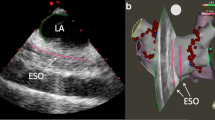
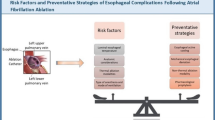
Abstract
Purpose of review
Atrial fibrillation ablation is an increasingly common procedure adapted by electrophysiologists across the world. Any procedure naturally comes with inherent risks of complications. The goal of this review is to elaborate latest techniques and strategies to avoid complications of ablation.
Recent findings
There is increased focus on new tools for avoiding esophageal injury as well as minimizing phrenic nerve injury in addition to utilization of newer ablation technologies to address safer and effective ablation.
Summary
A combination of improved patient selection and better treatment protocols combined with methods for early detection of complications will significantly reduce the incidence of complications. Newer innovative technologies like esophageal temperature monitoring, mechanical deviation, and integration of ablation parameters are helping to avoid or minimize collateral damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 October 2020
In the recently published review “Techniques to Avoid Complications of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation,” the following author name was inadvertently misspelled as Amit Shreshta.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
•• Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, Kim Y-H, Saad EB, Aguinaga L, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(10):e275–444 A consensus statement from expert faculty with a detailed chart regarding complications associated with catheter and surgical ablation and techniques to prevent and manage these complications.
Abdur Rehman K, Wazni OM, Barakat AF, Saliba WI, Shah S, Tarakji KG, et al. Life-threatening complications of atrial fibrillation ablation. JACC: Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;5:284–91.
Deshmukh A, Patel Nileshkumar J, Pant S, Shah N, Chothani A, Mehta K, et al. In-hospital complications associated with catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the United States between 2000 and 2010. Circulation. 2013;128(19):2104–12.
Gupta A, Perera T, Ganesan A, Sullivan T, Lau DH, Roberts-Thomson KC, et al. Complications of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(6):1082–8.
Hoyt H, Bhonsale A, Chilukuri K, Alhumaid F, Needleman M, Edwards D, et al. Complications arising from catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: temporal trends and predictors. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(12):1869–74.
Lahewala S, Tripathi B, Arora S, Patel N, Kumar V, Patel N, et al. Abstract 21338: Temporal trends of in-hospital complications associated with catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in United States. Circulation. 2017;136(suppl_1):A21338–A.
Muthalaly RG, John RM, Schaeffer B, Tanigawa S, Nakamura T, Kapur S, et al. Temporal trends in safety and complication rates of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29(6):854–60.
• Tripathi B, Arora S, Kumar V, Abdelrahman M, Lahewala S, Dave M, et al. Temporal trends of in-hospital complications associated with catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the United States: an update from Nationwide Inpatient Sample database (2011-2014). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29(5):715–24 A recent study describing the decreasing incidence of complications associated with catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation from a large inpatient database.
Cappato R, Calkins H, Fau-Chen S-A, Chen S, Fau-Davies W, Davies W, et al. Prevalence and causes of fatal outcome in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(19):1798–803.
Ruzieh M, Foy AJ, Aboujamous NM, Moroi MK, Naccarelli GV, Ghahramani M, et al. Meta-analysis of atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with systolic heart failure. Cardiovasc Ther. 2019;2019:8181657 Published 2019 Jan 6.
Deyell MW, Leather RA, Macle L, Forman J, Khairy P, Zhang R, et al. Efficacy and safety of same-day discharge for atrial fibrillation ablation. JACC: Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(6):609–19.
Bartoletti S, Mann M, Gupta A, Khan AM, Sahni A, El-Kadri M, et al. Same-day discharge in selected patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;42(11):1448–55.
Giudici MC, Paul DL, Sloane C, Press G, Petersen A, Garrison A, et al. Abstract P65: Outpatient atrial fibrillation ablation on therapeutic warfarin-safety, efficacy, and cost savings. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2011, 4(suppl_1):AP65–AP.
Bode K, Ueberham L, Gawlik S, Hindricks G, Bollmann A. Inguinal vascular complications after ablation of atrial fibrillation: an economic impact assessment. Europace. 2019;21(1):91–8.
Errahmouni A, Bun S-S, Latcu DG, Saoudi N. Ultrasound-guided venous puncture in electrophysiological procedures: a safe method, rapidly learned. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2014;37(8):1023–8.
