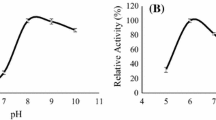
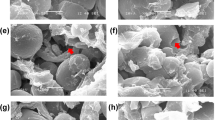
Abstract
The conformational properties of hydrolysates derived from brewer’s spent grain protein (BSGP) pretreatment with and without ultrasound were investigated, and the effect of BSGP hydrolysate (BSGPH) supplementation on the brewer’s yeast growth and fermentation performances were examined. Results demonstrated that BSGPH had substantial influences on the biomass, viability, sugar consumption, and ethanol production of yeast. Specifically, medium supplemented with hydrolysates derived from BSGP pretreated with ultrasound (UBPH) for 4-h hydrolysis (UBPH-4) increased biomass by 7.7%, viability by 9.78%, sugar consumption by 37.16%, and ethanol yields by 20.20% (v/v), respectively, compared with the blank. UBPH-4 exhibited a looser morphology and disordered secondary structure, with a decrease in α-helix and increased random coil. Meanwhile, a higher proportion of short peptides and hydrophilic amino acids in UBPH-4 might account for its preferred bioactivity. All findings revealed that UBPH were effective nitrogen sources for yeast growth and fermentation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abadia-Garcia, L., Castano-Tostado, E., Cardador-Martinez, A., Teresita Martin-del-Campo, S., & Amaya-Llano, S. L. (2021). Production of ACE inhibitory peptides from whey proteins modified by high intensity ultrasound using bromelain. Foods, 10(9), 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092099
Abdualrahman, M. A. Y., Ma, H., Zhou, C., Yagoub, A. E. A., Hu, J., & Yang, X. (2016). Thermal and single frequency counter-current ultrasound pretreatments of sodium caseinate: Enzymolysis kinetics and thermodynamics, amino acids composition, molecular weight distribution and antioxidant peptides. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 96(15), 4861–4873. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7996
Appiah-Nkansah, N. B., Zhang, K., Rooney, W., & Wang, D. (2018). Ethanol production from mixtures of sweet sorghum juice and sorghum starch using very high gravity fermentation with urea supplementation. Industrial Crops and Products, 111, 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.028
Ashraf, J., Liu, L. Y., Awais, M., Xiao, T. Z., Wang, L. L., Zhou, X. R., ... & Zhou, S. M. (2020). Effect of thermosonication pre-treatment on mung bean (Vigna radiata) and white kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) proteins: Enzymatic hydrolysis, cholesterol lowering activity and structural characterization. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 66, 105121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105121
Auesukaree, C. (2017). Molecular mechanisms of the yeast adaptive response and tolerance to stresses encountered during ethanol fermentation. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 124(2), 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2017.03.009
Barekat, S., & Soltanizadeh, N. (2018). Effects of ultrasound on microstructure and enzyme penetration in beef Longissimus lumborum muscle. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(3), 680–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-2043-8
Chin, Y. L., Chai, K. F., & Chen, W. N. (2022). Upcycling of brewers’ spent grains via solid-state fermentation for the production of protein hydrolysates with antioxidant and techno-functional properties. Food Chemistry-X, 13, 100184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2021.100184
Dabbour, M., He, R. H., Mintah, B., Golly, M. K., & Ma, H. L. (2020a). Ultrasound pretreatment of sunflower protein: Impact on enzymolysis, ACE-inhibition activity, and structure characterization. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 44(4), e14398. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14398
Dabbour, M., Xiang, J. H., Mintah, B., He, R. H., Jiang, H., & Ma, H. L. (2020b). Localized enzymolysis and sonochemically modified sunflower protein: Physical, functional and structure attributes. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 63, 104957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104957
Deesuth, O., Laopaiboon, P., & Laopaiboon, L. (2016). High ethanol production under optimal aeration conditions and yeast composition in a very high gravity fermentation from sweet sorghum juice by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Industrial Crops and Products, 92, 263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.07.042
Ding, Y., Wang, Y., Qu, W., Ren, X., Lu, F., Tian, W., ... & Ma, H. (2022). Effect of innovative ultrasonic frequency excitation modes on rice protein: Enzymolysis and structure. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 153(7), 112435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112435
Fadimu, G. J., Gill, H., Farahnaky, A., & Tuyen, T. (2021). Investigating the impact of ultrasound pretreatment on the physicochemical, structural, and antioxidant properties of lupin protein hydrolysates. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(11), 2004–2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02700-4
Fischer, M., Gruppen, H., Piersma, S. R., Kofod, L. V., Schols, H. A., & Voragen, A. G. J. (2002). Aggregation of peptides during hydrolysis as a cause of reduced enzymatic extractability of soybean meal proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(16), 4512–4519. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0114785
Hu, H., Wu, J., Li-Chan, E. C. Y., Zhu, L., Zhang, F., Xu, X., ... & Pan, S. (2013). Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocolloids, 30(2), 647–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.08.001
Ikram, S., Zhang, H., Ahmed, M. S., & Wang, J. (2020). Ultrasonic pretreatment improved the antioxidant potential of enzymatic protein hydrolysates from highland barley brewer’s spent grain (BSG). Journal of Food Science, 85(4), 1045–1059. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15063
