Abstract
Objective
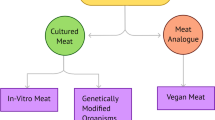
Cultured meat is considered to be a viable alternative to conventional flesh to satisfy the increasing human demand for meat. However, current cultured meat products fail to meet consumer expectations. This paper aims to summarize existing methods of cultured meat production, especially 3D bioprinting of cultured meat, which is an emerging approach with unique advantages. By discussing the advantages and shortcomings of the existing techniques, the prospect for the future development of cultured meat is provided.
Methods
The potential ecological sustainability of cultured meat is evaluated in order to determine the necessity for its development. The advancements and limitations of cultured meat based on tissue engineering, 3D printing of meat, and 3D bioprinting of cultured meat are discussed. Future trends in 3D bioprinting of cultured meat are predicted, as well as potential challenges in this field.
Results
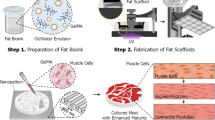
(1) Cultured meat is an ecologically sustainable alternative to conventional meat. (2) Cultured meat based on tissue engineering has allowed the creation of cultured muscle, adipose, and multi-component meat. The issues are that the shape of the products is unpredictable, and the process of producing large-size and multi-component cultured meat is arduous, which is not conducive to sustainable manufacturing. (3) 3D printing has been utilized in the customized processing of meat to achieve personalized demands. However, it relies on natural meat for its raw materials and cannot replace livestock production. (4) There have been preliminary attempts to use 3D bioprinting technology for cultured meat production. It combines the advantages of tissue engineering and 3D printing, which is able to create cultured beef, pork, and seafood. (5) The potential advantages of 3D bioprinting of cultured meat are higher quality and yield, enhanced cost-effectiveness, and superior ecological sustainability. (6) In the future, 3D bioprinting of cultured meat will move towards multi-component products, integrated fabrication, and cloud manufacturing. (7) The urgent issues in 3D bioprinting of cultured meat are the development of edible and printable biomaterials, the advancement of bioprinting techniques, and the life cycle assessment of manufacturing process.
Conclusion
3D bioprinting is a promising avenue to improve the quality and yield, reduce production costs, and enhance the ecological sustainability of cultured meat. It may allow people to satisfy the growing demand for meat in a sustainable manner.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Aditya, A., & Kim, N. P. (2022). 3D printing of meat following supercritical fluid extraction. Foods, 11(4), https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040554.
Antoshin, A. A., Churbanov, S. N., Minaev, N. V., Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Shpichka, A. I., & Timashev, P. S. (2019). LIFT-bioprinting, is it worth it? Bioprinting, 15, e00052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bprint.2019.e00052.
Ashammakhi, N., Hasan, A., Kaarela, O., Byambaa, B., Sheikhi, A., Gaharwar, A. K., & Khademhosseini, A. (2019). Advancing frontiers in bone bioprinting. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 8(7), 24. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201801048.
Balasubramanian, B., Liu, W. C., Pushparaj, K., & Park, S. (2021). The epic of in vitro meat production-A fiction into reality. Foods, 10(6), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061395.
Ben-Arye, T., Shandalov, Y., Ben-Shaul, S., Landau, S., Zagury, Y., Ianovici, I., Lavon, N., & Levenberg, S. (2020). Textured soy protein scaffolds enable the generation of three-dimensional bovine skeletal muscle tissue for cell-based meat. Nature Food, 1(4), 18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-020-0046-5.
Bhat, Z. F., Morton, J. D., Kumar, S., Bhat, H. F., Aadil, R. M., & Bekhit, A. (2021). 3D printing: Development of animal products and special foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 118, 87–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.09.020.
Bilici, C., Tatar, A. G., Senturk, E., Dikyol, C., & Koc, B. (2022). Bisulfite-initiated crosslinking of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels for embedded 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication, 14(2), https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/ac4dd9.
Blaeser, A., Campos, D. F. D., Puster, U., Richtering, W., Stevens, M. M., & Fischer, H. (2016). Controlling shear stress in 3D bioprinting is a key factor to balance printing resolution and stem cell integrity. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 5(3), 326–333. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201500677.
Bociaga, D., Bartniak, M., Grabarczyk, J., & Przybyszewska, K. (2019). Sodium alginate/gelatine hydrogels for direct bioprinting-the effect of composition selection and applied solvents on the bioink properties. Materials, 12(17), https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172669.
Boonlai, W., Tantishaiyakul, V., & Hirun, N. (2022). Characterization of kappa-carrageenan/methylcellulose/cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels for 3D bioprinting. Polymer International, 71(2), 181–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.6298.
Breithaupt, H., & Levy, S. (2014). Tackling resistence: Bacteria, humans, animals and the environment. Embo Reports, 15(2), 127–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/embr.201338299.
Bulut, E. G., & Candogan, K. (2022). Development and characterization of a 3D printed functional chicken meat based snack: Optimization of process parameters and gelatin level. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112768.
Cambra-Lopez, M., Aarnink, A. J. A., Zhao, Y., Calvet, S., & Torres, A. G. (2010). Airborne particulate matter from livestock production systems: A review of an air pollution problem. Environmental Pollution, 158(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.011.
Caro, D., Davis, S. J., Bastianoni, S., & Caldeira, K. (2014). Global and regional trends in greenhouse gas emissions from livestock. Climatic Change, 126(1–2), 203–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1197-x.
Castilho, M., de Ruijter, M., Beirne, S., Villette, C. C., Ito, K., Wallace, G. G., & Malda, J. (2020). Multitechnology biofabrication: A new approach for the manufacturing of functional tissue structures? Trends in Biotechnology, 38(12), 1316–1328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.04.014.
Chai, N., Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., Du, H., He, X., Yang, J., Zhou, X., He, J., & He, C. (2021). Construction of 3D printed constructs based on microfluidic microgel for bone regeneration. Composites Part B-Engineering, 223, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109100.
Chand, R., Muhire, B. S., & Vijayavenkataraman, S. (2022). Computational fluid dynamics assessment of the effect of bioprinting parameters in extrusion bioprinting. International Journal of Bioprinting, 8(2), 45–60. https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v8i2.545.
