Abstract
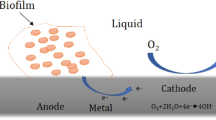
In this study, the prevention of the attachment of test microorganism Enterobacter sakazakii onto stainless steel (SS 316) surfaces by radio frequency (RF) plasma polymerization (PlzP) technique using several hydrophilic monomers as precursors was reported. Different plasma conditions (RF discharge power of 20–80 W with exposure time of 10 min) were employed during the modifications. PlzP-modified surfaces were characterized in detail by static contact angle measurements in order to state the change of surface hydrophilicity. The surface topology of unmodified and PlzP [ethylenediamine (EDA)]-modified SS 316 plates was characterized by atomic force microscopy. The attachment of the model microorganism on the SS 316 surface modified by plasma using EDA at 45 W and 10 min was reduced by 99.74% in comparison to the unmodified control surface. For equilibrium adsorption behavior, Freundlich and Langmuir models were attempted and model parameters for Freundlich (K F and 1/n) and for Langmuir (a and b) were obtained. The values of the K F and 1/n were 5.6 and 0.58 and 0.9 and 0.39, respectively; the values of a and b were 25 × 104 and 1.82 × 10−8 and 0.3 × 104 and 7.96 × 10-8, for bare and PlzP-EDA-modified SS 316 surfaces, respectively. As a result, PlzP technique was found to be an alternative simple method to decrease the microbial attachment and create bacterial anti-fouling surfaces.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyth, N., Yudovin-Farberb, I., Bahira, R., Domb, A. J., & Weiss, E. I. (2006). Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans. Biomaterials, 27, 3995–4002.
Beyth, N., Houri-Haddad, Y., Baraness-Hadar, L., Yudovin-Farber, I., Domb, A. J., & Weiss, E. I. (2008). Surface antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of incorporated polyethylenimine nanoparticles. Biomaterials, 29, 4157–4163.
Biederman, H., Boyaci, I. H., Bilkova, P., Slavinska, D., Mutlu, S., Zemek, J., et al. (2001). Characterization of glow-discharge-treated cellulose acetate membrane surfaces for single-layer enzyme electrode studies. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 81(6), 1341–1352.
Boyd, R. D., Verran, J., Jones, M. V., & Bhakoo, M. (2002). Use of atomic force microscope to determine the effect of substratum surface topography on bacterial adhesion. Langmuir, 18, 2343–2346.
Chua, P. K., Chena, J. Y., Wanga, L. P., & Huangb, N. (2002). Plasma-surface modification of biomaterials. Materials Science and Engineering, 36, 143–206.
Costerton, J. W., & Lappin Scott, H. M. (1989). Behaviour of bacteria in biofilms. American Society for Microbiology News, 55, 650–654.
Costerton, J. W., Cheng, K.-J., Geesey, G. G., Ladd, T. L., Nickel, J. C., Dasgupta, M., et al. (1987). Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annual Reviews of Microbiology, 41, 435–464.
Criado, M. T., Suarez, B., & Ferreiros, C. M. (1994). The importance of bacterial adhesion in the dairy industry. Food Technology, 48, 123–126.
Doğan, M., Alkan, M., & Onganer, Y. (2000). Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto perlite. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 120, 229–248.
Flint, S. H., Bremer, P. J., & Brooks, J. D. (1997). Biofilms in dairy manufacturing plant- description, current concerns and methods of control. Biofouling, 11, 81–97.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 57, 385–470.
Güleç, H. A., Sarıoğlu, K., & Mutlu, M. (2006). Modification of food contacting surfaces by plasma polymerisation technique: part I: determination of hydrophilicity, hydrophobicity and surface free energy by contact angle method. Journal of Food Engineering, 75, 187–195.
Janocha, A., Hegemann, D., Oehr, C., Brunner, H., Rupp, F., & Geis-Gerstorfer, J. (2001). Adsorption of protein on plasma-polysiloxane layers of different surface energies. Surface and Coatings Technology, 142–144, 1051–1055.
