Abstract
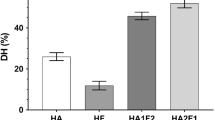
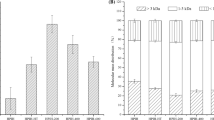
In our study, the effects of high-power (400 W) and low-frequency (20 kHz) ultrasound pretreatment applied for different durations (5, 10, and 20 min) and proteases (alcalase and flavourzyme) on the physicochemical, structural, and antioxidant properties of lupin protein hydrolysates (LPH) were examined. Changes in structural characteristics of the isolates and the resulting hydrolysates were measured using circular dichroism (CD), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), and UV–Vis spectroscopic techniques. Antioxidant activities of the LPH were assessed using 2,2-diphenyl-1picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) assays. Physicochemical properties including the yield of hydrolysate, relative crystallinity, and surface charge were also evaluated. FTIR analysis revealed that ultrasound pretreatment altered the secondary structure of the proteins as indicated by the movement of absorption peaks to higher wavelength. Also, CD studies showed a reduction in α-helix and increase in the β-sheet component of LPH samples after ultrasound pre-treatment except hydrolysates prepared using flavourzyme. The particle size, zeta potential, and relative crystallinity of the hydrolysates were significantly affected by ultrasonication time and enzyme type. Also, ultrasonication had a noticeable impact on the antioxidant activity as maximum DPPH activity was recorded after 10 min sonication in hydrolysates prepared using alcalase and flavourzyme. In addition, yield of hydrolysate increased significantly (p < 0.05) after ultrasonication pretreatment. Principal component analysis also produced a two-principal component model that explained 65.33% of total data variation. It may be suggested that application of ultrasound treatment to lupin protein could enhance the various characteristics including physicochemical and antioxidant activities of its hydrolysate.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Abadía-García, L., Castaño-Tostado, E., Ozimek, L., Romero-Gómez, S., Ozuna, C., & Amaya-Llano, S. L. (2016). Impact of ultrasound pretreatment on whey protein hydrolysis by vegetable proteases. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 37(PA), 84–90.
Adjonu, R., Doran, G., Torley, P., & Agboola, S. (2013). Screening of whey protein isolate hydrolysates for their dual functionality: Influence of heat pre-treatment and enzyme specificity. Food Chemistry, 136(3–4), 1435–1443.
Adler-Nissen, J. (1979). Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 27(6), 1256–1262.
Aluko, R. (2018). Food protein-derived peptides: Production, isolation, and purification. Proteins in food processing (pp. 389–412). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100722-8.00016-4
AOAC. (2005). Official methods of analysis of the association of analytical chemists international. Gaithersburg: AOAC.
Bähr, M., Fechner, A., Kiehntopf, M., & Jahreis, G. (2015). Consuming a mixed diet enriched with lupin protein beneficially affects plasma lipids in hypercholesterolemic subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition, 34(1), 7–14.
Barth, A. (2007). Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta -Bioenergetics, 1767(9), 1073–1101.
Bendit, E. (1960). A quantitative x-ray diffraction study of the alpha-beta transformation in wool keratin. Textile Research Journal, 30(8), 547–555.
Benjakul, S., & Morrissey, M. T. (1997). Protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting solid wastes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45(9), 3423–3430.
Bi, X., Hemar, Y., Balaban, M. O., & Liao, X. (2015). The effect of ultrasound on particle size, color, viscosity and polyphenol oxidase activity of diluted avocado puree. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 27, 567–575.
Binsan, W., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., Roytrakul, S., Tanaka, M., & Kishimura, H. (2008). Antioxidative activity of Mungoong, an extract paste, from the cephalothorax of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Food Chemistry, 106(1), 185–193.
Carvajal-Larenas, F., Linnemann, A., Nout, M., Koziol, M., & Van Boekel, M. (2016). Lupinus mutabilis: Composition, uses, toxicology, and debittering. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 56(9), 1454–1487.