Chao, C., Hwang, J. S., Kim, I. W., Choi, R. Y., Kim, H. W., & Park, H. J. (2022). Coaxial 3D printing of chicken surimi incorporated with mealworm protein isolate as texture-modified food for the elderly. Journal of Food Engineering, 333, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111151.
Chen, B. Q., Dong, J. P., Ruelas, M., Ye, X. Y., He, J. X., Yao, R. J., Fu, Y. Q., Liu, Y., Hu, J. P., Wu, T. Y., Zhou, C. P., Li, Y., Huang, L., Zhang, Y. S., & Zhou, J. H. (2022). Artificial intelligence-assisted high-throughput screening of printing conditions of hydrogel architectures for accelerated diabetic wound healing. Advanced Functional Materials, 32(38), 14. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202201843.
Choudhury, D., Tseng, T. W., & Swartz, E. (2020). The business of cultured meat. Trends in Biotechnology, 38(6), 573–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.02.012.
Chriki, S., & Hocquette, J. F. (2020). The myth of cultured meat: A review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00007.
Chriki, S., Ellies-Oury, M. P., & Hocquette, J. F. (2022). Is cultured meat a viable alternative to slaughtering animals and a good comprise between animal welfare and human expectations? Animal Frontiers, 12(1), 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/af/vfac002.
Chu, Y., Huang, L., Hao, W. P., Zhao, T. T., Zhao, H. T., Yang, W., Xie, X., Qian, L., Chen, Y. Y., & Dai, J. W. (2021). Long-term stability, high strength, and 3D printable alginate hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering application. Biomedical Materials, 16(6), 12. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/ac2595.
Cui, J., Ren, L., Mai, J. G., Zheng, P., & Zhang, L. (2022). 3D printing in the context of cloud manufacturing. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 74, 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2021.102256.
Dai, X. W., Sun, Z. L., & Muller, D. (2021). Driving factors of direct greenhouse gas emissions from China’s pig industry from 1976 to 2016. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 20(1), 319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2095-3119(20)63425-6.
Datar, I., & Betti, M. (2010). Possibilities for an in vitro meat production system. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 11(1), 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2009.10.007.
de Noordhout, C. M., Devleesschauwer, B., Angulo, F. J., Verbeke, G., Haagsma, J., Kirk, M., Havelaar, A., & Speybroeck, N. (2014). The global burden of listeriosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infectious Diseases, 14(11), 1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(14)70870-9.
de Vries, M., & de Boer, I. J. M. (2010). Comparing environmental impacts for livestock products: A review of life cycle assessments. Livestock Science, 128(1–3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2009.11.007.
Demirtas, T. T., Irmak, G., & Gumusderelioglu, M. (2017). A bioprintable form of chitosan hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Biofabrication, 9(3), 12. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/aa7b1d.
Dick, A., Bhandari, B., & Prakash, S. (2019a). 3D printing of meat. Meat Science, 153, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.03.005.
Dick, A., Bhandari, B., & Prakash, S. (2019b). Post-processing feasibility of composite-layer 3D printed beef. Meat Science, 153, 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.02.024.
Dick, A., Bhandari, B., Dong, X., & Prakash, S. (2020). Feasibility study of hydrocolloid incorporated 3D printed pork as dysphagia food. Food Hydrocolloids, 107, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105940.
Dick, A., Bhandari, B., & Prakash, S. (2021a). Effect of reheating method on the post-processing characterisation of 3D printed meat products for dysphagia patients. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 150, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111915.
Dick, A., Dong, X. P., Bhandari, B., & Prakash, S. (2021b). The role of hydrocolloids on the 3D printability of meat products. Food Hydrocolloids, 119, 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106879.
Dohmen, R. G. J., Hubalek, S., Melke, J., Messmer, T., Cantoni, F., Mei, A., Hueber, R., Mitic, R., Remmers, D., Moutsatsou, P., Post, M. J., Jackisch, L., & Flack, J. E. (2022). Muscle-derived fibro-adipogenic progenitor cells for production of cultured bovine adipose tissue. Npj Science of Food, 6(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-021-00122-2.
Dolgin, E. (2020). Cell-based meat with a side of science. Nature, 588(7837), S64–S67. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03448-1.
Domingos, M., Intranuovo, F., Russo, T., De Santis, R., Gloria, A., Ambrosio, L., Ciurana, J., & Bartolo, P. (2013). The first systematic analysis of 3D rapid prototyped poly(epsilon-caprolactone) scaffolds manufactured through BioCell printing: The effect of pore size and geometry on compressive mechanical behaviour and in vitro hMSC viability. Biofabrication, 5(4), https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5082/5/4/045004.
Dutta, S. D., Ganguly, K., Jeong, M. S., Patel, D. K., Patil, T. V., Cho, S. J., & Lim, K. T. (2022). Bioengineered lab-grown meat-like constructs through 3D bioprinting of antioxidative protein hydrolysates. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 14(30), 34513–34526. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c10620.
Espinosa, R., Tago, D., & Treich, N. (2020). Infectious diseases and meat production. Environmental & Resource Economics, 76(4), 1019–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-020-00484-3.
European Food Safety, A., Prevention, E. C. D., C., & Ecdc (2019). The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. Efsa Journal, 17(12), 276. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5926.
Fan, D., Liu, W., Chen, H., & Zhang, M. (2022). 3D printing characteristics and rheological properties of surimi gel based on near infrared spectroscopy. Food and Fermentation Industries, 48(9), 163–169.
Fraeye, I., Kratka, M., Vandenburgh, H., & Thorrez, L. (2020). Sensorial and nutritional aspects of cultured meat in comparison to traditional meat: Much to be inferred. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00035.
Furuhashi, M., Morimoto, Y., Shima, A., Nakamura, F., Ishikawa, H., & Takeuchi, S. (2021). Formation of contractile 3D bovine muscle tissue for construction of millimetre-thick cultured steak. Npj Science of Food, 5(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-021-00090-7.
Gantenbein, S., Colucci, E., Kach, J., Trachsel, E., Coulter, F. B., Ruhs, P. A., Masania, K., & Studart, A. R. (2023). Three-dimensional printing of mycelium hydrogels into living complex materials. Nature Materials, 22(1), 128–134. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-022-01429-5.
