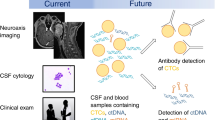
Abstract
Leptomeningeal metastases (LM) constitute an involvement of cancer which is associated with marked morbidity and mortality. The contemporary diagnostic and therapeutic management of LM from solid tumors is reviewed. Therapeutic modalities including systemic therapies, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-directed therapies, and radiation therapy are discussed. This is to provide context for how the field of LM management may evolve in the near term. The future directions currently undergoing investigation for diagnostic, response assessment, and therapeutic purposes are highlighted. This is done within the context of the pathophysiology of the disease. Specifically the role of CSF circulating tumor cells and cell free circulating tumor DNA in diagnosis and response assement are reviewed. Novel therapeutic approaches across a range of modalities are discussed. Numerous ongoing studies which have the potential to alter the management of LM are referenced.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thakkar JP, Kumthekar P, Dixit KS, Stupp R, Lukas RV (2020) Leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. J Neurol Sci 411:116706
Clarke JL, Perez HR, Jacks LM, Panageas KS, Deangelis LM (2010) Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology 74(18):1449–1454
Hyun JW, Jeong IH, Joung A, Cho HJ, Kim SH, Kim HJ (2016) Leptomeningeal metastasis: clinical experience of 519 cases. Eur J Cancer 56:107–114
Glass JP, Melamed M, Chernik NL, Posner JB (1979) Malignant cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): the meaning of a positive CSF cytology. Neurology 29(10):1369–1375
Lamba N, Wen PY, Aizer AA (2021) Epidemiology of brain metastases and leptomeningeal disease. Neuro Oncol 23(9):1447–1456
Le Ruhn E, Weller M, Brandsma D et al (2017) EANO-ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. Ann Oncol 28(Suppl_4):iv84–iv99
Chamberlain M, Junck L, Brandsma D et al (2017) Leptomeningeal metastases: a RANO proposal for response criteria. Neuro Oncol 19(4):484–492
Nevel KS, DiStefano N, Lin X et al (2020) A retrospective, quantitative assessment of disease burden in patients with leptomeningeal metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol 22(5):675–683
Le Ruhn E, Devos P, Boulanger T et al (2019) The RANO leptomeningeal metastasis group proposal to assess response to treatment: lack of feasibility and clinical utility and a revised proposal. Neuro Oncol 21(5):648–658
Chamberlian MS, Kormanik PA, Glantz MJ (2001) A comparison between ventricular and lumbar cerebrospinal fluid cytology in adult patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Neuro Oncol 3(1):42–45
Weller M, Le Ruhn E (2020) 40. An update on the development of a new tool to assess response in leptomeningeal metastasis. Neuro Oncol Adv 2(Suppl2):ii7
Boire A, Brandsma D, Brastianos PK et al (2019) Liquid biopsy in central nervous system metastases: a RANO review and proposals for clinical applications. Neuro Oncol 21(5):571–584
Van Bussel MTJ, Pluim D, Milojkovic Kerklaan B et al (2020) Circulating epithelial cell analysis in CSF in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology 94(5):e521–e528
Angus L, Deger T, Jager A, et al (2021) Detection of aneuploidy in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with breast cancer can improve diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastases. Clin Cancer Res. [EPub ahead of print]
Sperduto PW, Mesko S, Li J et al (2020) Survival in patients with brain metastases: summary report of the updated diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment and definition of the eligibility quotient. J Clin Oncol 38(32):3773–3784
Murakami Y, Ichikawa M, Bakhit M et al (2018) Palliative shunt surgery for patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 168:175–178
Lee SH, Kong DS, Seol HJ, Nam DH, Lee JI (2011) Ventriculoperitoneal shunt for hydrocephalus caused by central nervous system metastasis. J Neurooncol 104(2):545–551
Jung TY, Chung WK, Oh IJ (2014) The prognostic significance of surgically treated hydrocephalus in leptomeningeal metastases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 119:80–83
Yang JCH, Kim SW, Kim DW et al (2020) Osimertinib in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer and leptomeningeal metastases: the BLOOM study. J Clin Oncol 38(6):538–547
Park S, Lee MH, Seong M et al (2020) A phase II, multicenter, two cohort study of 160 mg osimertinib in EGFR T790M-positive non-small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease who progressed on prior EGFR TKI therapy. Ann Oncol 31(10):1397–1404
Morikawa A, de Stanchina E, Pentsova E et al (2019) Phase I study of intermittent high-dose lapatinib alternating with capecitabine for HER2-positive breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases. Clin Cancer Res 25(13):3784–3792
Lassman AB, Abrey LE, Shah GD et al (2006) Systemic high-dose intravenous methotrexate for central nervous system metastases. J Neurooncol 78(3):255–260