Jin, Z., Lan, Y., Ohm, J. B., Gillespie, J., Schwarz, P., & Chen, B. C. (2022). Physicochemical composition, fermentable sugars, free amino acids, phenolics, and minerals in brewers’ spent grains obtained from craft brewing operations. Journal of Cereal Science, 104, 103413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2022.103413
Kawa-Rygielska, J., & Pietrzak, W. (2014). Ethanol fermentation of very high gravity (VHG) maize mashes by Saccharomyces cerevisiae with spent brewer’s yeast supplementation. Biomass & Bioenergy, 60, 50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.10.028
Kriisa, M., Taivosalo, A., Föste, M., Kütt, M.-L., Viirma, M., Priidik, R., ... & Vilu, R. (2022). Effect of enzyme-assisted hydrolysis on brewer’s spent grain protein solubilization–peptide composition and sensory properties. Applied Food Research, 2(1), 100108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afres.2022.100108
Lei, H., Li, H., Mo, F., Zheng, L., Zhao, H., & Zhao, M. (2013). Effects of Lys and His supplementations on the regulation of nitrogen metabolism in lager yeast. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(20), 8913–8921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5137-x
Li, K., Kang, Z. L., Zhao, Y. Y., Xu, X. L., & Zhou, G. H. (2014). Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve functional properties of batter suspensions prepared from PSE-like chicken breast meat. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(12), 3466–3477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1358-y
Li, Q., Yang, H., Coldea, T. E., Andersen, M. L., Li, W., & Zhao, H. (2022). Enzymolysis kinetics, thermodynamics and structural property of brewer’s spent grain protein pretreated with ultrasound. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 132, 130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2022.01.001
Li, W., Yang, H., Coldea, T. E., & Zhao, H. (2021). Modification of structural and functional characteristics of brewer’s spent grain protein by ultrasound assisted extraction. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 139, 110582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110582
Li, Y., Wang, D. Q., Zhang, S., Zhong, M. M., Zhao, C. B., Xie, F. Y., & Qi, B. K. (2020). Stability and in vitro simulated release characteristics of ultrasonically modified soybean lipophilic protein emulsion. Food & Function, 11(5), 3800–3810. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo00238k
Magalhaes, R. S. S., Popova, B., Braus, G. H., Outeiro, T. F., & Eleutherio, E. C. A. (2018). The trehalose protective mechanism during thermal stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: The roles of Ath1 and Agt1. FEMS Yeast Research, 18(6), foy066. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foy066.
Marcet, I., Alvarez, C., Paredes, B., Rendueles, M., & Diaz, M. (2018). Transparent and edible films from ultrasound-treated egg yolk granules. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(4), 735–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-2049-2
McCarthy, A. L., O’Callaghan, Y. C., Connolly, A., Piggott, C. O., FitzGerald, R. J., & O’Brien, N. M. (2013). In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of brewers’ spent grain protein rich isolate and its associated hydrolysates. Food Research International, 50(1), 205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.10.022
Mecozzi, M. (2005). Estimation of total carbohydrate amount in environmental samples by the phenol-sulphuric acid method assisted by multivariate calibration. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 79(1–2), 84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2005.04.005
Musa, A., Gasmalla, M. A. A., Ma, H., Sarpong, F., Wali, A., Awad, F. N., & Duan, Y. (2019). Effect of a multi-frequency counter-current S-type ultrasound pretreatment on the defatted corn germ protein: Enzymatic hydrolysis, ACE inhibitory activity and structural characterization. Food & Function, 10(9), 6020–6029. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo01531k
Nasiru, M. M., Boateng, E. F., Wang, Z. B., Yan, W. J., Zhuang, H., & Zhang, J. H. (2022). Ultrasound-assisted high-voltage cold atmospheric plasma treatment on the inactivation and structure of lysozyme: Effect of treatment voltage. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(3), 462–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02842-z
Ngamsuk, S., Hsu, J.-L., Huang, T.-C., & Suwannaporn, P. (2020). Ultrasonication of milky stage rice milk with bioactive peptides from rice bran: Its bioactivities and absorption. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(3), 462–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02371-2
Nielsen, P. M., Petersen, D., & Dambmann, C. (2001). Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. Journal of Food Science, 66(5), 642–646. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2001.tb04614.x
Sfakianakis, P., Topakas, E., & Tzia, C. (2015). Comparative study on high-intensity ultrasound and pressure milk homogenization: Effect on the kinetics of yogurt fermentation process. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(3), 548–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1412-9
Shi, D. F., Yin, C. M., Feng, X., Zhou, R. R., Fan, X. Z., Qiao, Y., ... & Cheng, W. (2020). Effect of ultrasound and cellulase pre-treatment on the water distribution, physical properties, and nutritional components of Lentinula edodes chips. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(4), 625–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02422-z
Stefanovic, A. B., Jovanovic, J. R., Dojcinovic, M. B., Levic, S. M., Nedovic, V. A., Bugarski, B. M., & Knezevic-Jugovic, Z. D. (2017). Effect of the controlled high-intensity ultrasound on improving functionality and structural changes of egg white proteins. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(7), 1224–1239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1884-5
Tang, S. Q., Du, Q. H., & Fu, Z. (2021). Ultrasonic treatment on physicochemical properties of water-soluble protein from Moringa oleifera seed. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 71, 105357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105357