Gao, Q., He, Y., Fu, J. Z., Liu, A., & Ma, L. (2015). Coaxial nozzle-assisted 3D bioprinting with built-in microchannels for nutrients delivery. Biomaterials, 61, 203–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.05.031.
Garrison, G. L., Biermacher, J. T., & Brorsen, B. W. (2022). How much will large-scale production of cell-cultured meat cost? Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 10, 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100358.
Gebler, M., Uiterkamp, A., & Visser, C. (2014). A global sustainability perspective on 3D printing technologies. Energy Policy, 74, 158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.08.033.
Godfray, H. C. J., Aveyard, P., Garnett, T., Hall, J. W., Key, T. J., Lorimer, J., Pierrehumbert, R. T., Scarborough, P., Springmann, M., & Jebb, S. A. (2018). Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science, 361(6399), 8. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam5324.
Grigoryan, B., Paulsen, S. J., Corbett, D. C., Sazer, D. W., Fortin, C. L., Zaita, A. J., Greenfield, P. T., Calafat, N. J., Gounley, J. P., Ta, A. H., Johansson, F., Randles, A., Rosenkrantz, J. E., Louis-Rosenberg, J. D., Galie, P. A., Stevens, K. R., & Miller, J. S. (2019). Multivascular networks and functional intravascular topologies within biocompatible hydrogels. Science, 364(6439), 458–. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav9750.
Guan, X., Lei, Q., Yan, Q., Li, X., Zhou, J., Du, G., & Chen, J. (2021). Trends and ideas in technology, regulation and public acceptance of cultured meat. Future Foods, 3, 100032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fufo.2021.100032.
Guan, X., Zhou, J. W., Du, G. C., & Chen, J. (2022). Bioprocessing technology of muscle stem cells: Implications for cultured meat. Trends in Biotechnology, 40(6), 721–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2021.11.004.
Gyawali, R., & Ibrahim, S. A. (2014). Natural products as antimicrobial agents. Food Control, 46, 412–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.05.047.
Han, S. L., & Liu, X. W. (2022). Can imported cold food cause COVID-19 recurrent outbreaks? A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 20(1), 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01312-w.
Handral, H. K., Tay, S. H., Chan, W. W., & Choudhury, D. (2022). 3D printing of cultured meat products. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62(1), 272–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1815172.
He, N., Wang, X. N., Shi, L. Y., Li, J., Mo, L., Chen, F., Huang, Y. T., Liu, H. R., Zhu, X. L., Zhu, W., Mao, Y. Q., & Han, X. X. (2023). Photoinhibiting via simultaneous photoabsorption and free-radical reaction for high-fidelity light-based bioprinting. Nature Communications, 14(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38838-2.
Hoekstra, A. Y., & Mekonnen, M. M. (2012). The water footprint of humanity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(9), 3232–3237. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1109936109.
Hu, Y. A., Cheng, H. F., & Tao, S. (2017). Environmental and human health challenges of industrial livestock and poultry farming in China and their mitigation. Environment International, 107, 111–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.07.003.
Huh, J., Moon, Y. W., Park, J., Atala, A., Yoo, J. J., & Lee, S. J. (2021). Combinations of photoinitiator and UV absorber for cell-based digital light processing (DLP) bioprinting. Biofabrication, 13(3), https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/abfd7a.
Ianovici, I., Zagury, Y., Redenski, I., Lavon, N., & Levenberg, S. (2022). 3D-printable plant protein-enriched scaffolds for cultivated meat development. Biomaterials, 284, 121487–121487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121487.
Immohr, M. B., Adrego, F. D. S., Teichert, H. L., Schmidt, V., Sugimura, Y., Bauer, S., Barth, M., Lichtenberg, A., & Akhyari, P. (2023). 3D-bioprinting of aortic valve interstitial cells: Impact of hydrogel and printing parameters on cell viability. Biomedical Materials, 18(1), https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/ac9f91.
Jeong, D., Seo, J. W., Lee, H. G., Jung, W. K., Park, Y. H., & Bae, H. (2022). Efficient myogenic/adipogenic transdifferentiation of bovine fibroblasts in a 3D bioprinting system for steak-type cultured meat production. Advanced Science, 9(31), 16. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202202877.
Jia, W., Gungor-Ozkerim, P. S., Zhang, Y. S., Yue, K., Zhu, K., Liu, W., Pi, Q., Byambaa, B., Dokmeci, M. R., Shin, S. R., & Khademhosseini, A. (2016). Direct 3D bioprinting of perfusable vascular constructs using a blend bioink. Biomaterials, 106, 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.07.038.
Jin, Y., Xu, Y., Wu, Y., Sun, J., Guo, J., Gao, J., & Yang, Y. (2017). Microtissues enhance smooth muscle differentiation and cell viability of hADSCs for three dimensional bioprinting. Frontiers in Physiology, 8, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00703.
Jing, L. Z., Sun, J., Liu, H., Wang, X., & Huang, D. J. (2021). Using plant proteins to develop composite scaffolds for cell culture applications. International Journal of Bioprinting, 7(1), 66–77. https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v7i1.298.
Jo, Y., Hwang, D. G., Kim, M., Yong, U. J., & Jang, J. (2023). Bioprinting-assisted tissue assembly to generate organ substitutes at scale. Trends in Biotechnology, 41(1), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.07.001.
Kang, D. H., Louis, F., Liu, H., Shimoda, H., Nishiyama, Y., Nozawa, H., Kakitani, M., Takagi, D., Kasa, D., Nagamori, E., Irie, S., Kitano, S., & Matsusaki, M. (2021). Engineered whole cut meat-like tissue by the assembly of cell fibers using tendon-gel integrated bioprinting. Nature Communications, 12(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25236-9.
Khajehmohammadi, M., Tafti, R. A., & Nikukar, H. (2023). Effect of porosity on mechanical and biological properties of bioprinted scaffolds. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 111(2), 245–260. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.37455.
Kim, S. M., Kim, H. W., & Park, H. J. (2021). Preparation and characterization of surimi-based imitation crab meat using coaxial extrusion three-dimensional food printing. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102711.
Klak, M., Kowalska, P., Dobrzanski, T., Tymicki, G., Cywoniuk, P., Gomolka, M., Kosowska, K., Bryniarski, T., Berman, A., Dobrzyn, A., Sadowski, W., Gorecki, B., & Wszola, M. (2021). Bionic organs: Shear forces reduce pancreatic islet and mammalian cell viability during the process of 3D bioprinting. Micromachines, 12(3), https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12030304.
