Abstract
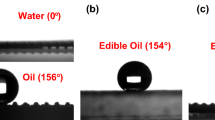
The design and development of efficient approaches for water–oil separation have had widespread interest. Most previously introduced techniques and materials used for development of the successful separation of oily wastewater could not answer all the desired demands, such as being efficient and environmentally and economically friendly. Therefore, in seeking a novel method capable of answering these expectations, surfaces with special wettability were introduced. A novel, reusable, and recyclable superhydrophilic and superoleophobic poly(Vsim-Vim)@PFOA@SiO2 nanocomposite-coated stainless steel mesh was synthesized through a facile preparation process. Since the most important factors of these coatings are their oleophobicity and hydrophilicity values, the water contact angle (WCA) and the oil contact angle (OCA) were measured. The coating indicated the excellent characteristics in which the results showed that WCA was 0°, while OCA was 142°, which confirmed remarkable superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity, respectively. It is worth mentioning that the coating owes its surface behavior mainly to the finer size of mesh and formation of silica, which causes the higher roughness and better oleophobicity, reduction of the surface energy of the synthesized poly(Vsim-Vim)@SiO2 nanocomposite by PFOA, the formation of hierarchical micro-nanometer scale roughness structures on the coating surface, and stable adhesion of SiO2 nanoparticles into poly(Vsim-Vim). Eventually, superb oil/water separation efficiency of 95% with high stability was attained. This result implied that the fabricated coating is a suitable candidate for water–oil emulsion separation which can potentially be employed in green industrial applications. Also, we believe this approach provides a potential application in controllable oil/water separation in large volumes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koenig, SG, Bee, C, Borovika, A, et al., “A Green Chemistry Continuum for a Robust and Sustainable Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Supply Chain.” ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 7 16937–16951 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02842
Wei, Y, Qi, H, Gong, X, Zhao, S, “Specially Wettable Membranes for Oil–Water Separation.” Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 5 1800576–1800603 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201800576
Lin, X, Hong, J, “Recent Advances in Robust Superwettable Membranes for Oil–Water Separation.” Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 6 1900126–1900149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201900126
Zhang, Y, Wang, H, Liu, B, et al., “NiCo2O4 Hierarchical Structure Coated Mesh with Long-Term Stable Underwater Superoleophobicity for High-Efficient, High-Flux Oil–Water Separation.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 504 144598–144608 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144598
Wang, X, Han, Z, Liu, Y, Wang, Q, “Micro-nano Surface Structure Construction and Hydrophobic Modification to Prepare Efficient Oil–Water Separation Melamine Formaldehyde Foam.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 504 144577–144588 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144577
Abdulredha, MM, Siti Aslina, H, Luqman, CA, “Overview on Petroleum Emulsions, Formation, Influence and Demulsification Treatment Techniques.” Arab. J. Chem., 13 3403–3428 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.11.014
Lv, J, Wang, B, Ma, Q, et al., “Preparation of Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponges Decorated with Polysiloxane Nanotubes by Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) Method for Oil/Water Separation.” Mater. Res. Express, 5 075025 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad0e1
Wang, B, Lei, B, Tang, Y, et al., “Facile Fabrication of Robust Superhydrophobic Cotton Fabrics Modified by Polysiloxane Nanowires for Oil/Water Separation.” J. Coat. Technol. Res., 15 611–621 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-017-0002-y
Gupta, RK, Dunderdale, GJ, England, MW, Hozumi, A, “Oil/Water Separation Techniques: A Review of Recent Progresses and Future Directions.” J. Mater. Chem. A, 5 16025–16058 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA02070H
Dong, X, Chen, J, Ma, Y, et al., “Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Hybrid Foam of Graphene and Carbon Nanotube for Selective Removal of Oils or Organic Solvents from the Surface of Water.” Chem. Commun., 48 10660–10662 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc35844a
Su, C, Yang, H, Song, S, et al., “A Magnetic Superhydrophilic/Oleophobic Sponge for Continuous Oil–Water Separation.” Chem. Eng. J., 309 366–373 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.082
