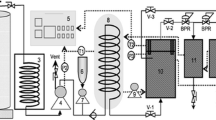
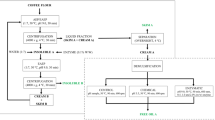
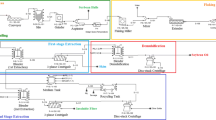
Abstract
Hexane extraction is the most common technique used to remove oil from full fat soy materials in the production of both soy oil and defatted soy. The popularity of hexane is based on its high oil extraction efficiency and its availability. The solvent, however, has some considerable economic, environmental, and safety drawbacks. A review of alternative soybean defatting techniques is carried out through the description of four main technological approaches including: (1) alternative organic (carbon-based) solvent extraction, (2) aqueous extraction, (3) supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction, and (4) enzymatically aided extraction. Through detailed discussions of experimental results, the advantages and disadvantages of each approach are presented. The optimum oil yield for the various extraction techniques discussed ranges from as high as 26.0% for mixed organic solvent extraction of full fat soy flour to as low as ∼7% for some enzymatic treatments of full fat soy brokens extracted by mechanical pressing. An environmentally friendly, safe, and cost-efficient alternative technique has yet to be developed to replace hexane extraction. Current aqueous and SC-CO2 techniques show promise but require further research and development to ensure their practicality in terms of industrial processing.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AE:
-
Aqueous extraction
- CFFSB:
-
Cracked full fat soybean
- CPG:
-
Compressed petroleum gas
- EFFSF:
-
Extruded full fat soy flakes
- EtOH:
-
Ethanol
- FAO:
-
Food and Agriculture Organisation (United Nations)
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration (United States)
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acid
- FFEC:
-
Expanded full fat soy collets
- FFF:
-
Full fat soy flour
- FFSB:
-
Full fat soy brokens
- FFSF:
-
Full fat soy flakes
- Hex:
-
Hexane
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- Incub. temp:
-
Incubation temperature
- Incub. time:
-
Incubation time
- IPA:
-
Isopropyl alcohol
- MIP:
-
Membrane isolation process
- n/a:
-
Not available
- Press temp:
-
Pressing temperature
- SC-CO2 :
-
Supercritical carbon dioxide
- SFFSF:
-
Steam-conditioned full fat soy flakes
- SPI:
-
Soy protein isolate
- Temp:
-
Temperature
- w/v:
-
Weight by volume
- w/w:
-
Weight by weight
References
Anderson, J. W. (2008). Beneficial effects of soy protein consumption for renal function. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 17(S1), 324–328.
Anonymous. (1998). Friolex process from Westfalia—A new concept in oil recovery. Oils and Fats International, 14(4), 32–34.
Bargale, P. C., Sosulski, K., & Sosulski, F. W. (2000). Enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean for solvent and mechanical oil extraction. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 23(4), 321–327.
Beckel, A. C., Belter, A., & Smith, A. K. (1948). Solvent effects on the products of soybean oil extraction. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 25(1), 7–9.
Bhatnagar, S., & Johari, B. N. (1987). Microbial enzymes in the processing of oilseeds. Current Science, 56(15), 775–776.
Boye, J. I., Aksay, S., Roufik, S., Ribérea, S., Mondor, M., Farnworth, E., et al. (2010). Comparison of the functional properties of pea, chickpea and lentil protein concentrates processed using ultrafiltration and isoelectric precipitation techniques. Food Research International, 43(2), 537–546.
Cater, C. M., Rhee, K. C., Hagenmaier, R. D., & Mattil, K. F. (1974). Aqueous extraction—An alternative oilseed milling process. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 51(4), 137–141.
Chabrand, R. M., Kim, H. J., Zhang, C., Glatz, C. E., & Jung, S. (2008). Destabilization of the emulsion formed during aqueous extraction of soybean oil. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 85(4), 383–390.
de Moura, J. M. L. N., & Johnson, L. A. (2009). Two stage countercurrent enzyme assisted aqueous extraction processing of oil and protein form soybeans. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 86(3), 283–289.
de Moura, J. M. L. N., Campbell, K., Mahfuz, A., Jung, S., Glatz, C. E., & Johnson, L. (2008). Enzyme assisted aqueous extraction of oil and protein from soybeans and cream de-emulsification. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 85(10), 985–995.
Dobarganes Nodar, M., Molero Gomez, A., & Martinez de la Ossa, E. (2002). Characterisation and process development of supercritical fluid extraction of soybean oil. Science and Technology International, 8(6), 337–342.