Chalamaiah, M., Hemalatha, R., & Jyothirmayi, T. (2012). Fish protein hydrolysates: Proximate composition, amino acid composition, antioxidant activities and applications: A review. Food Chemistry, 135(4), 3020–3038.
Dabbour, M., He, R., Mintah, B., Golly, M. K., & Ma, H. (2020). Ultrasound pretreatment of sunflower protein: Impact on enzymolysis, ACE-inhibition activity, and structure characterization. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 44(4), e14398.
Ding, Q., Zhang, T., Niu, S., Cao, F., Wu-Chen, R. A., Luo, L., & Ma, H. (2018). Impact of ultrasound pretreatment on hydrolysate and digestion products of grape seed protein. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 42, 704–713.
Drenth, J. (2007). Principles of protein X-ray crystallography. Springer.
Duranti, M., Consonni, A., Magni, C., Sessa, F., & Scarafoni, A. (2008). The major proteins of lupin seed: Characterisation and molecular properties for use as functional and nutraceutical ingredients. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 19(12), 624–633.
Flores-Jiménez, N. T., Ulloa, J. A., Silvas, J. E. U., Ramírez, J. C. R., Ulloa, P. R., Rosales, P. U. B., Carrillo, Y. S., & Leyva, R. G. (2019). Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the compositional, physicochemical, biochemical, functional and structural properties of canola (Brassica napus L.) protein isolate. Food Research International, 121, 947–956.
Gao, H., Ma, L., Li, T., Sun, D., Hou, J., Li, A., & Jiang, Z. (2019). Impact of ultrasonic power on the structure and emulsifying properties of whey protein isolate under various pH conditions. Process Biochemistry, 81, 113–122.
Girgih, A. T., He, R., Malomo, S., Offengenden, M., Wu, J., & Aluko, R. E. (2014). Structural and functional characterization of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein-derived antioxidant and antihypertensive peptides. Journal of Functional Foods, 6, 384–394.
Guo, X., Shang, W., Strappe, P., Zhou, Z., & Blanchard, C. (2018). Peptides derived from lupin proteins confer potent protection against oxidative stress. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98(14), 5225–5234.
Idowu, A. T., Benjakul, S., Sinthusamran, S., Sookchoo, P., & Kishimura, H. (2019). Protein hydrolysate from salmon frames: Production, characteristics and antioxidative activity. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 43(2), e12734.
Intarasirisawat, R., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., & Wu, J. (2012). Antioxidative and functional properties of protein hydrolysate from defatted skipjack (Katsuwonous pelamis) roe. Food Chemistry, 135(4), 3039–3048.
Jia, J., Ma, H., Zhao, W., Wang, Z., Tian, W., Luo, L., & He, R. (2010). The use of ultrasound for enzymatic preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptides from wheat germ protein. Food Chemistry, 119(1), 336–342.
Jin, J., Ma, H., Wang, K., Yagoub, A.E.-G.A., Owusu, J., Qu, W., He, R., Zhou, C., & Ye, X. (2015). Effects of multi-frequency power ultrasound on the enzymolysis and structural characteristics of corn gluten meal. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 24, 55–64.
Kadam, S. U., Tiwari, B. K., Álvarez, C., & O’Donnell, C. P. (2015). Ultrasound applications for the extraction, identification and delivery of food proteins and bioactive peptides. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 46(1), 60–67.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational Psychological Measurement, 20(1), 141–151.
Kaiser, H. F. (1970). A second generation little jiffy. Psychometrika, 35(4), 401–415.
Karamać, M., Kosińska-Cagnazzo, A., & Kulczyk, A. (2016). Use of different proteases to obtain flaxseed protein hydrolysates with antioxidant activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1027.
Kristinsson, H. G., & Rasco, B. A. (2000). Fish protein hydrolysates: Production, biochemical, and functional properties. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 40(1), 43–81.
Lee, S. Y., & Hur, S. J. (2017). Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chemistry, 228, 506–517.
Lees, J. G., Miles, A. J., Wien, F., & Wallace, B. A. (2006). A reference database for circular dichroism spectroscopy covering fold and secondary structure space. Bioinformatics, 22(16), 1955–1962.