Cheryan, M, Rajagopalan, N, “Membrane Processing of Oily Streams. Wastewater Treatment and Waste Reduction.” J. Membr. Sci., 151 13–28 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(98)00190-2
Ashaghi, KS, Ebrahimi, M, Czermak, P, “Ceramic Ultra- and Nanofiltration Membranes for Oilfield Produced Water Treatment: A Mini Review.” Open Environ. Sci., 1 1–8 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2174/1876325100701010001
Wenzel, RN, “Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water.” Ind. Eng. Chem., 28 988–994 (1936). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50320a024
Yousefi, E, Ghadimi, MR, Amirpoor, S, Dolati, A, “Preparation of New Superhydrophobic and Highly Oleophobic Polyurethane Coating with Enhanced Mechanical Durability.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 454 201–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.125
Feng, XQ, Gao, X, Wu, Z, et al., “Superior Water Repellency of Water Strider Legs with Hierarchical Structures: Experiments and Analysis.” Langmuir, 23 4892–4896 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/la063039b
Gu, H, Li, G, Li, P, et al., “Superhydrophobic and Breathable SiO2/Polyurethane Porous Membrane for Durable Water Repellent Application and Oil–Water Separation.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 512 144837–144849 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144837
Reza Ghadimi, M, Azad, M, Amirpoor, S, et al., “Design and Fabrication of a Highly Efficient, Stable and Durable New Wettability Coated Stainless Steel Mesh for Oil/Water Separation.” Mater. Lett., 256 126627–126631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2019.126627
Chu, Z, Feng, Y, Seeger, S, “Oil/Water Separation with Selective Superantiwetting/Superwetting Surface Materials.” Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 54 2328–2338 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201405785
Feng, L, Zhang, Z, Mai, Z, et al., “A Super-hydrophobic and Super-oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water.” Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 43 2012–2014 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200353381
Reynolds, JG, Coronado, PR, Hrubesh, LW, “Hydrophobic Aerogels for Oil-Spill Clean Up—Synthesis and Characterization.” J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 292 127–137 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(01)00882-1
Inagaki, M, Kawahara, A, Nishi, Y, Iwashita, N, “Heavy Oil Sorption and Recovery by Using Carbon Fiber Felts.” Carbon N. Y., 40 1487–1492 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00319-0
Matin, A, Baig, U, Gondal, MA, et al., “Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Microporous Membranes by Spray-Coating Ytterbium Oxide Particles for Efficient Oil–Water Separation.” J. Membr. Sci., 548 390–397 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.045
Goetz, LA, Jalvo, B, Rosal, R, Mathew, AP, “Superhydrophilic Anti-fouling Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Membranes Coated with Chitin Nanocrystals for Water Filtration.” J. Membr. Sci., 510 238–248 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.02.069
Zhou, S, Xiong, Z, Liu, F, et al., “Novel Janus Membrane with Unprecedented Osmosis Transport Performance.” J. Mater. Chem. A, 7 632–638 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta08541b
Ge, J, Zhang, J, Wang, F, et al., “Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Nanofibrous Membrane with Hierarchical Structured Skin for Effective Oil-In-Water Emulsion Separation.” J. Mater. Chem. A, 5 497–502 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta07652a
Pan, S, Kota, AK, Mabry, JM, Tuteja, A, “Superomniphobic Surfaces for Effective Chemical Shielding.” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 135 578–581 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja310517s
Liu, T, Kim, CJ, “Turning a Surface Superrepellent Even to Completely Wetting Liquids.” Science, 346 1096–1100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254787
Deng, X, Butt, HJ, Vollmer, D, “Candle Soot as a Template for a Transparent Robust Superamphiphobic Coating.” Science, 335 67–70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1207115
Siavash Moakhar, R, AbdelFatah, T, Sanati, A, et al., “A Nanostructured Gold/Graphene Microfluidic Device for Direct and Plasmonic-Assisted Impedimetric Detection of Bacteria.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c02654
Siavash Moakhar, R, Jalali, M, Kushwaha, A, et al., “AuPd Bimetallic Nanoparticle Decorated TiO2 Rutile Nanorod Arrays for Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting.” J. Appl. Electrochem., (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1231-1
Ghartavol, HM, Moakhar, RS, Dolati, A, “Electrochemical Investigation of Electrodeposited Platinum Nanoparticles on Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Methanol Electro-oxidation.” J. Chem. Sci., 129 1399–1410 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-017-1346-7