Dominguez, H., Nunez, M. J., & Lema, J. M. (1993). Oil extractability from enzymatically treated soybean and sunflower: Range of operational variables. Food Chemistry, 46(3), 277–284.
Dominguez, H., Nunez, M. J., & Lema, J. M. (1994). Enzymatic pretreatment to enhance oil extraction from fruits and oilseeds: A review. Food Chemistry, 49(3), 271–286.
Dominguez, H., Nunez, M. J., & Lema, J. M. (1995). Enzyme-assisted hexane extraction of soya bean oil. Food Chemistry, 54(2), 223–231.
Eldridge, A. C., Friedrich, J. P., Warner, K., & Kwolek, W. F. (1986). Preparation and evaluation of supercritical carbon dioxide defatted soybean flakes. Journal of Food Science, 51(3), 584–587.
Fredrikson, M., Biot, P., Alminger, M. L., Carlsson, N. G., & Sandberg, A. S. (2001). Production process for high quality pea protein isolate with low content of oligosaccharides and phytate. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(3), 1208–1212.
Friedman, M., & Brandon, D. L. (2001). Nutritional and health benefits of soy proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(3), 1069–1086.
Friedrich, J. P., & Eldridge, A. C. (1985). Production of defatted soybean products by supercritical fluid extraction. US Patent No 4493854.
Friedrich, J. P., & List, G. R. (1982). Characterization of soybean oil extracted by supercritical carbon dioxide and hexane. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 30(1), 192–193.
Friedrich, J. P., & Pryde, E. H. (1984). Supercritical CO2 extraction of lipid-bearing materials and characterization of the products. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 61(2), 223–228.
Friedrich, J. P., List, G. R., & Heakin, A. J. (1982). Petroleum-free extraction of oil from soybeans with supercritical CO2. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 59(7), 288–292.
Fullbrook, P. D. (1983). The use of enzymes in the processing of oilseeds. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 60(2), 476–478.
Fullbrook, P. D. (1984). Extraction of vegetable oils. UK Patent No 2127425.
Gandhi, A. P., Joshi, K. C., Jha, K., Parihar, V. S., Srivastav, D. C., Raghunadh, P., et al. (2003). Studies on alternative solvents for the extraction of oil-I soybean. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 38(3), 369–375.
Goudedranche, H., Fauquant, J., & Maubois, J. L. (2000). Fractionation of globular milk fat by membrane microfiltration. Lait, 80(1), 93–98.
Hruschka, S., & Frische, R. (1998). A new oil extraction process: Friolex. Oleagineux Corps Gras Lipides, 5(5), 356–360.
Johnson, L. A., & Lusas, E. W. (1983). Comparison of alternative solvents for oils extraction. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 60(2), 181A–194A.
Jung, S., Lamsal, B. P., Stepien, V., Johnson, L. A., & Murphy, P. A. (2006). Functionality of soy protein produced by enzyme-assisted extraction. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 83(1), 71–78.
Kashyap, M. C., Agrawal, Y. C., Sarkar, B. C., & Singh, B. P. N. (1997). Response surface analysis of enzyme aided extraction of soybean. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 34(5), 386–390.
Kashyap, M. C., Agrawal, Y. C., Ghosh, P. K., Jayas, D. S., Sarker, B. C., & Singh, B. P. N. (2006). Enzymatic hydrolysis pretreatment to solvent extraction of soybrokens for enhanced oil availability and extractability. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 29(6), 664–674.
Kashyap, M. C., Agrawal, Y. C., Ghosh, P. K., Jayas, D. S., Sarker, B. C., & Singh, B. P. N. (2007). Oil extraction rates of enzymatically hydrolyzed soybeans. Journal of Food Engineering, 81(3), 611–617.
Kim, I. H., & Yoon, S. H. (1991). Extraction of soybean oil using supercritical carbon dioxide and its characteristics. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 23(6), 677–682.
Kinsella, J. E. (1979). Functional properties of soy proteins. The Journal of American Oil Chemists’ Society, 56(3), 242–256.
Lamsal, B. P., & Johnson, L. A. (2007). Separating oil from aqueous extraction fractions of soybean. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 84(8), 785–792.
Lamsal, B. P., Murphy, P. A., & Johnson, L. A. (2006). Flaking and extrusion as mechanical treatments for enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of oil from soybeans. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 83(11), 973–979.
Lancas, F. M., Queiroz, M. E. C., & da Silva, I. C. E. (1994). Seed oil extraction with supercritical carbon dioxide modified with pentane. Chromatographia, 39(11/12), 687–692.