Lanzoni, D., Bracco, F., Cheli, F., Colosimo, B. M., Moscatelli, D., Baldi, A., Rebucci, R., & Giromini, C. (2022). Biotechnological and technical challenges related to cultured meat production. Applied Sciences-Basel, 12(13), https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136771.
Lee, A., Hudson, A. R., Shiwarski, D. J., Tashman, J. W., Hinton, T. J., Yerneni, S., Bliley, J. M., Campbell, P. G., & Feinberg, A. W. (2019). 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science, 365(6452), 482–. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav9051.
Lee, M., Rizzo, R., Surman, F., & Zenobi-Wong, M. (2020). Guiding lights: Tissue bioprinting using photoactivated materials. Chemical Reviews, 120(19), 10670–10747. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00077.
Lee, C. H., Kim, M. E., Yang, Y., Son, Y. J., Lee, J. A., Soon, L. E., Ju, J. U., Kang, B., & Lee, S. G. (2021). Optimization of the salt content in fish surimi ink for food 3D printing. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(1), 29–33.
Lee, D. Y., Lee, S. Y., Yun, S. H., Jeong, J. W., Kim, J. H., Kim, H. W., Choi, J. S., Kim, G. D., Joo, S. T., Choi, I., & Hur, S. J. (2022). Review of the current research on fetal bovine serum and the development of cultured meat. Food Science of Animal Resources, 42(5), 775–799. https://doi.org/10.5851/kosfa.2022.e46.
Lee, S. H., Kim, H. W., & Park, H. J. (2023a). Integrated design of micro-fibrous food with multi-materials fabricated by uniaxial 3D printing. Food Research International, 165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112529.
Lee, S. Y., Lee, D. Y., Jeong, J. W., Kim, J. H., Yun, S. H., Joo, S. T., Choi, I., Choi, J. S., Kim, G. D., & Hur, S. J. (2023b). Studies on meat alternatives with a focus on structuring technologies. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02992-0.
Leip, A., Billen, G., Garnier, J., Grizzetti, B., Lassaletta, L., Reis, S., Simpson, D., Sutton, M. A., de Vries, W., Weiss, F., & Westhoek, H. (2015). Impacts of European livestock production: Nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus and greenhouse gas emissions, land-use, water eutrophication and biodiversity. Environmental Research Letters, 10(11), 13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/11/115004.
Letcher, S. M., Rubio, N. R., Ashizawa, R. N., Saad, M. K., Rittenberg, M. L., McCreary, A., Ali, A., Calkins, O. P., Trimmer, B. A., & Kaplan, D. L. (2022). In vitro insect fat cultivation for cellular agriculture applications. Acs Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 8(9), 3785–3796. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00093.
Li, Y., Mao, Q., Li, X., Yin, J., Wang, Y., Fu, J., & Huang, Y. (2019). High-fidelity and high-efficiency additive manufacturing using tunable pre-curing digital light processing. Additive Manufacturing, 30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100889.
Li, X. D., Liu, B. X., Pei, B., Chen, J. W., Zhou, D. Z., Peng, J. Y., Zhang, X. Z., Jia, W., & Xu, T. (2020). Inkjet bioprinting of biomaterials. Chemical Reviews, 120(19), 10596–10636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00008.
Li, Y., Liu, W., Li, S., Zhang, M., Yang, F., & Wang, S. (2021). Porcine skeletal muscle tissue fabrication for cultured meat production using three-dimensional bioprinting technology. Journal of Future Foods, 1(1), 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfutfo.2021.09.005.
Li, C. H., Yang, I. H., Ke, C. J., Chi, C. Y., Matahum, J., Kuan, C. Y., Celikkin, N., Swieszkowski, W., & Lin, F. H. (2022a). The production of fat-containing cultured meat by stacking aligned muscle layers and adipose layers formed from gelatin-soymilk scaffold. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.875069.
Li, L., Chen, L., Chen, X., Chen, Y., Ding, S., Fan, X., Liu, Y., Xu, X., Zhou, G., Zhu, B., Ullah, N., & Feng, X. (2022b). Chitosan-sodium alginate-collagen/gelatin three-dimensional edible scaffolds for building a structured model for cell cultured meat. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 209, 668–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.052.
Li, G., Zhan, J., Hu, Z., Huang, J., Yao, Q., Yuan, C., Chen, J., & Hu, Y. (2023). Effects of nano starch-lutein on 3D printing properties of functional surimi: Enhancement mechanism of printing effects and anti-oxidation. Journal of Food Engineering, 346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2023.111431.
Lindner, N., & Blaeser, A. (2022). Scalable biofabrication: A perspective on the current state and future potentials of process automation in 3D-bioprinting applications. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.855042.
Liu, Z. B., Zhang, M., Bhandari, B., & Wang, Y. C. (2017). 3D printing: Printing precision and application in food sector. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 69, 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.08.018.
Liu, K., Zhao, N., Xiang, C., Li, Y., Jiang, X., Zeng, M., Xu, H., Wang, H., Wu, H., Yu, X., & Zhao, Y. (2022a). Three-dimensional printing properties of polysaccharide hydrocolloids-unrinsed sturgeon surimi complex hydrogels. Foods, 11(19), https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192947.
Liu, P., Dang, X., Woo, M. W., Chattha, S. A., An, J., & Shan, Z. (2022b). Feasibility study of starch-based biomass incorporated 3D printed beef. Starch-Starke, 74, 5–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.202200030.
Liu, Y., Wang, R., Ding, S., Deng, L., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Shi, Z., Wu, Z., Liang, K., Yan, X., Liu, W., & Du, Y. (2022c). Engineered meatballs via scalable skeletal muscle cell expansion and modular micro-tissue assembly using porous gelatin micro-carriers. Biomaterials, 287, 121615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121615.
Liu, P., Song, W., Bassey, A. P., Tang, C., Li, H., Ding, S., & Zhou, G. (2023). Preparation and quality evaluation of cultured fat. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c08004.
