Abstract
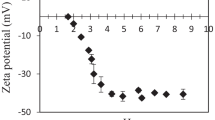
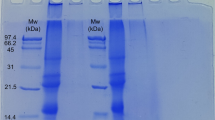
In this study, we evaluated the emulsifying properties of the hydrocolloids extracted from ora-pro-nóbis (Pereskia aculeata Miller) (HOPN) in soy oil emulsions (20% w/w) in water after different processing conditions. These properties were evaluated in terms of index of creaming, activity and emulsifying stability, electrical conductivity, zeta potential, rheology, particle size distribution, and optical microscopy. A two-level factorial was used to evaluate the effects of changes in pH (4–7), sucrose concentration (0–15% w/w), and NaCl concentration (0–1% w/w) and different processing conditions. This study has important implications for the application of HOPN in the food industry, since it was found that the HOPN were efficient in forming emulsions with desirable characteristics under all conditions and that the presence of sucrose favored the characteristics of these emulsions. However, the presence of NaCl and acidic pH negatively influenced these characteristics leading to the conclusion that, under these conditions, the HOPN should be used in synergy with a stabilizing agent.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolmaleki, K., Mohammadifar, M. A., Mohammadi, R., Fadavi, G., & Meybodi, N. M. (2016). The effect of pH and salt on the stability and physicochemical properties of oil-in-water emulsions prepared with gum tragacanth. Carbohydrate Polymers, 140, 342–348.
Amaral, T. N., Junqueira, L. A., Prado, M. E. T., Cirillo, M. A., Abreu, L. R., Costa, F. F., & Resende, J. V. (2018). Blends of Pereskia aculeata Miller mucilage, guar gum, and gum Arabic added to fermented milk beverages. Food Hydrocolloids, 79, 331–342.
AOAC - Association of Official Analytical Chemists (2006). Official methods of the association of the agricultural chemists. 18 Ed. Washington.
Bouyer, E., Mekhloufi, G., Rosilio, V., Grossiord, J. L., & Agnely, F. (2012). Proteins, polysaccharides, and their complexes used as stabilizers for emulsions: alternatives to synthetic surfactants in the pharmaceutical field? International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 436(1-2), 359–378.
Capitani, M. I., Nolasco, S. M., & Tomás, M. C. (2016). Stability of oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions with chia (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage. Food Hydrocolloids, 61, 537–546.
Chanamai, R., & McClements, D. J. (2002). Comparison of gum Arabic, modified starch, and whey protein isolate as emulsifiers: influence of pH, CaCl2 and temperature. Journal of Food Science, 67(1), 120–125.
Chen, L., Chen, J., Ren, J., & Zhao, M. (2011). Modifications of soy protein isolates using combined extrusion pre-treatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis for improved emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 887–897.
Conceição, M. C., Junqueira, L. A., Guedes Silva, K. C., Prado, M. E. T., & de Resende, J. V. (2014). Thermal and microstructural stability of a powdered gum derived from Pereskia aculeata Miller leaves. Food Hydrocolloids, 40, 104–114.
Demetriades, K., Coupland, J. N., & McClements, D. J. (1997). Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. Journal of Food Science, 62(2), 342–347.
Dickinson, E. (1989). Food colloids—an overview. Colloids and Surfaces, 42(1), 191–204.
Dubois, M. G., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28(3), 350–356.
Farshchi, A., Ettelaie, R., & Holmes, M. (2013). Influence of pH value and locust bean gum concentration on the stability of sodium caseinate-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 32(2), 402–411.
Garti, N. (1999). Hydrocolloids as emulsifying agents for oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 20(1-2), 327–355.
Hayati, I. N., Man, Y. B. C., Tan, C. P., & Aini, I. N. (2007). Stability and rheology of concentrated O/W emulsions based on soybean oil/palm kernel olein blends. Food Research International, 40(8), 1051–1061.
Huang, X., Kakuda, Y., & CUI, W. (2001). Hydrocolloids in emulsions: particle size distribution and interfacial activity. Food Hydrocolloids, 15(4-6), 533–542.