Lawhon, J. T., Manak, L. J., Rhee, K. C., Rhee, K. S., & Lusas, E. W. (1981a). Combining aqueous extraction and membrane isolation techniques to recover protein and oil from soybeans. Journal of Food Science, 46(3), 912–916. 919.
Lawhon, J. T., Rhee, K. C., & Lusas, E. W. (1981b). Soya protein ingredients prepared by new processes—Aqueous processing and industrial membrane isolation. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 58(3), 377–384.
Li, H., Pordesimo, L., & Weiss, J. (2004). High intensity ultrasound-assisted extraction of oil from soybeans. Food Research International, 37(7), 731–738.
Liu, K. (1997). Soybeans: Chemistry, technology and utilization (pp. 25–95). New York: Chapman and Hall.
Lusas, E. W. (1997). Final report: IPA as an extraction solvent. INFORM, 8(3), 290–292. 294-306.
Lusas, E. W., & Gregory, S. R. (1998). New solvents and extractors. In S. S. Koseoglu, K. C. Rhee, & R. F. Wilson (Eds.), Proceedings of the World Conference on oilseed and edible oils processing, volume 1, emerging technologies, current practices, quality control, technology transfer and environmental issues (pp. 204–219). Champaign: AOCS.
Lusas, E. W., Lawhon, J. T., & Rhee, K. C. (1982). Producing edible oil and protein from oilseeds by aqueous processing. Oil Mill Gazetteer, 86(10), 28–30. 32–34.
Lusas, E. W., Watkins, L. R., & Rhee, K. C. (1990). Separation of fats and oils by solvent extraction: Non-traditional methods. In D. R. Erickson (Ed.), Edible fats and oils processing: Basic principles and modern practices (pp. 56–78). Champaign: AOCS.
Lusas, E. W., Watkins, L. R., & Koseoglu, S. S. (1991). Isopropyl alcohol to be tested as solvent. INFORM, 2(11), 970–976.
Lusas, E. W., Koseoglu, S. S., Rhee, K. C., Watkins, L. R., Hernandez, E., Doty, S. C., et al. (1995). Progress in IPA extraction. Oil Mill Gazetteer, 101(4), 24–27. 29–34.
Marek, E., Schalinatus, E., Weigelt, E., Mieth, G., Kerns, G., & Kude, J. (1990). On the application of enzymes in the production of vegetable oil. Progress in Biotechnology, 6, 471–474.
Mattil, K. F., Rhee, K. C., & Cater, C. M. (1979). Soybean protein extract. US Patent No 4151310.
Messina, M. J. (1997). Soyfoods: Their role in disease prevention and treatment. In K. Liu (Ed.), Soybeans: Chemistry, technology and utilization (pp. 442–477). New York: Chapman and Hall.
Mondor, M., Aksay, S., Drolet, H., Roufik, S., Farnworth, E., & Boye, J. I. (2009). Influence of processing on composition and antinutritional factors of chick pea protein concentrates produced by isoelectric precipitation and ultrafiltration. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 10(3), 342–347.
Morin, P., Pouliot, Y., & Jiménez-Flores, R. (2006). A comparative study of the fractionation of regular buttermilk and whey buttermilk by microfiltration. Journal of Food Engineering, 77(3), 521–528.
Mustakas, G. C. (1980). Recovery of oil from soybeans. In D. R. Erickson, E. H. Pryde, O. L. Brekke, T. L. Mounts, & R. A. Falb (Eds.), Handbook of soy oil processing and utilization (pp. 49–65). Champaign: American Soybean Association and AOCS.
Nelson, A. I., Wijeratne, W. B., Yeh, S. W., Wei, T. M., & Wei, L. S. (1987). Dry extrusion as an aid to mechanical expelling of oil from soybeans. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 64(9), 1341–1347.
Nieh, C. D., & Snyder, H. E. (1991). Solvent extraction of oil from soybean flour. II. Pilot plant and two-solvent extractions. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 68(4), 250–253.
NIOSH/OSHA/DOE Health Guidelines (1996). Occupational safety and health guideline for n-hexane. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), United States Department of Labour, Washington DC, USA. Available at: http://www.osha.gov/SLTC/healthguidelines/n-hexane/recognition.html). Accessed 12 July 2009.
Pereira, C. M., & Meireles, A. A. (2010). Supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds: Fundamentals, applications and economic perspectives. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3(3), 340–372. doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0263-2.
Peter, S. (1996). Supercritical fractionation of lipids. In J. W. King & G. R. List (Eds.), Supercritical fluid technology in oil and lipid chemistry (pp. 74–75). Champaign: AOCS Press.