Mrugala MM, Kim B, Sharma A et al (2019) Phase II study of systemic high-dose methotrexate and intrathecal liposomal cytarabine for treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 19(5):311–316
Kumthekar P, Grimm SA, Avram MJ et al (2013) Pharmacokinetics and efficacy of pemetrexed in patients with brain or leptomeningeal metastases. J Neurooncol 112(2):247–255
Burger MC, Wagner M, Franz K et al (2018) Ventriculoperitoneal shunts equipped with on-off valves for intraventricular therapies in patients with communicating hydrocephalus due to leptomeningeal metastases. J Clin Med 7(8):216
Groves MD, Glantz MJ, Chamberlain MC et al (2008) A multicenter phase II trial of intrathecal topotecan in patients with meningeal malignancies. Neuro Oncol 10(2):208–215
Blaney SM, Heideman R, Berg S et al (2003) Phase I clinical trial of intrathecal topotecan in patients with neoplastic meningitis. J Clin Oncol 21(1):143–147
Chamberlain MC, Tsao-Wei DD, Groshen S et al (2006) Phase II trial of intracerebrospinal fluid etoposide in the treatment of neoplastic meningitis. Cancer 106(9):2021–2027
Fan C, Zhao Q, Li L et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of intrathecal pemetrexed combined with dexamethasone for treating tyrosine kinase inhibitor-failed leptoeningeal metastases from EGFR-mutant NSCLC, a prospective, open-label, single-arm phase 1/2 clinical trial (Unique identifier: ChiCTR1800016615). J Thorac Oncol 16(8):1359–1368
Glantz MJ, Jaeckle KA, Chamberlain MC et al (1999) A randomized controlled trial comparing intrathecal sustained-release cytarabine (DepoCyt) to intrathecal methotrexate in patients with neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 5(11):3394–3402
Perissinotti AJ, Reeves DJ (2010) Role of intrathecal rituximab and trastuzumab in the management of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Pharmacother 44(10):1633–1640
Figura NB, Long W, Yu M et al (2018) Intrathecal trastuzumab in the management of HER2+ breast leptomeningeal disease: a single institution experience. Breast Cancer Res Treat 169(2):391–396
Bonneau C, Paintaud G, Tredan O et al (2018) Phase I feasibility study for intrathecal administration of trastuzumab in patients with HER2 positive breast carcinomatous meningitis. Eur J Cancer 95:75–84
Park WY, Kim HJ, Kim K et al (2016) Intrathecal trastuzumab treatment in patients with breast cancer and leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Res Treat 48(2):843–847
Mir O, Ropert S, Alexandre J, Lemare F, Goldwasser F (2008) High-dose intrathecal trastuzumab for leptomeningeal metastases secondary to HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer. Ann Oncol 19(11):1978–1980
Law V, Baldwin M, Ramamoorthi G, et al (2021) A murine Ommya xenograft model to study direct-targeted therapy of leptomeningeal disease. J Vis Exp. (167)
Shapiro WR, Young DF, Posner JB (1975) Methotrexate: distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med 293(4):161–166
de Oca M, Delgado M, Cacho Diaz B, Santos Zambrano J et al (2018) The comparative treatment of intraventricular chemotherapy vs lumbar puncture in patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Front Oncol 8:509
El Shafie RA, Bohm K, Weber D et al (2018) Palliative radiotherapy for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis-analysis of outcome, prognostic factors, and symptom response. Front Oncol 8:641
Lai R, Abrey LE, Rosenblum MK, DeAngelis LM (2004) Treatment-induced leukoencephalopathy in primary CNS lymphoma: a clinical and autopsy study. Neurology 62(3):451–456
Yang TJ, Wijetunga NA, Yamada J et al (2020) Clinical trial of proton craniospinal irradiation for leptomeningeal metastases. Neuro Oncol 23(1):134–143
Ron DA, Labandeira CM, Manrique MCA, et al. Dramatic response of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis to nivolumab in PD-L1 highly expressive non-small cell lung cancer: a case report. Front Oncol. 20
Paget S (1889) The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet 133(3421):571–573
Remsik J, Chi Y, Tong X, et al (2020) Leptomeningeal metastatic cells adopt two phenotypic states. Cancer Rep. e1236
Raizer J, Pentsova E, Omuro A, et al (2014) Phase 1 tria of intrathecal trastuzumab in HER2 positive leptomeningeal metastases. AT-47. Neuro Onco. 16(Supp 5):v19
Reijneveld JC, Brandsma D, Boogerd W et al (2005) CSF levels of angiogenesis-related proteins in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology 65(7):1120–1122
Smalley I, Law V, Wyatt C et al (2020) Proteomic analysis of CSF from patients with leptomeningeal melanoma metastases identifies signatures associated with disease progression and therapeutic resistance. Clin Cancer Res 26(9):2163–2175
Chi Y, Remsik J, Kiseliovas V et al (2020) Cancer cells deploy lipocalin-2 to collect limiting iron in leptomeningeal metastasis. Science 369(6501):276–282
Boire A, Zou Y, Shieh J, Macalinao DG, Pentsova E, Massague J (2017) Complement component 3 adapts the cerebrospinal fluid for leptomeningeal metastasis. Cell 168(6):1101-1113.e13
