a haptic device. The user can escape from the proposed solution if he wants to explore a possible better way. In this case, the interactive system detects the users intention and computes in real-time a new path starting from the users guess. Experiments illustrate the different aspects of the approach: multi-representation of the environment, path planning process, users intent prediction and control sharing.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarno, D., Ekvall, S., Kragic, D.: Adaptive virtual fixtures for machine-assisted teleoperation tasks. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1139–1144. IEEE (2005)
Abbink, D.A., Mulder, M.: Neuromuscular analysis as a guideline in designing shared control. Adv. Haptics 109, 499–516 (2010)
Ahmadi-Pajouh, M.A., Towhidkhah, F., Gharibzadeh, S., Mashhadimalek, M.: Path planning in the hippocampo-prefrontal cortex pathway: an adaptive model based receding horizon planner. Med Hypotheses 68(6), 1411–1415 (2007)
Anderson, S.J., Peters, S.C., Iagnemma, K., Overholt, J.: Semi-autonomous stability control and hazard avoidance for manned and unmanned ground vehicles. In: Tech. rep, DTIC Document. MIT (2010)
Bordegoni, M., Cugini, U., Belluco, P., Aliverti, M.: Evaluation of a haptic-based interaction system for virtual manual assembly. In: VMR, Conférence on Virtual and Mixed Reality, pp. 303–312. Springer (July 2009, San Diego (USA))
CGAL: CGAL, computational geometry algorithms library. http://www.cgal.org. Accessed Mar 2014 (2014)
Choset, H., Lynch, K.M., Hutchinson, S., Kantor, G., Burgard, W., Kavraki, L.E., Thrun, S.: Principles of Robot Motion: Theory, Algorithms, and Implementations (Intelligent Robotics and Autonomous Agents). The MIT Press, Cambridge (2005)
Dijkstra, E.W.: A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1(1), 269–271 (1959)
Dragan, A.D., Srinivasa, S.S.: A policy blending formalism for shared control. Int. J. Robot. Res. 32(7), 690–805 (2013)
Fagg, A.H., Rosenstein, M., Platt, R., Grupen, R.A.: Extracting user intent in mixed initiative teleoperator control. In: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Intelligent Systems Technical Conference. AIAA IST, Chicago (2004)
Fillatreau, P., Fourquet, J.Y., Le Bolloch, R., Cailhol, S., Datas, A., Puel, B.: Using virtual reality and 3d industrial numerical models for immersive interactive checklists. Comput. Ind. 64(9), 1253–1262 (2013)
Fiorentino, M., Radkowski, R., Stritzke, C., Uva, A.E., Monno, G.: Design review of cad assemblies using bimanual natural interface. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 7(4), 249–260 (2013)
Flemisch, F.O., Heesen, M., Hesse, T., Kelsch, J., Schieben, A., Beller, J.: Towards a dynamic balance between humans and automation: authority, ability, responsibility and control in shared and cooperative control situations. Cognit. Technol. Work 14(1), 3–18 (2012)
Iacob, R., Mitrouchev, P., Léon, J.C.: Assembly simulation incorporating component mobility modelling based on functional surfaces. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 5(2), 119–132 (2011)
Iacob, R., Popescu, D., Mitrouchev, P.: Assembly/disassembly analysis and modeling techniques: a review. Stroj. Vestn. J. Mech. Eng. 58(11), 653–664 (2012)
Ladevèze, N., Fourquet, J.Y., Puel, B.: Interactive path planning for haptic assistance in assembly tasks. Comput. Graph. 34(1), 17–25 (2010)
LaValle, S.M.: Planning Algorithms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Li, M., Okamura, A.M.: Recognition of operator motions for real-time assistance using virtual fixtures. In: Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems. HAPTICS., pp. 125–131. IEEE (2003)
Loizou, S.G., Kumar, V.: Mixed initiative control of autonomous vehicles. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1431–1436. IEEE (2007)
Lozano-Perez, T.: Spatial planning: a configuration space approach. Trans. Comput. 100(2), 108–120 (1980)
Marayong, P., Li, M., Okamura, A.M., Hager, G.D.: Spatial motion constraints: Theory and demonstrations for robot guidance using virtual fixtures. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 2, pp. 1954–1959. IEEE (2003)
Taïx, M., Flavigné, D., Ferré, E.: Human interaction with motion planning algorithm. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 67(3–4), 285–306 (2012)
Weber, C., Nitsch, V., Unterhinninghofen, U., Farber, B., Buss, M.: Position and force augmentation in a telepresence system and their effects on perceived realism. In: EuroHaptics conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems. World Haptics, pp. 226–231. IEEE (2009)
You, E., Hauser, K.: Assisted teleoperation strategies for aggressively controlling a robot arm with 2d input. In: Robotics: Science and Systems, vol. VII, p. 354. MIT Press (2012)
Yu, W., Alqasemi, R., Dubey, R., Pernalete, N.: Telemanipulation assistance based on motion intention recognition. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1121–1126. IEEE (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cailhol, S., Fillatreau, P., Fourquet, JY. et al. A hierarchic approach for path planning in virtual reality. Int J Interact Des Manuf 9, 291–302 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-015-0272-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-015-0272-5