Abstract
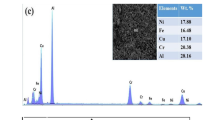
Tungsten boride (WB) powder was used as a wear-resistance material, then clad on a Ti–6Al–4V substrate by the gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) method. The titanium boride (TiB) reinforcing phase was formed in situ in the clad layer during the cladding process. Since the TiB and tungsten (W) reinforcing phase exist in the clad layer, the hardness of the clad layer is double that of the substrate. Wear test results reveal that the tribological performance of the WB-clad layer is superior to that of the Ti–6Al–4V substrate. This investigation also discusses the forming mechanism of the clad layer microstructure.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, YQ, Batchelor, AW, Wang, Y, Khor, KA, “Fretting Wear Behaviors of Thermal Sprayed Hydroxyapatite (HA) Coating Under Unlubricated Conditions.” Friction Wear, 217 132–139 (1998)
Bell, T, Proceedings of the First Asian International Conference on Tribology, Tsinghua University Press, Vol. 2, 1998, p. 421
Khor, KA, Gu, YW, Quek, CH, Cheang, P, “Plasma Spraying of Functionally Graded Hydroxyapatite/Ti–6Al–4V Coatings.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 168 195–201 (2003)
Jiang, P, He, XL, Li, XX, Yu, LG, Wang, HM, “Wear Resistance of a Laser Surface Alloyed Ti–6Al–4V Alloy.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 130 24–28 (2000)
Itoh, Y, Itoh, A, Azuma, H, Hioki, T, “Improving the Tribological Properties of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy by Nitrogen-Ion Implantation.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 111 172–176 (1999)
Wang, SW, Lin, YC, Tsai, YY, “The Effects of Various Ceramic–Metal on Wear Performance of Clad Layer.” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 140 682–687 (2003)
Eroğlu, M, Özdemir, N, “Tungsten-Inert Gas Surface Alloying of a Low Carbon Steel.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 154 209–217 (2002)
Buytoz, S, Ulutan, M, Yildirim, MM, “Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of TIG Welding Clad WC Composite Coatings.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 252 1313–1323 (2005)
Cheng, FT, Lo, KH, Man, HC, “NiTi Cladding on Stainless Steel by TIG Surfacing Process: Part I. Cavitation Erosion Behavior.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 172 308–315 (2003)
Cai, LF, Zhang, YH, Shi, LK, “Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Titanium Matrix Composites Coating on Ti–6A1–4V by Laser Cladding.” Rare Met., 26 342–346 (2007)
Lin, YC, Cho, YH, “Elucidating the Microstructure and Wear Behavior for Multicomponent Alloy Clad Layers by In Situ Synthesis.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 202 4666–4672 (2008)
ASM Handbook, Vol. 3, Alloy Phase Diagrams
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China, Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. NSC97-2221-E-011-035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Lin, YC. Elucidation of microstructure and wear behaviors of Ti–6Al–4V cladding using tungsten boride powder by the GTAW method. J Coat Technol Res 8, 247–253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-010-9281-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-010-9281-2