Moakhar, RS, Hariri, MB, Kushwaha, A, et al., “Au–Pd Bimetallic Nanoparticle Electrodes for Direct Electroreduction of Hexavalent Chromium Complexes.” Aust. J. Chem., 69 423–430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1071/CH15660
Siavash Moakhar, R, Goh, GKL, Dolati, A, Ghorbani, M, “Sunlight-Driven Photoelectrochemical Sensor for Direct Determination of Hexavalent Chromium Based on Au Decorated Rutile TiO2 Nanorods.” Appl. Catal. B Environ., 201 411–418 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.026
Siavash Moakhar, R, Gholipour, S, Masudy-Panah, S, et al., “Recent Advances in Plasmonic Perovskite Solar Cells.” Adv. Sci., 7 1902448 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201902448
Bakhtiargonbadi, F, Esfahani, H, Moakhar, RS, Dabir, F, “Fabrication of Novel Electrospun Al and Cu Doped ZnO Thin Films and Evaluation of Photoelectrical and Sunlight-Driven Photoelectrochemical Properties.” Mater. Chem. Phys., 252 123270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123270
Hosseini, HSM, Siavash Moakhar, R, Soleimani, F, et al., “One-Pot Microwave Synthesis of Hierarchical C-doped CuO Dandelions/g-C3N4 Nanocomposite with Enhanced Photostability for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 530 147271 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147271
Liu, J, Siavash Moakhar, R, Sudalaiyadum Perumal, A, et al., “An AgNP-Deposited Commercial Electrochemistry Test Strip as a Platform for Urea Detection.” Sci. Rep., 10 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66422-x
Lee, YC, Wang, PY, Lo, SL, Huang, CP, “Recovery of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) from Dilute Water Solution by Foam Flotation.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 173 280–285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.09.012
Suja, F, Pramanik, BK, Zain, SM, “Contamination, Bioaccumulation and Toxic Effects of Perfluorinated Chemicals (PFCs) in the Water Environment: A Review Paper.” Water Sci. Technol., 60 1533–1554 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.504
Yamashita, N, Taniyasu, S, Petrick, G, et al., “Perfluorinated Acids as Novel Chemical Tracers of Global Circulation of Ocean Waters.” Chemosphere, 70 1247–1255 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.07.079
Lv, J, Cheng, Z, Wu, H, et al., “In-situ Polymerization and Covalent Modification on Aramid Fiber Surface via Direct Fluorination for Interfacial Enhancement.” Compos. Part B Eng., 182 107608 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107608
Cheng, Z, Wu, P, Li, B, et al., “Surface Chain Cleavage Behavior of PBIA Fiber Induced by Direct Fluorination.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 384 480–486 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.055
Amirpoor, S, Siavash Moakhar, R, Dolati, A, “A Novel Superhydrophilic/Superoleophobic Nanocomposite PDMS-NH2/PFONa-SiO2 Coated-Mesh for the Highly Efficient and Durable Separation of Oil and Water.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 394 125859 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125859
Facio, DS, Mosquera, MJ, “Simple Strategy for Producing Superhydrophobic Nanocomposite Coatings In Situ on a Building Substrate.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 5 7517–7526 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am401826g
Yang, J, Yin, L, Tang, H, et al., “Polyelectrolyte-Fluorosurfactant Complex-Based Meshes with Superhydrophilicity and Superoleophobicity for Oil/Water Separation.” Chem. Eng. J., 268 245–250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.073
Steele, A, Bayer, I, Loth, E, “Inherently Superoleophobic Nanocomposite Coatings by Spray Atomization.” Nano Lett., 9 501–505 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl8037272
Motlagh, NV, Birjandi, FC, Sargolzaei, J, Shahtahmassebi, N, “Durable, Superhydrophobic, Superoleophobic and Corrosion Resistant Coating on the Stainless Steel Surface Using a Scalable Method.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 283 636–647 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.06.160
Ülkü, S, Balköse, D, Baltacboğlu, H, “Effect of Preparation pH on Pore Structure of Silica Gels.” Colloids Polym. Sci., 271 709–713 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652834
Zisman, WA, “Relation of the Equilibrium Contact Angle to Liquid and Solid Constitution.” UTC, pp 1–51 (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghadimi, M.R., Siavash Moakhar, R., Amirpoor, S. et al. Developing a new superhydrophilic and superoleophobic poly(4-(1-vinyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl) butane-1-sulfonate): vinyl imidazole@Perfluorooctanoic acid@SiO2 coated stainless steel mesh for highly efficient, stable, and durable oil/water separation. J Coat Technol Res 18, 511–521 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-020-00420-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-020-00420-6