Tanaka-Esposito CC, Chung MK, Abraham JM, Cantillon DJ, Abi-Saleh B, Tchou PJ. Real-time ultrasound guidance reduces total and major vascular complications in patients undergoing pulmonary vein antral isolation on therapeutic warfarin. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2013;37(2):163–8.
Rodríguez Muñoz D, Franco Díez E, Moreno J, Lumia G, Carbonell San Román A, Segura De La Cal T, et al. Wireless ultrasound guidance for femoral venous cannulation in electrophysiology: impact on safety, efficacy, and procedural delay. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2015;38(9):1058–65.
Kupó P, Pap R, Sághy L, Tényi D, Bálint A, Debreceni D, et al. Ultrasound guidance for femoral venous access in electrophysiology procedures—systematic review and meta-analysis. J Interv Cardiac Electrophysiol. 2019. A meta-analysis which showed ultrasound-guided vascular access resulted in lower vascular complications when compared with conventional access in patients undergoing electrophysiology procedures.
Mohanty S, Trivedi C, Gianni C, Burkhardt J, Sanchez J, Horton R, et al. P5755 Real-time ultrasound guidance for venous access reduces vascular complications in women aged 75 years or older undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation under uninterrupted anticoagulation. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(suppl_1).
Ströker E, de Asmundis C, Kupics K, Takarada K, Mugnai G, De Cocker J, et al. Value of ultrasound for access guidance and detection of subclinical vascular complications in the setting of atrial fibrillation cryoballoon ablation. EP Europace. 2018;21(3):434–9.
Yamagata K, Wichterle D, Roubicek T, Jarkovsky P, Sato Y, Kogure T, et al. Ultrasound-guided versus conventional femoral venipuncture for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a multicentre randomized efficacy and safety trial (ULTRA-FAST trial). Europace. 2018;20(7):1107–14.
Wiles BM, Child N, Roberts PR. How to achieve ultrasound-guided femoral venous access: the new standard of care in the electrophysiology laboratory. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2017;49(1):3–9.
Abhishek F, Heist EK, Barrett C, Danik S, Blendea D, Correnti C, et al. Effectiveness of a strategy to reduce major vascular complications from catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2011;30(3):211–5.
Ghannam M, Chugh A, Dillon P, Alyesh D, Kossidas K, Sharma S, et al. Protamine to expedite vascular hemostasis after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled trial. (1556–3871 (Electronic)).
Chilukuri K, Henrikson, Ca, Fau-Dalal D, Dalal D, Fau-Scherr D, Scherr D, Fau-MacPherson, EC, MacPherson, Ec, Fau-Cheng A, Cheng A, Fau-Spragg D, et al. Incidence and outcomes of protamine reactions in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. (1572–8595 (Electronic)).
Reddy YM, Singh D, Fau-Chikkam V, Chikkam V, Fau-Bommana S, Bommana S, Fau-Atkins D, Atkins D, Fau-Verma A, Verma A, Fau-Swarup V, et al. Postprocedural neuropathy after atrial fibrillation ablation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2013.
• Lakshmanadoss U, Wong WS, Kutinsky I, Khalid MR, Williamson B, Haines DE. Figure-of-eight suture for venous hemostasis in fully anticoagulated patients after atrial fibrillation catheter ablation. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2017;17(5):134–9 A single-center study which showed the feasibility of having figure of 8 sutures to facilitate early ambulation. The article also reviews the techniques with detailed images to understand the procedure.
Payne JA-O, Aznaurov S, Gautam SA-O. Three-way stopcock suture technique for hemostasis after ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;1540–8167.
Mahadevan VS, Jimeno S, Fau-Benson LN, Benson, Ln, Fau-McLaughlin, PR, McLaughlin, Pr, Fau-Horlick EM, Horlick EM. Pre-closure of femoral venous access sites used for large-sized sheath insertion with the Perclose device in adults undergoing cardiac intervention. Heart. 2008;1468–201X.
Maraj I, Budzikowski, As, Fau-Ali W, Ali W, Fau-Mitre CA, Mitre, Ca, Fau-Kassotis J, Kassotis J. Use of vascular closure device is safe and effective in electrophysiological procedures. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015;1572–8595 (Electronic).