Tran Hong, Q., & Benjakul, S. (2019). Production and characterisation of duck albumen hydrolysate using enzymatic process. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(11), 3015–3023. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14214
Vieira, E., Teixeira, J., & Ferreira, I. M. P. L. V. O. (2016). Valorization of brewers’ spent grain and spent yeast through protein hydrolysates with antioxidant properties. European Food Research and Technology, 242(11), 1975–1984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-016-2696-y
Xu, Y., Sun, M., Zong, X., Yang, H., & Zhao, H. (2019). Potential yeast growth and fermentation promoting activity of wheat gluten hydrolysates and soy protein hydrolysates during high-gravity fermentation. Industrial Crops and Products, 127, 179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.10.077
Yang, H., Zong, X., Cu, C., Mu, L., & Zhao, H. (2018). Peptide (Lys-Leu) and amino acids (Lys and Leu) supplementations improve physiological activity and fermentation performance of brewer’s yeast during very high-gravity (VHG) wort fermentation. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 65(4), 630–638. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1634
Yang, H., Zong, X., Xu, Y., Zeng, Y., & Zhao, H. (2019). Wheat gluten hydrolysates and their fractions improve multiple stress tolerance and ethanol fermentation performances of yeast during very high-gravity fermentation. Industrial Crops and Products, 128, 282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.026
Yang, X., Wang, L., Zhang, F., & Ma, H. (2020). Effects of multi-mode S-type ultrasound pretreatment on the preparation of ACE inhibitory peptide from rice protein. Food Chemistry, 331, 127216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127216
Ye, M., An, C., Liu, H., & Zheng, L. (2022). Synergistic effects and mechanisms of ultrasound-assisted pretreatments on the release of yak (Bos grunniens) bone collagen-derived osteogenic peptides in enzymatic hydrolysis. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(7), 1658–1675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02841-0
Yu, D., Sun, Y., Wang, W., O’Keefe, S. F., Neilson, A. P., Feng, H., ... & Huang, H. (2020). Recovery of protein hydrolysates from brewer’s spent grain using enzyme and ultrasonication. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 55(1), 357–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14314
Yu, J., Engeseth, N. J., & Feng, H. (2016). High intensity ultrasound as an abiotic elicitor-effects on antioxidant capacity and overall quality of Romaine lettuce. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(2), 262–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1616-7
Zhang, Y., Li, J., Li, S., Ma, H., & Zhang, H. (2018). Mechanism study of multimode ultrasound pretreatment on the enzymolysis of wheat gluten. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98(4), 1530–1538. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8624
Zhang, Y., Ma, H., Wang, B., Qu, W., Li, Y., He, R., & Wali, A. (2015). Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the enzymolysis and structural characterization of wheat gluten. Food Biophysics, 10(4), 385–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-015-9393-4
Zhang, Z. H., Poojary, M. M., Choudhary, A., Rai, D. K., Lund, M. N., & Tiwari, B. K. (2021). Ultrasound processing of coffee silver skin, brewer’s spent grain and potato peel wastes for phenolic compounds and amino acids: A comparative study. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore, 58(6), 2273–2282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04738-2
Zhao, H., Wan, C., Zhao, M., Lei, H., & Mo, F. (2014). Effects of soy protein hydrolysates on the growth and fermentation performances of brewer’s yeast. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 49(9), 2015–2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12503
Zheng, Z. J., Li, J. X., & Liu, Y. F. (2020). Effects of partial hydrolysis on the structural, functional and antioxidant properties of oat protein isolate. Food & Function, 11(4), 3144–3155. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo01783f
Zhou, Y., Yang, H., Zong, X., Cui, C., Mu, L., & Zhao, H. (2018). Effects of wheat gluten hydrolysates fractionated by different methods on the growth and fermentation performances of brewer’s yeast under high gravity fermentation. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(3), 812–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13657
Zhu, Y., Vanga, S. K., Wang, J., & Raghavan, V. (2018). Effects of ultrasonic and microwave processing on avidin assay and secondary structures of egg white protein. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(11), 1974–1984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2158-6
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the scholarships and financial support and School of Food Science and Engineering of South China University of Technology for supplying the equipment.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (201903010056), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31972062 and 32001675), the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2018A050506008), the 111 Project (B17018), and State Key Laboratory of Applied Microbiology Southern China (SKLAM010-2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qing Li: Investigation, conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. Moutong Chen: Visualization/data presentation, investigation. Teodora Emilia Coldea: Writing—review and editing. Huirong Yang: Data curation, software, validation. Haifeng Zhao: Project supervision and advice.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Chen, M., Coldea, T.E. et al. Ultrasound Pretreatment of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein Enhances the Yeast Growth- and Fermentation-Promoting Activity of Its Resultant Hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol 15, 2749–2761 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02912-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02912-2