Li, Y., Jiang, B., Zhang, T., Mu, W., & Liu, J. (2008). Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of chickpea protein hydrolysate (CPH). Food Chemistry, 106(2), 444–450.
Liu, F.-R., Wang, L., Wang, R., & Chen, Z.-X. (2013). Calcium-binding capacity of wheat germ protein hydrolysate and characterization of peptide–calcium complex. Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry, 61(31), 7537–7544.
Lobley, A., Whitmore, L., & Wallace, B. (2002). DICHROWEB: An interactive website for the analysis of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra. Bioinformatics, 18(1), 211–212.
Marambe, P., Shand, P., & Wanasundara, J. (2008). An in-vitro investigation of selected biological activities of hydrolysed flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) proteins. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 85(12), 1155–1164.
Morris, H. J., Almarales, A., Carrillo, O., & Bermúdez, R. C. (2008). Utilisation of Chlorellavulgaris cell biomass for the production of enzymatic protein hydrolysates. Bioresource Technology, 99(16), 7723–7729.
Noman, A., Ali, A. H., AL-Bukhaiti, W. Q., Mahdi, A. A., & Xia, W. (2020). Structural and physicochemical characteristics of lyophilized Chinese sturgeon protein hydrolysates prepared by using two different enzymes. Journal of Food Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15345
Noman, A., Xu, Y., AL-Bukhaiti, W. Q., Abed, S. M., Ali, A. H., Ramadhan, A. H., & Xia, W. (2018). Influence of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions on the degree of hydrolysis and functional properties of protein hydrolysate obtained from Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) by using papain enzyme. Process Biochemistry, 67, 19–28.
Ozuna, C., Paniagua-Martínez, I., Castaño-Tostado, E., Ozimek, L., & Amaya-Llano, S. L. (2015). Innovative applications of high-intensity ultrasound in the development of functional food ingredients: Production of protein hydrolysates and bioactive peptides. Food Research International, 77, 685–696.
Qingli, Y., Chushu, Z., Shaofang, L., Jie, B., Jie, S., & Lina, Y. (2012). Ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis to improve the antioxidant activities of peanut (Arachin conarachin) antioxidant hydrolysate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(7), 9051–9068.
Quan, T. H., & Benjakul, S. (2019). Production and characterisation of duck albumen hydrolysate using enzymatic process. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(11), 3015–3023.
Re, R., Pellegrini, N., Proteggente, A., Pannala, A., Yang, M., & Rice-Evans, C. (1999). Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 26(9–10), 1231–1237.
Roberts, P. R., Burney, J., Black, K. W., & Zaloga, G. P. (1999). Effect of chain length on absorption of biologically active peptides from the gastrointestinal tract. Digestion, 60(4), 332–337.
Sirtori, C. R., Triolo, M., Bosisio, R., Bondioli, A., Calabresi, L., De Vergori, V., Gomaraschi, M., Mombelli, G., Pazzucconi, F., & Zacherl, C. (2012). Hypocholesterolaemic effects of lupin protein and pea protein/fibre combinations in moderately hypercholesterolaemic individuals. British Journal of Nutrition, 107(8), 1176–1183.
Song, X., Zhou, C., Fu, F., Chen, Z., & Wu, Q. (2013). Effect of high-pressure homogenization on particle size and film properties of soy protein isolate. Industrial Crops Products, 43, 538–544.
Sujak, A., Kotlarz, A., & Strobel, W. (2006). Compositional and nutritional evaluation of several lupin seeds. Food Chemistry, 98(4), 711–719.
Teh, S.-S., Bekhit, A.E.-D.A., Carne, A., & Birch, J. (2016). Antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysates produced by the proteases AFP, HT, Pro-G, actinidin and zingibain. Food Chemistry, 203, 199–206.
Uddin, R., Saha, M. R., Subhan, N., Hossain, H., Jahan, I. A., Akter, R., & Alam, A. (2014). HPLC-analysis of polyphenolic compounds in Gardenia jasminoides and determination of antioxidant activity by using free radical scavenging assays. Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 4(3), 273.