Natale A, Mohanty S, Liu PY, Mittal S, Al-Ahmad A, De Lurgio DB, et al. Venous vascular closure system versus manual compression following multiple access electrophysiology procedures: the AMBULATE trial. Jacc Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(1):111–24.
Tarun Dalia MSR, Naeem A, Apte N, Swope J, Pimentel R, Emert M, Reddy M, Sheldon SH. Vascular complications after implementing micropuncture needle and ultrasound guided access in electrophysiology lab: a single tertiary center experience HRS Abstracts; 2020.
Ng C, Rozen G, Biton Y, Leyton-Mange J, Barrett C. P389 Direct ultrasound visualization in combination with micropuncture needle reduces vascular access complications in cardiac electrophysiological procedures. EP Europace. 2017;19(suppl_3):iii77–ii.
Yang E, Ipek EG, Balouch M, Mints Y, Chrispin J, Marine JE, et al. Factors impacting complication rates for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation from 2003 to 2015. EP Europace. 2016;19(2):241–9.
Lesh MD, Kalman JM, Fau-Karch MR, Karch MR. Use of intracardiac echocardiography during electrophysiologic evaluation and therapy of atrial arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998;1045–3873 (Print).
Honarbakhsh S, O’Brien B, Schilling RJ. A simplified trans-septal puncture technique using a needle free approach for cryoablation of atrial fibrillation. J Atr Fibrillation. 2017;10(2):1628.
Nakamura T, Okishige K, Kanazawa T, Yamashita M, Kawaguchi N, Kato N, et al. Incidence of silent cerebral infarctions after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation utilizing the second-generation cryoballoon. EP Europace. 2016;19(10):1681–8.
McCready JW, Nunn L, Fau-Lambiase PD, Lambiase Pd, Fau-Ahsan SY, Ahsan SY, Fau-Segal OR, Segal Or, Fau-Rowland E, Rowland E, Fau-Lowe MD, et al. Incidence of left atrial thrombus prior to atrial fibrillation ablation: is pre-procedural transoesophageal echocardiography mandatory? (1532–2092 (Electronic)).
Wu M, Gabriels J, Khan M, Shaban N, D’Amato S, Liu CF, et al. Left atrial thrombus and dense spontaneous echocardiographic contrast in patients on continuous direct oral anticoagulant therapy undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: comparison of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban. (1556–3871 (Electronic)).
Di Minno MN, Ambrosino P, Fau-Dello Russo A, Dello Russo A, Fau-Casella M, Casella M, Fau-Tremoli E, Tremoli E, Fau-Tondo C, Tondo C. Prevalence of left atrial thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. (2567-689X (Electronic)).
Malik R, Alyeshmerni DM, Wang Z, Goldstein SA, Torguson R, Lindsay J, et al. Prevalence and predictors of left atrial thrombus in patients with atrial fibrillation: is transesophageal echocardiography necessary before cardioversion? (1878–0938 (Electronic)).
Merino JL, Lip GYH, Heidbuchel H, Cohen AA, De Caterina R, de Groot JR, et al. Determinants of left atrium thrombi in scheduled cardioversion: an ENSURE-AF study analysis. (1532–2092 (Electronic)).
Romero J, Husain SF, Kelesidis I, Kelesidis I Sanz J, Medina HM, Garcia MJ. Detection of left atrial appendage thrombus by cardiac computed tomography in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. (1942–0080 (Electronic)).
Saksena S, Sra J Jordaens L, Kusumoto F, Knight B, Natale A, Kocheril A, et al. A prospective comparison of cardiac imaging using intracardiac echocardiography with transesophageal echocardiography in patients with atrial fibrillation: the intracardiac echocardiography guided cardioversion helps interventional procedures study. (1941–3084 (Electronic)).
Baran J, Stec S Pilichowska-Paszkiet E, Zaborska B, Sikora-Frąc M, Kryński T, Michałowska I, et al. Intracardiac echocardiography for detection of thrombus in the left atrial appendage: comparison with transesophageal echocardiography in patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation: the Action-Ice I study. (1941–3084 (Electronic)).
Sriram CS, Banchs JE, Moukabary T, Moradkhan R, Gonzalez MD. Detection of left atrial thrombus by intracardiac echocardiography in patients undergoing ablation of atrial fibrillation. (1572–8595 (Electronic)).