Reverchon, E., Poletto, M., Osseo, L. S., & Somma, M. (2000). Hexane elimination from soybean oil by continuous packed tower processing with supercritical CO2. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 77(1), 9–14.
Rombaut, R., Dejonckheere, V., & Dewettinck, K. (2007). Filtration of milk fat globule membrane fragments from acid buttermilk cheese whey. Journal of Dairy Science, 90(4), 1662–1673.
Rosenthal, A., Pyle, D. L., & Niranjan, K. (1996). Aqueous and enzymatic processes for edible oil extraction. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 19(6), 402–420.
Rosenthal, A., Pyle, D. L., & Niranjan, K. (1998). Simultaneous aqueous extraction of oil and protein from soybean: Mechanisms for process design. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 76(4), 224–230.
Rosenthal, A., Pyle, D. L., Niranjan, K., Gilmour, S., & Trinca, L. (2001). Combined effect of operational variables and enzyme activity on aqueous enzymatic extraction of oil and protein from soybean. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 28(6), 499–509.
Sachdeva, S., & Buchheim, W. (1997). Recovery of phospholipids from buttermilk using membrane processing. Kieler Milchwritschaftliche Forschungsberichte, 49(1), 47–68.
Serrato, A. G. (1981). Extraction of oil from soybeans. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 58(3), 157–159.
Seth, S., Agrawal, Y. C., Ghosh, P. K., Jayas, D. S., & Singh, B. P. N. (2007). Oil extraction rates of soya bean using isopropyl alcohol as solvent. Biosystems Engineering, 97(2), 209–217.
Seth, S., Agrawal, Y. C., Ghosh, P. K., & Jayas, D. S. (2010). Effect of moisture content on the quality of soybean oil and meal extracted by isopropyl alcohol and hexane. Food Bioprocess Technology, 3(1), 121–127.
Shankar, D., Agrawal, Y. C., Sarkar, B. C., & Singh, B. P. N. (1997). Enzymatic hydrolysis in conjunction with conventional pretreatments to soybean for enhanced oil availability and recovery. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 74(12), 1543–1547.
Singh, P., Kumar, R., Sabapathy, S. N., & Bawa, A. S. (2008). Functional and edible uses of soy protein products. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 7(1), 14–28.
Smith, D. D., Agrawal, Y. C., Sarkar, B. C., & Singh, B. P. N. (1993). Enzymatic hydrolysis pretreatment for mechanical expelling of soybeans. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 70(9), 885–890.
Snyder, J. M., Friedrich, J. P., & Christianson, D. D. (1984). Effect of moisture and particle size on the extractability of oils from seeds with supercritical CO2. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 61(12), 1851–1856.
Stahl, E., Schutz, E., & Mangold, H. K. (1980). Extraction of seed oils with liquid and supercritical carbon dioxide. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 28(6), 1153–1157.
Sugarman, N. (1956). Process for simultaneously extracting oil and protein from oleaginous materials. US Patent No 2762820.
Ueno, H., Tanaka, M., Machmudah, S., Sasaki, M., & Gotom, M. (2008). Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of valuable compounds from Citrus junos seed. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1(4), 357–363.
USDA-FAS. (2009). Oilseeds: World markets and trade. Circular Series FOP 1-09. Available at: http://www.fas.usda.gov/oilseeds/circular/2009/January/Oilseedsfull0109.pdf. Accessed 26 July 2009.
Wagner, Z., & Wichterle, I. (1987). High-pressure, vapour–liquid equilibrium in systems containing carbon dioxide, 1-hexene and hexane. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 33(1–2), 109–123.
Wiese, K. L., & Snyder, H. E. (1987). Analysis of the oil extraction process in soybeans: A new continuous procedure. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 64(3), 402–406.
Williams, M. A. (1995). Extrusion preparation for oil extraction. INFORM, 6(3), 289–293.
Woerfel, J. (1995). Extraction. In D. R. Erikson (Ed.), Practical handbook of soybean processing and utilization (pp. 65–92). Champaign: AOCS.
Xuede, W., & Liu, K. (2005). Extraction with compressed petroleum gases for speciality oil and meal products. INFORM, 16(4), 264–362.
Yoon, S. H., Kim, I. H., Kim, S. H., & Kwon, T. W. (1991). Effects of enzyme treatments and ultrasonification on extraction yields of lipids and protein from soybean in aqueous process. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 23(6), 673–676.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russin, T.A., Boye, J.I., Arcand, Y. et al. Alternative Techniques for Defatting Soy: A Practical Review. Food Bioprocess Technol 4, 200–223 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0367-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0367-8