Opinion statement
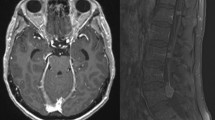
Leptomeningeal metastasis is becoming an increasingly important late complication of cancer as survival from systemic disease increases, and due to the fact that many novel cancer drugs fail to achieve therapeutic concentrations in the central nervous system. It occurs when neoplastic cells enter cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pathways, causing diffuse infiltration of the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord. Definitive diagnosis is established by the demonstration of malignant cells in the CSF. However, in certain circumstances the presence of leptomeningeal enhancement on brain or spinal MRI may be sufficient to make the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment may delay neurologic progression and can lead to prolonged survival and improvement of neurologic function in certain patients. The prognosis depends on the underlying malignancy but is often poor, with a median survival of 4 months, and most treatment interventions are palliative. Nevertheless, some patients respond to treatment, and some survive beyond 1 or 2 years after diagnosis. Areas of radiographic bulky disease or symptomatic tumor should receive radiotherapy. Intrathecal chemotherapy is most effective in patients with lymphoma, leukemia, or breast cancer and without evidence of bulky disease on neuroimaging. Intrathecal chemotherapy requires normal CSF flow, and the most commonly used agents are methotrexate, cytarabine, and thiotepa. In lieu of intrathecal therapy, systemic chemotherapy may occasionally be indicated in select patients in part based on its ability to penetrate into bulky disease. When hydrocephalus occurs, ventriculoperitoneal shunting frequently leads to rapid clinical improvement. There is hope that progress in diagnostic modalities and the development of more effective intrathecal antineoplastic drugs may decrease neurologic morbidity and improve quality of life and survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Posner JB, Chernik NL: Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol 1978, 19:579–592.
Olson ME, Chernik NL, Posner JB: Infiltration of the leptomeninges by systemic cancer. A clinical and pathologic study. Arch Neurol 1974, 30:122–137.
Wasserstrom WR, Glass JP, Posner JB: Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors: experience with 90 patients. Cancer 1982, 49:759–772.
Herrlinger U, Forschler H, Kuker W, et al.: Leptomeningeal metastasis: survival and prognostic factors in 155 patients. J Neurol Sci 2004, 223:167–178.
Engelhard HH, Corsten LA: Leptomeningeal metastasis of primary central nervous system (CNS) neoplasms. Cancer Treat Res 2005, 125:71–85.
Straathof CS, de Bruin HG, Dippel DW, Vecht CJ: The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurol 1999, 246:810–814.
Collie DA, Brush JP, Lammie GA, et al.: Imaging features of leptomeningeal metastases. Clin Radiol 1999, 54:765–771.
Freilich RJ, Krol G, DeAngelis LM: Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann Neurol 1995, 38:51–57.
Cheng TM, O’Neill BP, Scheithauer BW, Piepgras DG: Chronic meningitis: the role of meningeal or cortical biopsy. Neurosurgery 1994, 34:590–595; discussion 596.
Chamberlain MC: Neoplastic meningitis: a guide to diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Neurol 2000, 13:641–648.
DeAngelis LM: Current diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurooncol 1998, 38:245–252.
Glantz MJ, Hall WA, Cole BF, et al.: Diagnosis, management, and survival of patients with leptomeningeal cancer based on cerebrospinal fluid-flow status. Cancer 1995, 75:2919–2931.
Hitchins RN, Bell DR, Woods RL, Levi JA: A prospective randomized trial of single-agent versus combination chemotherapy in meningeal carcinomatosis. J Clin Oncol 1987, 5:1655–1662.
Glantz MJ, Kim L, Choy H, Akerley W: Concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy in patients with brain tumors. Oncology (Williston Park) 1999, 13(Suppl 5):78–82.
Glantz MJ, LaFollette S, Jaeckle KA, et al.: Randomized trial of a slow-release versus a standard formulation of cytarabine for the intrathecal treatment of lymphomatous meningitis. J Clin Oncol 1999, 17:3110–3116.
Siegal T: Leptomeningeal metastases: rationale for systemic chemotherapy or what is the role of intra-CSF-chemotherapy? J Neurooncol 1998, 38:151–157.
Boogerd W, Hart AA, van der Sande JJ, Engelsman E: Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer. Prognostic factors and influence of treatment. Cancer 1991, 67:1685–1695.
Fizazi K, Asselain B, Vincent-Salomon A, et al.: Meningeal carcinomatosis in patients with breast carcinoma. Clinical features, prognostic factors, and results of a high-dose intrathecal methotrexate regimen. Cancer 1996, 77:1315–1323.
Lassman AB, Abrey LE, Shah GD, et al.: Systemic high-dose intravenous methotrexate for central nervous system metastases. J Neurooncol 2006, 78:255–260.