Maleki K, Mohammadi R, Hart D, Cotiga D, Farhat N, Steinberg JS. Intracardiac ultrasound detection of thrombus on transseptal sheath: incidence, treatment, and prevention. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16(6):561–5.
Biase LD, Burkhardt JD, Santangeli P, Mohanty P, Sanchez JE, Horton R, et al. Periprocedural stroke and bleeding complications in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation with different anticoagulation management. Circulation. 2014;129(25):2638–44.
Di Biase L, Lakkireddy D, Trivedi C, Deneke T, Martinek M, Mohanty S, et al. Feasibility and safety of uninterrupted periprocedural apixaban administration in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: results from a multicenter study. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12(6):1162–8.
Lakkireddy D, Reddy YM, Di Biase L, Vallakati A, Mansour MC, Santangeli P, et al. Feasibility and safety of uninterrupted rivaroxaban for periprocedural anticoagulation in patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation: results from a multicenter prospective registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;1558–3597.
Hakalahti A, Uusimaa P, Ylitalo K, Raatikainen MJP. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with therapeutic oral anticoagulation treatment. EP Europace. 2011;13(5):640–5.
Schmidt M, Segerson NM, Marschang H, Akoum N, Rittger H, Clifford SM, et al. Atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with therapeutic international normalized ratios. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2009;32(8):995–9.
Kwak J-J, Pak H-N, Jang J-K, Kim SK, Park JH, Choi J-I, et al. Safety and convenience of continuous warfarin strategy during the periprocedural period in patients who underwent catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21(6):620–5.
Briceno DF, Spinetto PV, Brevik J, Maraboto C, Jagannath A, Kargoli F, et al. Clinical impact of intraprocedural activated clotting time during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: systemic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13 Supplement):766.
Tokuda M, Matsuo S, Kato M, Sato H, Oseto H, Okajima E, et al. Effect of air removal with extracorporeal balloon inflation on incidence of asymptomatic cerebral embolism during cryoballoon ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart, Rhythm. 2017;14(9):1291–6.
Barbhaiya CR, Kumar S, Guo Y, Zhong J, John RM, Tedrow UB, et al. Global survey of esophageal injury in atrial fibrillation ablation: characteristics and outcomes of esophageal perforation and fistula. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2016;2(2):143–50.
John RM, Kapur S, Ellenbogen KA, Koneru JN. Atrioesophageal fistula formation with cryoballoon ablation is most commonly related to the left inferior pulmonary vein. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(2):184–9.
Helms A, West JJ, Patel A, Mounsey JP, DiMarco JP, Mangrum JM, et al. Real-time rotational ICE imaging of the relationship of the ablation catheter tip and the esophagus during atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2009;20(2):130–7.
Rolf S, Boldt LH, Parwani AS, Wutzler A, Huemer M, Blaschke D, et al. Findings and outcome of fluoroscopic visualization of the oesophageal course during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2011;13(6):796–802.
Tsai WK, Koruth J, Reddy VY. Esophageal heating is not limited to left atrial ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7(1):178–9.
Cummings JE, Schweikert RA, Saliba WI, Burkhardt JD, Brachmann J, Gunther J, et al. Assessment of temperature, proximity, and course of the esophagus during radiofrequency ablation within the left atrium. Circulation. 2005;112(4):459–64.
Shah D, Dumonceau JM, Burri H, Sunthorn H, Schroft A, Gentil-Baron P, et al. Acute pyloric spasm and gastric hypomotility: an extracardiac adverse effect of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(2):327–30.
Martinek M, Bencsik G, Aichinger J, Hassanein S, Schoefl R, Kuchinka P, et al. Esophageal damage during radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: impact of energy settings, lesion sets, and esophageal visualization. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2009;20(7):726–33.
Martinek M, Meyer C, Hassanein S, Aichinger J, Bencsik G, Schoefl R, et al. Identification of a high-risk population for esophageal injury during radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: procedural and anatomical considerations. Heart Rhythm. 2010;7(9):1224–30.
Liu E, Shehata M, Liu T, Amorn A, Cingolani E, Kannarkat V, et al. Prevention of esophageal thermal injury during radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2012;35(1):35–44.
Di Biase L, Dodig M, Saliba W, Siu A, Santisi J, Poe S, et al. Capsule endoscopy in examination of esophagus for lesions after radiofrequency catheter ablation: a potential tool to select patients with increased risk of complications. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21(8):839–44.