Kaminska, A., Kaczmarek, H., & Kowalonek, J. (2002). The influence of side groups and polarity of polymers on the kind and effectiveness of their surface modification by air plasma action. European Polymer Journal, 38, 1915–1919.
Kim, H., Ryu, J.-H., & Beuchat, L. R. (2006). Attachment of and biofilm formation by Enterobacter sakazakii on stainless steel and enteral feeding tubes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 5846–5856.
Kratochvil, D., & Volesky, B. (1998). Advances in the biosorption of heavy metals-reviews. Trends in Biotechnology, 16, 291–300.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1368.
Liston, E. M., Martinu, W., & Wertheimer, W. R. (1993). Plasma surface modification of polymers for improved adhesion-a critical review. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 7, 1091–1127.
Mafu, A. A., Roy, D., Goulet, J., & Hagny, P. (1990). Attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel, glass, polypropylene and rubber surfaces after short contact times. Journal of Food Protection, 53, 742–746.
Mutlu, M., Mutlu, S., Rosenberg, M. F., Kane, J., Jones, M. N., & Vadgama, P. (1991). Matrix surface modification by plasma polymerization for enzyme immobilization. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 1(3), 447–450.
Mutlu, M., Mutlu, S., Alp, B., Boyacı, I. H., & Piskin, E. (1997). Preparation of a single layer enzyme electrode by plasma polymerization technique. In R. D’Agostino, P. Favia & F. Fracassi (Eds.), Plasma processing of polymers (pp. 477–485). The Netherlands: Kluwer.
Mutlu, S., Saber, R., Kocum, C., & Piskin, E. (1999). An immunosensor: immobilization of anti-HBs antibody on glow-discharge treated piezoelectric quartz crystal for HBs-AG detection. Analytical Letters, 32(2), 317–334.
Mutlu, S., Çökeliler, D., & Mutlu, M. (2007). Modification of food contacting surfaces by plasma polymerisation technique. Part II: static and dynamic adsorption behavior of a model protein “bovine serum albumin” on stainless steel surface. Journal of Food Engineering, 78, 494–499.
Mutlu, S., Cokeliler, D., Shard, A., Goktas, H., Ozansoy, B., & Mutlu, M. (2008). Preparation and characterization of ethylenediamine and cysteamine plasma polymerized films on piezoelectric quartz crystal surfaces for a biosensor. Thin Solid Films, 516(6), 1249–1255.
Niemira, B. A. (2008). Irradiation sensitivity of planktonic and biofilm-associated listeria monocytogenes and L. innocua as influenced by temperature of biofilm formation. Food and Bioprocess Technology, doi:10.1007/s11947-008-0079-5.
Norde, W., Arai, T., & Shirahama, H. (1991). Protein adsorption in model systems. Biofouling, 4, 37–51.
Saber, R., Mutlu, S., & Piskin, E. (2002). Glow-discharge treated piezoelectric quartz crystals as immunosensors for HSA detection. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 17(9), 727–734.
Roudman, A. R., & Di Giano, F. A. (2000). Surface energy of experimental and commercial nanofiltration membranes: effects of wetting and natural organic matter fouling. Journal of Membrane Science, 175, 61–73.
Ryu, J.-H., & Beuchat, L. R. (2005). Biofilm formation by Escherichia coli O157:H7 on stainless steel: effect of exopolysaccharide and curli production on ıts resistance to chlorine. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 247–254.
Weber, W. J., Jr. (1972). Physicochemical processes for water quality control (p. 208). New York: Wiley.
Acknowledgment
This research has been partly supported by The Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey TUBITAK 2209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şen, Y., Bağcı, U., Güleç, H.A. et al. Modification of Food-Contacting Surfaces by Plasma Polymerization Technique: Reducing the Biofouling of Microorganisms on Stainless Steel Surface. Food Bioprocess Technol 5, 166–175 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-009-0248-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-009-0248-1