Udenigwe, C. C., & Aluko, R. E. (2012). Food protein-derived bioactive peptides: Production, processing, and potential health benefits. Journal of Food Science, 77(1), R11–R24.
Uluko, H., Zhang, S., Liu, L., Chen, J., Sun, Y., Su, Y., Li, H., Cui, W., & Lv, J. (2013). Effects of microwave and ultrasound pretreatments on enzymolysis of milk protein concentrate with different enzymes. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 48(11), 2250–2257.
Wali, A., Ma, H., Shahnawaz, M., Hayat, K., Xiaong, J., & Jing, L. (2017). Impact of power ultrasound on antihypertensive activity, functional properties, and thermal stability of rapeseed protein hydrolysates. Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4373859
Wang, L., Ding, Y., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Wang, R., Luo, X., Li, Y., Li, J., & Chen, Z. (2018). Isolation of a novel calcium-binding peptide from wheat germ protein hydrolysates and the prediction for its mechanism of combination. Food Chemistry, 239, 416–426.
Wang, S., Li, F., Zhang, P., Jin, S., Tao, X., Tang, X., Ye, J., Nabi, M., & Wang, H. (2017). Ultrasound assisted alkaline pretreatment to enhance enzymatic saccharification of grass clipping. Energy Conversion and Management, 149, 409–415.
White, C. L., & Staines, V. E. (2007). A review of the nutritional value of lupins for dairy cows. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 58(3), 185–202.
Xue, F., Wu, Z., Tong, J., Zheng, J., & Li, C. (2017). Effect of combination of high-intensity ultrasound treatment and dextran glycosylation on structural and interfacial properties of buckwheat protein isolates. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 81(10), 1891–1898.
Yang, X., Li, Y., Li, S., Oladejo, A. O., Ruan, S., Wang, Y., Huang, S., & Ma, H. (2017). Effects of ultrasound pretreatment with different frequencies and working modes on the enzymolysis and the structure characterization of rice protein. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 38, 19–28.
Zhao, F., Liu, X., Ding, X., Dong, H., & Wang, W. (2019). Effects of high-intensity ultrasound pretreatment on structure, properties, and enzymolysis of soy protein isolate. Molecules, 24(20), 3637.
Zhao, J., Xiong, Y. L., & McNear, D. H. (2013). Changes in structural characteristics of antioxidative soy protein hydrolysates resulting from scavenging of hydroxyl radicals. Journal of Food Science, 78(2), C152–C159.
Zheng, Z., Li, J., & Liu, Y. (2020). Effects of partial hydrolysis on the structural, functional and antioxidant properties of oat protein isolate. Food & Function, 11(4), 3144–3155.
Zhou, B., Zhang, M., Fang, Z.-X., & Liu, Y. (2015). Effects of ultrasound and microwave pretreatments on the ultrafiltration desalination of salted duck egg white protein. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 96, 306–313.
Zhou, C., Ma, H., Ding, Q., Lin, L., Yu, X., Luo, L., Dai, C., & Yagoub, A.E.-G.A. (2013). Ultrasonic pretreatment of corn gluten meal proteins and neutrase: Effect on protein conformation and preparation of ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory peptides. Food Bioproducts Processing, 91(4), 665–671.
Zhu, K.-X., Su, C.-Y., Guo, X.-N., Peng, W., & Zhou, H.-M. (2011). Influence of ultrasound during wheat gluten hydrolysis on the antioxidant activities of the resulting hydrolysate. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 46(5), 1053.
Acknowledgements
The first author acknowledges the support from Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT University) for his PhD program. We also like to acknowledge RMIT Microscopy and Microanalysis Facility (RMMF) for allowing access to their microscopic equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FGJ: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, data curation, original draft preparation; FA: supervision, editing; GH: supervision, editing; TT: supervision, conceptualization, editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fadimu, G.J., Gill, H., Farahnaky, A. et al. Investigating the Impact of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Antioxidant Properties of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol 14, 2004–2019 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02700-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02700-4