Huck-Iriart, C., Rincón-Cardona, J. A., & Herrera, M. L. (2014). Stability of whey protein concentrate/sunflower oil emulsions as affected by sucrose and xanthan gum. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(9), 2646–2656.
Jambrak, A. R., Mason, T. J., Lelas, V., Herceg, Z., & Herceg, I. L. (2008). Effect of ultrasound treatment on solubility and foaming properties of whey protein suspensions. Journal of Food Engineering, 86(2), 281–287.
Junqueira, L. A., Amaral, T. N., Oliveira, N. L., Prado, M. E. T., & Resende, J. V. (2018). Rheological behavior and stability of emulsions obtained from Pereskia aculeata Miller via different drying methods. International Journal of Food Properties, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2018.1437177.
Kaushik, P., Dowling, K., Adhikari, R., Barrow, B. J., & Adhikari, B. (2017). Effect of extraction temperature on composition, structure and functional properties of flaxseed gum. Food Chemistry, 215, 333–340.
Kim, H. J., Decker, E. A., & McClements, D. J. (2002). Role of postadsorption conformation changes of β-lactoglobulin on its ability to stabilize oil droplets against flocculation during heating at neutral pH. Langmuir, 18(20), 7577–7583.
Kim, H. J., Decker, E. A., & McClements, D. J. (2003). Influence of sucrose on droplet flocculation in hexadecane oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by β-lactoglobulin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(3), 766–772.
Koocheki, A., Kadkhodaee, R., Mortazavi, S. A., Shahidi, F., & Taherian, A. R. (2009). Influence of Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum on the stability and flow properties of O/W emulsion prepared by high intensity ultrasound. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(8), 2416–2424.
Kulmyrzaev, A. A., & Schubert, H. (2004). Influence of KC1 on the physicochemical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 18(1), 13–19.
Liang, Y., Patel, H., Matia-Merino, L., Ye, A., & Golding, M. (2013). Structure and stability of heat-treated concentrated dairy-protein-stabilised oil-in-water emulsions: a stability map characterisation approach. Food Hydrocolloids, 33(2), 297–308.
Lima Junior, F. A., Conceição, M. C., Vilela de Resende, J., Junqueira, L. A., Pereira, C. G., & Torres Prado, M. E. (2013). Response surface methodology for optimization of the mucilage extraction process from Pereskia aculeata Miller. Food Hydrocolloids, 33(1), 38–47.
Lucca, A. (2017). Extraction, characterization and application of the plant biopolymer (Pereskia aculeata Miller) as a coagulant/flocculating aid in the water treatment process. 2017. 71 f. Dissertation (Master in Technology of Chemical and Biochemical Processes), Federal Technological University of Paraná. http://repositorio.utfpr.edu.br/jspui/handle/1/2328. Accessed 21 Nov 2018.
Lucyszyn, N., Ono, L., Lubambo, A. F., Woehl, M. A., Sens, C. V., de Souza, C. F., & Sierakowski, M. R. (2016). Physicochemical and in vitro biocompatibility of films combining reconstituted bacterial cellulose with arabinogalactan and xyloglucan. Carbohydrate Polymers, 151, 889–898.
Malavolta, E., Vitti, G. C., & de Oliveira, S. A. (1989). Avaliação do estado nutricional das plantas: princípios e aplicações. Piracicaba: Potafos 201 p.
Martin, A. A., Freitas, R. A., Sassaki, G. L., Evangelista, P. H. L., & Sierakowski, M. R. (2017). Chemical structure and physical-chemical properties of mucilage from the leaves of Pereskia aculeata. Food Hydrocolloids, 70, 20–28.
Maskan, M., & Göǧüş, F. (2000). Effect of sugar on the rheological properties of sun flower oil in water emulsions. Journal of Food Engineering, 43(3), 173–177.
McClements, D. J. (2004). Protein-stabilized emulsions. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science, 9(5), 305–313.