Luo, L., Ma, Y. B., Zhang, S. Z., Wei, D. P., & Zhu, Y. G. (2009). An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(8), 2524–2530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.01.011.
Lynch, J., & Pierrehumbert, R. (2019). Climate impacts of cultured meat and beef cattle. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 3, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2019.00005.
Ma, X. Y., Liu, J., Zhu, W., Tang, M., Lawrence, N., Yu, C., Gou, M. L., & Chen, S. C. (2018). 3D bioprinting of functional tissue models for personalized drug screening and in vitro disease modeling. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 132, 235–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2018.06.011.
Machovina, B., Feeley, K. J., & Ripple, W. J. (2015). Biodiversity conservation: The key is reducing meat consumption. Science of the Total Environment, 536, 419–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.022.
MacQueen, L. A., Alver, C. G., Chantre, C. O., Ahn, S., Cera, L., Gonzalez, G. M., O’Connor, B. B., Drennan, D. J., Peters, M. M., Motta, S. E., Zimmerman, J. F., & Parker, K. K. (2019). Muscle tissue engineering in fibrous gelatin: Implications for meat analogs. Npj Science of Food, 3(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-019-0054-8.
Manojlovic, D., Dramicanin, M. D., Miletic, V., Mitic-Culafic, D., Jovanovic, B., & Nikolic, B. (2017). Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of a low-shrinkage monomer and monoacylphosphine oxide photoinitiator: Comparative analyses of individual toxicity and combination effects in mixtures. Dental Materials, 33(4), 454–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2017.02.002.
Mattick, C. S., Landis, A. E., Allenby, B. R., & Genovese, N. J. (2015). Anticipatory life cycle analysis of in vitro biomass cultivation for cultured meat production in the United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(19), 11941–11949. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01614.
Mekonnen, M. M., & Hoekstra, A. Y. (2012). A global assessment of the water footprint of farm animal products. Ecosystems, 15(3), 401–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-011-9517-8.
Messmer, T., Klevernic, I., Furquim, C., Ovchinnikova, E., Dogan, A., Cruz, H., Post, M. J., & Flack, J. E. (2022). A serum-free media formulation for cultured meat production supports bovine satellite cell differentiation in the absence of serum starvation. Nature Food, 3(1), 74–. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00419-1.
Mohammadpour, Z., Kharaziha, M., & Zarrabi, A. (2023). 3D-printing of silk nanofibrils reinforced alginate for soft tissue engineering. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030763.
Mohammadrezaei, D., Moghimi, N., Vandvajdi, S., Powathil, G., Hamis, S., & Kohandel, M. (2023). Predicting and elucidating the post-printing behavior of 3D printed cancer cells in hydrogel structures by integrating in-vitro and in-silico experiments. Scientific Reports, 13(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-28286-9.
Murphy, S. V., & Atala, A. (2014). 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nature Biotechnology, 32(8), 773–785. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2958.
Nachal, N., Moses, J. A., Karthik, P., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2019). Applications of 3D printing in food processing. Food Engineering Reviews, 11(3), 123–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-019-09199-8.
Naghieh, S., Sarker, M. D., Abelseth, E., & Chen, X. (2019). Indirect 3D bioprinting and characterization of alginate scaffolds for potential nerve tissue engineering applications. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 93, 183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.02.014.
Newswire, P. R. (2021, February 9). Aleph farms and the technion reveal world’s first cultivated ribeye steak. Retrieved January 6, 2023, from https://www.prnewswire.com/il/news-releases/aleph-farms-and-the-technion-reveal-worlds-first-cultivated-ribeye-steak-301224800.html.
Ng, W. L., Lee, J. M., Zhou, M. M., Chen, Y. W., Lee, K. X. A., Yeong, W. Y., & Shen, Y. F. (2020). Vat polymerization-based bioprinting-Process, materials, applications and regulatory challenges. Biofabrication, 12(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/ab6034.
Ng, W. L., Huang, X., Shkolnikov, V., Goh, G. L., Suntornnond, R., & Yeong, W. Y. (2022). Controlling droplet impact velocity and droplet volume: Key factors to achieving high cell viability in sub-nanoliter droplet-based bioprinting. International Journal of Bioprinting, 8(1), https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v8i1.424.
Ngo, T. D., Kashani, A., Imbalzano, G., Nguyen, K. T. Q., & Hui, D. (2018). Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Composites Part B-Engineering, 143, 172–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.012.
Nguyen, A. K., Goering, P. L., Reipa, V., & Narayan, R. J. (2019). Toxicity and photosensitizing assessment of gelatin methacryloyl-based hydrogels photoinitiated with lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate in human primary renal proximal tubule epithelial cells. Biointerphases, 14(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.5095886.
Nguyen, A. K., Goering, P. L., Elespuru, R. K., Das, S. S., & Narayan, R. J. (2020). The photoinitiator lithium phenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphinate with exposure to 405 nm light is cytotoxic to mammalian cells but not mutagenic in bacterial reverse mutation assays. Polymers, 12(7), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071489.
Nie, J., Gao, Q., Fu, J. Z., & He, Y. (2020). Grafting of 3D bioprinting to in vitro drug screening: A review. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 9(7), 18. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201901773.
Norris, S. C. P., Kawecki, N. S., Davis, A. R., Chen, K. K., & Rowat, A. C. (2022). Emulsion-templated microparticles with tunable stiffness and topology: Applications as edible microcarriers for cultured meat. Biomaterials, 287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121669.
Ong, K. J., Johnston, J., Datar, I., Sewalt, V., Holmes, D., & Shatkin, J. A. (2021). Food safety considerations and research priorities for the cultured meat and seafood industry. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(6), 5421–5448. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12853.
Ouyang, L., Yao, R., Zhao, Y., & Sun, W. (2016). Effect of bioink properties on printability and cell viability for 3D bioplotting of embryonic stem cells. Biofabrication, 8(3), https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/8/3/035020.
Ozbolat, I. T., & Hospodiuk, M. (2016). Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials, 76, 321–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.10.076.
Pajcin, I., Knezic, T., Azoulay, I. S., Vlajkov, V., Djisalov, M., Janjusevic, L., Grahovac, J., & Gadjanski, I. (2022). Bioengineering outlook on cultivated meat production. Micromachines, 13(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030402.
