Abstract
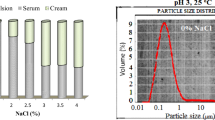
The effect of the addition of sucrose and xanthan gum, protein concentration, and processing method on the stability and destabilization mechanism type of emulsions formulated with two commercial whey protein concentrate powders was described and quantified following system changes with a Turbiscan TMA 2000, a light scattering equipment and a confocal laser scanning microscope. Two different processing methods that gave particle sizes with different orders of magnitude were compared: homogenization by ULTRA-TURRAX (UT) and by ultrasound (US). The addition of sucrose to the aqueous phase of emulsions significantly diminished volume-weighted mean diameter (D 4,3) and improved stability. When the aqueous phase contained xanthan gum, the main destabilization mechanism for UT emulsions changed from creaming to flocculation. For US emulsions, although some aggregation was detected by confocal laser scanning microscopy, it was not great enough to modify the backscattering average (BSav) in the middle zone of the tube (20–50 mm). At low protein concentrations, the profiles corresponded to destabilization of small aggregates. In those conditions, creaming was markedly enhanced as evident from creaming rate values. Independently of aqueous phase composition, US emulsions stabilized by protein concentrations higher than 5 wt% were stable, indicating that whey proteins were good emulsion stabilizers at pH close to 7. This study shows the relevance of protein type on stability and describes for the first time a behavior for whey proteins different from the one reported for caseins in literature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez Cerimedo, M. S., Huck Iriart, C., Candal, R. J., & Herrera, M. L. (2010). Stability of emulsions formulated with high concentrations of sodium caseinate and trehalose. Food Reseach International, 43(5), 1482–1493.
Bernard, C., Regnault, S., Gendreau, S., Charbonneau, S., & Relkin, P. (2011). Enhancement of emulsifying properties of whey proteins by controlling spray-drying parameters. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(4), 758–763.
Bordes, C., García, F., Frances, C., Biscans, B., & Snabre, P. (2001). The on-line optical investigation of concentrated dispersions in precipitation and grinding processes. Kona, 19, 94–108.
Box, E. P., Hunter, W. G., & Hunter, J. S. (1978). Statistics for experimenters. New York: Wiley.
Cerdeira, M., Palazolo, G. G., Candal, R. J., & Herrera, M. L. (2007). Factors affecting initial retention of a microencapsulated sunflower seed oil/milk fat fraction blend. Journal of American Oil Chemists’ Society, 84(6), 523–531.
Chandrapala, J., Zisu, B., Palmer, M., Kentish, S., & Ashokkumar, M. (2011). Effects of ultrasound on the thermal and structural characteristics of proteins in reconstituted whey protein concentrate. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 18(5), 951–957.
Chauvierre, C., Labarre, D., Couvreur, P., & Vauthier, C. (2004). A new approach for the characterization of insoluble amphiphilic copolymers based on their emulsifying properties. Colloid and Polymer Science, 282(10), 1097–1104.
Dickinson, E., & Golding, M. (1997). Rheology of sodium caseinate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 191(1), 166–176.
Huck Iriart, C., Álvarez Cerimedo, M. S., Candal, R. J., & Herrera, M. L. (2011). Structures and stability of lipid emulsions formulated with sodium caseinate. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 16(5), 412–420.
Huck Iriart, C., Pizones Ruiz-Henestrosa, V. M., Candal, R. J., & Herrera, M. L. (2013). Effect of aqueous phase composition on stability of sodium caseinate/sunflower oil emulsions. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(9), 2406–2418.
Kaltsa, O., Michon, C., Yanniotis, S., & Mandala, I. (2013). Ultrasonic energy input influence οn the production of sub-micron o/w emulsions containing whey protein and common stabilizers. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20(3), 881–891.
Kobori, T., Matsumoto, A., & Sugiyama, S. (2009). pH-dependent interaction between sodium caseinate and xanthan gum. Carbohydrate Polymers, 75(4), 719–723.
Lizarraga, M. S., Pan, L. G., Añon, M. C., & Santiago, L. G. (2008). Stability of concentrated emulsions measured by optical and rheological methods. Effect of processing conditions-I. Whey protein concentrate. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(5), 868–878.
Mengual, O., Meunier, G., Cayré, I., Puech, K., & Snabre, P. (1999). Turbiscan MA 2000: Multiple light scattering measurements for concentrated emulsion and suspension instability analysis. Talanta, 50(2), 445–456.
Palazolo, G. G., Sorgentini, D. A., & Wagner, J. R. (2005). Coalescence and flocculation in o/w emulsions of native and denatured whey soy proteins in comparison with soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocolloids, 19(3), 595–604.
Pan, L. G., Tomás, M. C., & Añón, M. C. (2002). Effect of sunflower lecithins on the stability of water in oil (W/O) and oil in water (O/W) emulsions. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 5(2), 135–143.
Panaras, G., Moatsou, G., Yanniotis, S., & Mandala, I. (2011). The influence of functional properties of different whey protein concentrates on the rheological and emulsification capacity of blends with xanthan gum. Carbohydrate Polymers, 86(2), 433–440.
Perez, A. A., Carrara, C. R., Sanchez, C. C., Santiago, L. G., & Patino, J. M. R. (2009). Interfacial dynamic properties of whey protein concentrate/polysaccharide mixtures at neutral pH. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(5), 1253–1262.
Relkin, P., & Sourdet, S. (2005). Factors affecting fat droplet aggregation in whipped frozen protein-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 19(3), 503–511.
Thanasukarn, P., Pongsawatmanit, R., & McClements, D. J. (2006). Utilization of layer-by-layer interfacial deposition technique to improve freeze-thaw stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Food Research International, 39(6), 721–729.
Tippetts, M., & Martini, S. (2009). Effect of oil content and processing conditions on the thermal behavior and physicochemical stability of oil-in-water emulsions. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 44(1), 206–215.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Council of Argentina (CONICET) through Project PIP 11220080101504, by the National Agency for the Promotion of Science and Technology (ANPCyT) through Project PICT 0060, and by the University of Buenos Aires through Project 20020100100467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huck-Iriart, C., Rincón-Cardona, J.A. & Herrera, M.L. Stability of Whey Protein Concentrate/Sunflower Oil Emulsions as Affected by Sucrose and Xanthan Gum. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 2646–2656 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1290-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1290-1