McClements, D. J. (2005). Food emulsion: principle, practices, and techniques. 3. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
McClements, D. J. (2007). Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 47(7), 611–649.
Mikkonen, K. S., Xu, C., Berton-Carabin, C., & Schroën, K. (2016). Spruce galactoglucomannans in rapeseed oil-in-water emulsions: efficient stabilization performance and structural partitioning. Food Hydrocolloids, 52, 615–624.
Mirhosseini, H., Tan, C. P., Hamid, N. S. S., & Yusof, S. (2008). Optimization of the contents of Arabic gum, xanthan gum and orange oil affecting turbidity, average particle size, polydispersity index and density in orange beverage emulsion. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(7), 1212–1223.
Nakauma, M., Funami, T., Noda, S., Ishihara, S., al-Assaf, S., Nishinari, K., & Phillips, G. O. (2008). Comparison of sugar beet pectin, soybean soluble polysaccharide, and gum Arabic as food emulsifiers. 1. Effect of concentration, pH, and salts on the emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(7), 1254–1267.
Niu, F., Niu, D., Zhang, H., Chang, C., Gu, L., Su, Y., & Yang, Y. (2016). Ovalbumin/gum Arabic-stabilized emulsion: rheology, emulsion characteristics, and Raman spectroscopic study. Food Hydrocolloids, 52, 607–614.
Osano, J. P., Hosseini-Parvar, S. H., Matia-Merino, L., & Golding, M. (2014). Emulsifying properties of a novel polysaccharide extracted from basil seed (Ocimum bacilicum L.): effect of polysaccharide and protein content. Food Hydrocolloids, 37, 40–48.
Owens, C., Griffin, K., Khouryieh, H., & Williams, K. (2018). Creaming and oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein-xanthan-locust bean complexes: impact of pH. Food Chemistry, 239, 314–322.
Pearce, K. N., & Kinsella, J. E. (1978). Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 26(3), 716–723.
Sabolović, M. B., Brnčić, S. R., & Lelas, V. (2013). Emulsifying properties of tribomechanically treated whey proteins. Mljekarstvo, 63, 64–71.
Sierakowski, M. R., Gorin, P. A. J., Reicher, F., & Corrêa, J. B. C. (1990). Location of O-acetyl groups in the heteropolysaccharide of the cactus Pereskia aculeata. Carbohydrate Research, 201(2), 277–284.
Sui, X., Bi, S., Qi, B., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Li, Y., & Jiang, L. (2017). Impact of ultrasonic treatment on an emulsion system stabilized with soybean protein isolate and lecithin: its emulsifying property and emulsion stability. Food Hydrocolloids, 63, 727–734.
Sun, C., Gunasekaran, S., & Richards, M. P. (2007). Effect of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties of whey protein isolate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 21(4), 555–564.
Tadros, T. F. (1994). Fundamental principles of emulsion rheology and their applications. Colloids and Surfaces, 91, 39–55.
Thanasukarn, P., Pongsawatmanit, R., & McClements, D. J. (2004). Influence of emulsifier type on freeze-thaw stability of hydrogenated palm oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 18(6), 1033–1043.
Walstra, P. (2003). Physical chemistry of foods. New York: Marcel Decker.
Xu, Y., Wang, C., Fu, X., Huang, Q., & Zhang, B. (2018). Effect of pH and ionic strength on the emulsifying properties of two Octenylsuccinate starches in comparison with gum Arabic. Food Hydrocolloids, 76, 96–102.
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – Brazil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001. The authors wish to thank the financial support the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – Brazil (CNPq) (Grant numbers 478376/2013-8 and 308043/2015-4) and the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais – Brazil (FAPEMIG) (Grant numbers CAG - APQ-01308-12 and CAG - APQ-03851-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junqueira, L.A., Amaral, T.N., Félix, P.C. et al. Effects of Change in PH and Addition of Sucrose and NaCl on the Emulsifying Properties of Mucilage Obtained from Pereskia aculeata Miller. Food Bioprocess Technol 12, 486–498 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2223-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2223-1