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Recht L, et al.: High-dose intravenous methotrexate for patients with nonleukemic leptomeningeal cancer: is intrathecal chemotherapy necessary? J Clin Oncol 1998, 16:1561–1567.
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Forsyth PA, et al.: Practice parameter: anticonvulsant prophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2000, 54:1886–1893.
Grossman SA, Finkelstein DM, Ruckdeschel JC, et al.: Randomized prospective comparison of intraventricular methotrexate and thiotepa in patients with previously untreated neoplastic meningitis. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 1993, 11:561–569.
Gajjar A, Fouladi M, Walter AW, et al.: Comparison of lumbar and shunt cerebrospinal fluid specimens for cytologic detection of leptomeningeal disease in pediatric patients with brain tumors. J Clin Oncol 1999, 17:1825–1828.
Chamberlain MC, Corey-Bloom J: Leptomeningeal metastases: 111indium-DTPA CSF flow studies. Neurology 1991, 41:1765–1769.
Mason WP, Yeh SD, DeAngelis LM: 111Indium-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid cerebrospinal fluid flow studies predict distribution of intrathecally administered chemotherapy and outcome in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology 1998, 50:438–444.
Chamberlain MC, Kormanik PA: Prognostic significance of 111indium-DTPA CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology 1996, 46:1674–1677.
Chamberlain MC: Radioisotope CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. J Neurooncol 1998, 38:135–140.
Mehta M, Bradley K: Radiation therapy for leptomeningeal cancer. Cancer Treat Res 2005, 125:147–158.
Hanssens PE, Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC: Principles of radiotherapy of neoplastic meningosis. J Neurooncol 1998, 38:145–150.
Addeo R, Caraglia M, Faiola V, et al.: Concomitant treatment of brain metastasis with whole brain radiotherapy [WBRT] and temozolomide [TMZ] is active and improves quality of life. BMC Cancer 2007, 7:18.
Verger E, Gil M, Yaya R, et al.: Temozolomide and concomitant whole brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: a phase II randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005, 61:185–191.
Omuro AM, Lallana EC, Bilsky MH, DeAngelis LM: Ventriculoperitoneal shunt in patients with leptomeningeal metastasis. Neurology 2005, 64:1625–1627.
Sandberg DI, Bilsky MH, Souweidane MM, et al.: Ommaya reservoirs for the treatment of leptomeningeal metastases. Neurosurgery 2000, 47:49–54; discussion 54–55.
Blaney SM, Balis FM, Berg S, et al.: Intrathecal mafosfamide: a preclinical pharmacology and phase I trial. J Clin Oncol 2005, 23:1555–1563.
Gammon DC, Bhatt MS, Tran L, et al.: Intrathecal topotecan in adult patients with neoplastic meningitis. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2006, 63:2083–2086.
Berg SL, Balis FM, Zimm S, et al.: Phase I/II trial and pharmacokinetics of intrathecal diaziquone in refractory meningeal malignancies. J Clin Oncol 1992, 10:143–148.
Gururangan S, Petros WP, Poussaint TY, et al.: Phase I trial of intrathecal spartaject busulfan in children with neoplastic meningitis: a Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study (PBTC-004). Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12:1540–1546.
Rubenstein JL, Fridlyand J, Abrey L, et al.: Phase I study of intraventricular administration of rituximab in patients with recurrent CNS and intraocular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2007, 25:1350–1356.
Stemmler HJ, Schmitt M, Harbeck N, et al.: Application of intrathecal trastuzumab (Herceptin trade mark) for treatment of meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Oncol Rep 2006, 15:1373–1377.
Laufman LR, Forsthoefel KF: Use of intrathecal trastuzumab in a patient with carcinomatous meningitis. Clin Breast Cancer 2001, 2:235.
Platini C, Long J, Walter S: Meningeal carcinomatosis from breast cancer treated with intrathecal trastuzumab. Lancet Oncol 2006, 7:778–780.
Kramer K, Cheung NK, Humm JL, et al.: Targeted radioimmunotherapy for leptomeningeal cancer using (131)I-3F8. Med Pediatr Oncol 2000, 35:716–718.
Herrlinger U, Weller M, Schabet M: New aspects of immunotherapy of leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurooncol 1998, 38:233–239.
Drappatz J, Batchelor T: Leptomeningeal and peripheral nerve metastases. Continuum 2005, 11:47–68.
Berg SL, Chamberlain MC: Current treatment of leptomeningeal metastases: systemic chemotherapy, intrathecal chemotherapy and symptom management. Cancer Treat Res 2005, 125:121–146.
Balm M, Hammack J: Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Presenting features and prognostic factors. Arch Neurol 1996, 53:626–632.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drappatz, J., Batchelor, T.T. Leptomeningeal neoplasms. Curr Treat Options Neurol 9, 283–293 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-007-0014-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-007-0014-5