Park, S., Jung, S., Choi, M., Lee, M., Choi, B., Koh, W. G., Lee, S., & Hong, J. (2021a). Gelatin MAGIC powder as nutrient-delivering 3D spacer for growing cell sheets into cost-effective cultured meat. Biomaterials, 278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121155.
Park, S., Jung, S., Heo, J., Koh, W. G., Lee, S., & Hong, J. (2021b). Chitosan/cellulose-based porous nanofilm delivering C-phycocyanin: A novel platform for the production of cost-effective cultured meat. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13(27), 32193–32204. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c07385.
Park, J. W., Lee, S. H., Kim, H. W., & Park, H. J. (2023). Application of extrusion-based 3D food printing to regulate marbling patterns of restructured beef steak. Meat Science, 202, 109203–109203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2023.109203.
Parodi, A., Leip, A., De Boer, I. J. M., Slegers, P. M., Ziegler, F., Temme, E. H. M., Herrero, M., Tuomisto, H., Valin, H., Van Middelaar, C. E., Van Loon, J. J. A., & Van Zanten, H. H. E. (2018). The potential of future foods for sustainable and healthy diets. Nature Sustainability, 1(12), 782–789. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-018-0189-7.
Pasitka, L., Cohen, M., Ehrlich, A., Gildor, B., Reuveni, E., Ayyash, M., Wissotsky, G., Herscovici, A., Kaminker, R., Niv, A., Bitcover, R., Dadia, O., Rudik, A., Voloschin, A., Shimoni, M., Cinnamon, Y., & Nahmias, Y. (2022). Spontaneous immortalization of chicken fibroblasts generates stable, high-yield cell lines for serum-free production of cultured meat. Nature Food, 28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-022-00658-w.
Pepelanova, I., Kruppa, K., Scheper, T., & Lavrentieva, A. (2018). Gelatin-methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels with defined degree of functionalization as a versatile toolkit for 3D cell culture and extrusion bioprinting. Bioengineering-Basel, 5(3), 55–Article. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5030055.
Poore, J., & Nemecek, T. (2018). Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science, 360(6392), 987–. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaq0216.
Post, M. J., Levenberg, S., Kaplan, D. L., Genovese, N., Fu, J. A., Bryant, C. J., Negowetti, N., Verzijden, K., & Moutsatsou, P. (2020). Scientific, sustainability and regulatory challenges of cultured meat. Nature Food, 1(7), 403–415. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-020-0112-z.
Ramachandraiah, K. (2021). Potential development of sustainable 3D-printed meat analogues: A review. Sustainability, 13(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020938.
Rechsteiner, D., Schrade, S., Zahner, M., Muller, M., Hollender, J., & Bucheli, T. D. (2020). Occurrence and fate of natural estrogens in Swiss cattle and pig slurry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68(20), 5545–5554. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00858.
Rodriguez Escobar, M. I., Cadena, E., Nhu, T. T., Cooreman-Algoed, M., De Smet, S., & Dewulf, J. (2021). Analysis of the cultured meat production system in function of its environmental footprint: Current status, gaps and recommendations. Foods, 10(12), https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122941.
Rubio, N. R., Xiang, N., & Kaplan, D. L. (2020). Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production. Nature Communications, 11(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20061-y.
Rutz, A. L., Lewis, P. L., & Shah, R. N. (2017). Toward next-generation bioinks: Tuning material properties pre- and post-printing to optimize cell viability. Mrs Bulletin, 42(8), 563–570. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2017.162.
Samsonstuen, S., Aby, B. A., Crosson, P., Beauchemin, K. A., Bonesmo, H., & Aass, L. (2019). Farm scale modelling of greenhouse gas emissions from semi-intensive suckler cow beef production. Agricultural Systems, 176, 9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.102670.
Schiell, C., Portanguen, S., Scislowski, V., Astruc, T., & Mirade, P. S. (2023). Investigation into the physicochemical and textural properties of an iron-rich 3D-printed hybrid food. Foods, 12(7), https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071375.
Seyedmahmoud, R., Celebi-Saltik, B., Barros, N., Nasiri, R., Banton, E., Shamloo, A., Ashammakhi, N., Dokmeci, M. R., & Ahadian, S. (2019). Three-dimensional bioprinting of functional skeletal muscle tissue using gelatin methacryloyl-alginate bioinks. Micromachines, 10(10), https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10100679.
Shang, S., Liu, Y., Jiang, P., Wang, Y., Fu, B., & Qi, L. (2023). Effects of partial replacement of unwashed Antarctic krill surimi by Litopenaeus vannamei surimi on the heat-induced gelling and three-dimensional-printing properties. Journal of Texture Studies. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtxs.12739.
Song, L., Pan, C. P., Yang, J., Zeng, S. J., & Han, Y. T. (2020). Dual-layer column filtration cleanup and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection for the analysis of 39 pesticide residues in porcine meat. Journal of Separation Science, 43(7), 1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900850.
Song, W. J., Liu, P. P., Zheng, Y. Y., Meng, Z. Q., Zhu, H. Z., Tang, C. B., Li, H. X., Ding, S. J., & Zhou, G. H. (2022a). Production of cultured fat with peanut wire-drawing protein scaffold and quality evaluation based on texture and volatile compounds analysis. Food Research International, 160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111636.
Song, W. J., Liu, P. P., Meng, Z. Q., Zheng, Y. Y., Zhou, G. H., Li, H. X., & Ding, S. J. (2022b). Identification of porcine adipose progenitor cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting for the preparation of cultured fat by 3D bioprinting. Food Research International, 162, 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111952.
Srutee, R., Sowmya, R. S., & Uday, S. A. (2022). Clean meat: Techniques for meat production and its upcoming challenges. Animal Biotechnology, 33(7), 1721–1729. https://doi.org/10.1080/10495398.2021.1911810.
Su, L., Jing, L., Zeng, X., Chen, T., Liu, H., Kong, Y., Wang, X., Yang, X., Fu, C., Sun, J., & Huang, D. (2022). 3D-printed prolamin scaffolds for cell-based meat culture. Advanced Materials, e2207397. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202207397.
Sun, J., Zhou, W. B., Huang, D. J., Fuh, J. Y. H., & Hong, G. S. (2015a). An overview of 3D printing technologies for food fabrication. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(8), 1605–1615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1528-6.