Malani R, Fleischer M, Kumthekar P et al (2020) Cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells as a quantifiable measurement of leptomeningeal metastases in patients with HER2 positive cancer. J Neurooncol 148(3):599–606
Jiang BY, Li YS, Guo WB et al (2017) Detection of driver and resistance mutations in leptomeningeal metastases of NSCLC by next –generation sequencing of cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res 23(18):5480–5488
Lin X, Fleisher M, Rosenblum M et al (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells: a novel tool to diagnose leptomeningeal metastases from epithelial tumors. Neuro Oncol 19(9):1248–1254
Wijetunga NA, Boire AA, Yamada Y et al (2021) Cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells as a predictive biomarker for proton craniospinal irradiation for leptomeningeal metastases. J Clin Oncol 39(15_suppl):2011
Bale TA, Yang SR, Solomon JP et al (2021) Clinical experience of cerebrospinal fluid –based liquid biopsy demonstrates superiority of cell-free DNA over cell-pellet genomic DNA for molecular profiling. J Mol Diagn S1525–1578(21):00065–00069
Zheng MM, Li YS, Tu HY et al (2021) Genotyping of cerebrospinal fluid associated with osimertinib response and resistance for leptomeningeal metastases in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 16(2):250–258
Kumthekar P, Tang SC, Brenner AJ et al (2020) ANG1005, a brain penetrating peptide-drug conjugate, shows activity in patients with breast cancer with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis and brain metastases. Clin Cancer Res 26(12):2789–2799
Tawbi HA, Forsyth PA, Algazi A et al (2018) Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in melanoma metastatic to the brain. N Engl J Med 379(8):722–730
Gadgeel SM, Lukas RV, Goldschmidt J et al (2019) Atezolizumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and history of asymptomatic, treated brain metastases: Exploratory analyses of the phase III OAK study. Lung Cancer 128:105–112
Goldeberg SB, Schalper KA, Gettinger SN et al (2020) Pembrolizumab for management of patients with NSCLC and brain metastases: long-term results and biomarker analysisfrom a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 21(5):655–663
Brastianos PK, Lee EQ, Cohen JV et al (2020) Single-arm, open-label phase 2 trial of pembrolizumab in patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Nat Med 26(8):1280–1284
Dudnik E, Yust-Katz S, Nechushtan H et al (2016) Intracranial response to nivolumab in NSCLC patients with untreated or progressing CNS metastases. Lung Cancer 98:114–117
Bonomi L, Bettini AC, Arnoldi E, et al (2020) Nivolumab efficacy in leptomeningeal metastasis of renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Tumori. 106(6):NP76-NP78
Lum LG, Thakur A, Al-Kadhimi Z et al (2015) Targted T-cell therapy in stage IV breast cancer: a phase I clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res 21(10):2305–2314
Murthy RK, Loi S, Okines A et al (2020) Tucatinib, trastuzumab, and capecitabine for HER1-positive metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 382:597–609
Kanojia D, Panek WK, Cordero A et al (2020) BET inhibition increases βIII-tubulin expression and sensitizes metastatic breast cancer in the brain to vinorelbine. Sci Transl Med. 12(558):eaax2879
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste Y (2018) Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:113–125
Teh HS, Fadilah SA, Leong CF (2007) Transverse myelopathy following intrathecal administration of chemotherapy. Singapore Med J 48(2):e46–e49
Tariq H, Gilbert A, Sharkey FE (2018) Intrathecal Methotrexate-Induced Necrotizing Myelopathy: A Case Report and Review of Histologic Features. Clin Med Insights Pathol 11:1179555718809071
Chamberlain MC (2012) Neurotoxicity of intra-CSF liposomal cytarabine (DepoCyt) administered for the treatment of leptomeningeal metastases: a retrospective case series. J Neurooncol 109(1):143–148
Byrnes DM, Vargas F, Dermarkarian C et al (2019) Complications of intrathecal chemotherapy in adults: single-institution experience in 109 consecutive patients. J Oncol 2019:4047617
Olmos-Jimenez R, Diaz-Carrasco MS, Cabanas-Perianes V, Valderrey-Pulido M, Espuny-Miro A (2017) Evaluation of standardized triple intrathecal therapy toxicity in oncohematological adult patients. Farm Hosp 41(5):611–617
Kim JY, Kim ST, Nam DH, Lee JI, Park K, Kong DS (2011) Leukoencephalopathy and disseminated necrotizing leukoencephalopathy following intrathecal methotrexate chemotherapy and radiation therapy for central nerve system lymphoma or leukemia. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 50(4):304–310
Boogerd W, vd Sande JJ, Moffie D, (1988) Acute fever and delayed leukoencephalopathy following low dose intraventricular methotrexate. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51(10):1277–1283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukas, R.V., Thakkar, J.P., Cristofanilli, M. et al. Leptomeningeal metastases: the future is now. J Neurooncol 156, 443–452 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03924-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03924-2