Sun, Z. C., Yu, Q. L., & Han, L. (2015b). The environmental prospects of cultured meat in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(2), 234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2095-3119(14)60891-1.
Suntornnond, R., Ng, W. L., Huang, X., Yeow, C. H. E., & Yeong, W. Y. (2022). Improving printability of hydrogel-based bio-inks for thermal inkjet bioprinting applications via saponification and heat treatment processes. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 10(31), 5989–6000. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2tb00442a.
Takahashi, H., Yoshida, A., Gao, B., Yamanaka, K., & Shimizu, T. (2022). Harvest of quality-controlled bovine myogenic cells and biomimetic bovine muscle tissue engineering for sustainable meat production. Biomaterials, 287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121649.
Tanaka, R., Sakaguchi, K., Yoshida, A., Takahashi, H., Haraguchi, Y., & Shimizu, T. (2022). Production of scaffold-free cell-based meat using cell sheet technology. Npj Science of Food, 6(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-022-00155-1.
The Good Food Institute (2020). Cultivated meat 2019 State of the industry report. Retrieved December 30, 2022, from https://gfi.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/INN-CM-SOTIR-2020-0512.pdf.
Tian, S., Stevens, R., McInnes, B., & Lewinski, N. (2021). Machine assisted experimentation of extrusion-based bioprinting systems. Micromachines, 12(7), https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12070780.
Tibrewal, K., Dandekar, P., & Jain, R. (2023). Extrusion-based sustainable 3D bioprinting of meat & its analogues: A review. Bioprinting, 29, e00256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bprint.2022.e00256.
Tilman, D., & Clark, M. (2014). Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature, 515(7528), 518–. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13959.
Treich, N. (2021). Cultured meat: Promises and challenges. Environmental & Resource Economics, 79(1), 33–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-021-00551-3.
Tuomisto, H. L. (2019). The eco-friendly burger could cultured meat improve the environmental sustainability of meat products? Embo Reports, 20(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201847395.
Tuomisto, H. L., & de Mattos, M. J. T. (2011). Environmental impacts of cultured meat production. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(14), 6117–6123. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200130u.
Unagolla, J. M., & Jayasuriya, A. C. (2020). Hydrogel-based 3D bioprinting: A comprehensive review on cell-laden hydrogels, bioink formulations, and future perspectives. Applied Materials Today, 18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2019.100479.
United Nations (2019). World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights. United Nations Department of Economic and Social. Retrieved December 18, 2022, from https://www.un.org/development/desa/publications/world-population-prospects-2019-highlights.html.
Van Boeckel, T. P., Brower, C., Gilbert, M., Grenfell, B. T., Levin, S. A., Robinson, T. P., Teillant, A., & Laxminarayan, R. (2015). Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(18), 5649–5654. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1503141112.
Wang, S. H., Xiong, Y. J., Lalevee, J., Xiao, P., Liu, J., & Xing, F. Y. (2020). Biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of novel photoinitiator pi-conjugated dithienophosphole derivatives and their triggered polymers. Toxicology in Vitro, 63, 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104720.
Wang, S., Sun, B., Li, S., Li, Y., Sun, J., & Li, Y. (2021). Development status and strategic thinking of cultivated meat. Food Science, 42(15), 1–9.
Wang, T., Kaur, L., Furuhata, Y., Aoyama, H., & Singh, J. (2022). 3D printing of textured soft hybrid meat analogues. Foods, 11(3), https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030478.
Wang, J., Cui, Z., & Maniruzzaman, M. (2023). Bioprinting: A focus on improving bioink printability and cell performance based on different process parameters. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123020.
Whenish, R., Ramakrishna, S., Jaiswal, A. K., & Manivasagam, G. (2022). A framework for the sustainability implications of 3D bioprinting through nature-inspired materials and structures. Bio-Design and Manufacturing, 5(2), 412–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-021-00168-x.
Willett, W., Rockstrom, J., Loken, B., Springmann, M., Lang, T., Vermeulen, S., Garnett, T., Tilman, D., DeClerck, F., Wood, A., Jonell, M., Clark, M., Gordon, L. J., Fanzo, J., Hawkes, C., Zurayk, R., Rivera, J. A., De Vries, W., Sibanda, L. M., et al. (2019). Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet, 393(10170), 447–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31788-4.
Wilson, A., Anukiruthika, T., Moses, J. A., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2020). Customized shapes for chicken meat-based products: Feasibility study on 3D-printed nuggets. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(11), 1968–1983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02537-3.
Wilson, A., Anukiruthika, T., Moses, J. A., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2023). Preparation of fiber-enriched chicken meat constructs using 3D printing. Journal of Culinary Science & Technology, 21(1), 127–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/15428052.2021.1901817.
Wohler, L., Hogeboom, R. J., Berger, M., & Krol, M. S. (2023). Water pollution from pharmaceutical use in livestock farming: Assessing differences between livestock types and production systems. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.4761.
Wu, W., DeConinck, A., & Lewis, J. A. (2011). Omnidirectional printing of 3D microvascular networks. Advanced Materials, 23(24), H178–H183. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201004625.
Xu, H., Casillas, J., Krishnamoorthy, S., & Xu, C. (2020). Effects of Irgacure 2959 and lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate on cell viability, physical properties, and microstructure in 3D bioprinting of vascular-like constructs. Biomedical Materials, 15(5), https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/ab954e.
Xu, H. Q., Liu, J. C., Zhang, Z. Y., & Xu, C. X. (2022a). A review on cell damage, viability, and functionality during 3D bioprinting. Military Medical Research, 9(1), https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-022-00429-5.
Xu, H., Liu, Q., Casillas, J., McAnally, M., Mubtasim, N., Gollahon, L. S., Wu, D., & Xu, C. (2022b). Prediction of cell viability in dynamic optical projection stereolithography-based bioprinting using machine learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 33(4), 995–1005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01708-5.
Xu, E., Niu, R., Lao, J., Zhang, S., Li, J., Zhu, Y., Shi, H., Zhu, Q., Chen, Y., Jiang, Y., Wang, W., Yin, J., Chen, Q., Huang, X., Chen, J., & Liu, D. (2023a). Tissue-like cultured fish fillets through a synthetic food pipeline. Npj Science of Food, 7(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-023-00194-2.
Xu, J., Fan, Y., Chen, Q., Sun, F., Li, M., Kong, B., & Xia, X. (2023b). Effects of kappa-carrageenan gum on 3D printability and rheological properties of pork pastes. Meat Science, 197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2022.109078.
Xuan, Z., Peng, Q., Larsen, T., Gurevich, L., Christiansen, J. C., Zachar, V., & Pennisi, C. P. (2023). Tailoring hydrogel composition and stiffness to control smooth muscle cell differentiation in bioprinted constructs. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 20(2), 199–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-022-00500-1.
Yang, G., Han, Y., Tao, Y., Zhu, X., & Xu, X. (2022a). Effect of gelatin on the 3D printing forming stability of chicken meat paste. Food Science, 43(12), 51–57.
Yang, G., Tao, Y., Wang, P., Xu, X., & Zhu, X. (2022b). Optimizing 3D printing of chicken meat by response surface methodology and genetic algorithm: Feasibility study of 3D printed chicken product. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112693.
Yin, J., Yan, M., Wang, Y., Fu, J., & Suo, H. (2018). 3D bioprinting of low-concentration cell-laden gelatin methacrylate (GelMA) bioinks with a two-step cross-linking strategy. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(8), 6849–6857. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b16059.
You, S., Xiang, Y., Hwang, H. H., Berry, D. B., Kiratitanaporn, W., Guan, J., Yao, E., Tang, M., Zhong, Z., Ma, X., Wangpraseurt, D., Sun, Y., Lu, T., & Chen, S. (2023). High cell density and high-resolution 3D bioprinting for fabricating vascularized tissues. Science Advances, 9(8), https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ade7923.
Yu, N., Gong, H., Yuan, H., Bao, Y., & Wang, W. (2022a). Effects of calcium chloride as a salt substitute on physicochemical and 3D printing properties of silver carp surimi gels. Cyta-Journal of Food, 20(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2021.2008510.
Yu, N., Yang, F., Gong, H., Zhou, J., Jie, C., Wang, W., Chen, X., & Sun, L. (2022b). Gel & three-dimensional printing properties of sheep plasma protein-surimi induced by transglutaminase. Journal of Food Engineering, 323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111006.
Yuan, J. J., Xiang, J., Liu, D. Y., Kang, H., He, T. H., Kim, S., Lin, Y. X., Freeman, C., & Ding, W. X. (2019). Rapid growth in greenhouse gas emissions from the adoption of industrial-scale aquaculture. Nature Climate Change, 9(4), 318–. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-019-0425-9.
Zeng, B. N., Cai, Z. L., Lalevee, J., Yang, Q. Z., Lai, H. W., Xiao, P., Liu, J., & Xing, F. Y. (2021). Cytotoxic and cytocompatible comparison among seven photoinitiators-triggered polymers in different tissue cells. Toxicology in Vitro, 72, 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105103.
Zhang, G. Q., Zhao, X. R., Li, X. L., Du, G. C., Zhou, J. W., & Chen, J. (2020). Challenges and possibilities for bio-manufacturing cultured meat. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 97, 443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.026.
Zhang, L., Hu, Y. Y., Badar, I. H., Xia, X. F., Kong, B. H., & Chen, Q. (2021a). Prospects of artificial meat: Opportunities and challenges around consumer acceptance. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 116, 434–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.07.010.
Zhang, Y. S., Haghiashtiani, G., Hubscher, T., Kelly, D. J., Lee, J. M., Lutolf, M., McAlpine, M. C., Yeong, W. Y., Zenobi-Wong, M., & Malda, J. (2021b). 3D extrusion bioprinting. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 1(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00073-8.
Zheng, Y. Y., Chen, Y., Zhu, H. Z., Li, C. B., Song, W. J., Ding, S. J., & Zhou, G. H. (2022). Production of cultured meat by culturing porcine smooth muscle cells in vitro with food grade peanut wire-drawing protein scaffold. Food Research International, 159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111561.
Zhou, F. F., Hong, Y., Liang, R. J., Zhang, X. Z., Liao, Y. G., Jiang, D. M., Zhang, J. Y., Sheng, Z. X., Xie, C., Peng, Z., Zhuang, X. H., Bunpetch, V., Zou, Y. W., Huang, W. W., Zhang, Q., Alakpa, E. V., Zhang, S. F., & Ouyang, H. W. (2020). Rapid printing of bio-inspired 3D tissue constructs for skin regeneration. Biomaterials, 258, 15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120287.
Zhu, Z. J., Ng, D. W. H., Park, H. S., & McAlpine, M. C. (2021b). 3D-printed multifunctional materials enabled by artificial-intelligence-assisted fabrication technologies. Nature Reviews Materials, 6(1), 27–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-020-00235-2.
Zhu, H., Wu, Z., Ding, X., Post, M. J., Guo, R., Wang, J., Wu, J., Tang, W., Ding, S., & Zhou, G. (2022a). Production of cultured meat from pig muscle stem cells. Biomaterials, 287, 121650–121650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121650.
Zhu, X. C., Yuan, X. Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, H. L., Wang, J., & Sun, B. G. (2022b). The global concern of food security during the COVID-19 pandemic: Impacts and perspectives on food security. Food Chemistry, 370, 6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130830.
Zhu, J., Cheng, Y., Ouyang, Z., Yang, Y., Ma, L., Wang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2023). 3D printing surimi enhanced by surface crosslinking based on dry-spraying transglutaminase, and its application in dysphagia diets. Food Hydrocolloids, 140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108600.
Acknowledgements
The authors were grateful to the authorities of their institutes for their support.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (22193052, 22106167), Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RCEES-TDZ-2021-22), and the University and Institute Innovation Team Project of Jinan Science and Technology Bureau, China (No. 202228050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xudong Guo and Ligang Hu: conceptualization; Xudong Guo: writing—original draft preparation; Dingyi Wang, Bin He, Ligang Hu, Guibin Jiang, and Xudong Guo: writing—review and editing; Xudong Guo: visualization; Ligang Hu: funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Wang, D., He, B. et al. 3D Bioprinting of Cultured Meat: A Promising Avenue of Meat Production. Food Bioprocess Technol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03195-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03195-x