Di Biase L, Conti S, Mohanty P, Bai R, Sanchez J, Walton D, et al. General anesthesia reduces the prevalence of pulmonary vein reconnection during repeat ablation when compared with conscious sedation: results from a randomized study. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(3):368–72.
Tschabrunn CM, Silverstein J, Berzin T, Ellis E, Buxton AE, Josephson ME, et al. Comparison between single- and multi-sensor oesophageal temperature probes during atrial fibrillation ablation: thermodynamic characteristics. Europace. 2015;17(6):891–7.
Crozier I, Daly M, Lim G, Roper G. Esophageal infrared thermography during atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2015;1556–3871.
Daly MG, Melton I, Roper G, Lim G, Crozier IG. High-resolution infrared thermography of esophageal temperature during radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018;11(2):e005667.
Parikh V, Swarup V, Hantla J, Vuddanda V, Dar T, Yarlagadda B, et al. Feasibility, safety, and efficacy of a novel preshaped nitinol esophageal deviator to successfully deflect the esophagus and ablate left atrium without esophageal temperature rise during atrial fibrillation ablation: the DEFLECT GUT study. Heart Rhythm. 2018;15(9):1321–7.
Bhardwaj R, Naniwadekar A, Whang W, Mittnacht AJ, Palaniswamy C, Koruth JS, et al. Esophageal deviation during atrial fibrillation ablation: clinical experience with a dedicated esophageal balloon retractor. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;4(8):1020–30.
Kassim G, Bsrat M, Hershman M, Mamun R, Dong R, Smith MS. Major esophageal bleeding secondary to mechanical injury from esophageal deviation during pulmonary vein isolation: 1786. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:S1002.
Miyazaki S, Taniguchi H, Kusa S, Komatsu Y, Ichihara N, Takagi T, et al. Factors associated with periesophageal vagal nerve injury after pulmonary vein antrum isolation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3(5):e001209.
Barkagan M, Contreras-Valdes FM, Leshem E, Buxton AE, Nakagawa H, Anter E. High-power and short-duration ablation for pulmonary vein isolation: safety, efficacy, and long-term durability. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29(9):1287–96.
Tsuchiya T, Ashikaga K, Nakagawa S, Hayashida K, Kugimiya H. Atrial fibrillation ablation with esophageal cooling with a cooled water-irrigated intraesophageal balloon: a pilot study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007;18(2):145–50.
Kuwahara T, Takahashi A, Okubo K, Takagi K, Yamao K, Nakashima E, et al. Oesophageal cooling with ice water does not reduce the incidence of oesophageal lesions complicating catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: randomized controlled study. Europace. 2014;16(6):834–9.
Bunch TJ, May HT, Crandall BG, Weiss JP, Bair TL, Osborn JS, Anderson JL, et al. Intracardiac ultrasound for esophageal anatomic assessment and localization during left atrial ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;1540–8167.
Buch E, Nakahara S, Shivkumar K. Intra-pericardial balloon retraction of the left atrium: a novel method to prevent esophageal injury during catheter ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2008;5(10):1473–5.
Schmidt M, Nolker G, Marschang H, Gutleben KJ, Schibgilla V, Rittger H, et al. Incidence of oesophageal wall injury post-pulmonary vein antrum isolation for treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2008;10(2):205–9.
Bunch TJ, Nelson J, Foley T, Allison S, Crandall BG, Osborn JS, et al. Temporary esophageal stenting allows healing of esophageal perforations following atrial fibrillation ablation procedures. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17(4):435–9.
Gilcrease GW, Stein JB. A delayed case of fatal atrioesophageal fistula following radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21(6):708–11.
Contreras-Valdes FM, Heist EK, Danik SB, Barrett CD, Blendea D, Brugge WR, et al. Severity of esophageal injury predicts time to healing after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(12):1862–8.
Singh SM, d’Avila A, Doshi SK, Brugge WR, Bedford RA, Mela T, et al. Esophageal injury and temperature monitoring during atrial fibrillation ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2008;1(3):162–8.
Su W, Aryana A, Passman R, Singh G, Hokanson R, Kowalski M, et al. Cryoballoon best practices II: practical guide to procedural monitoring and dosing during atrial fibrillation ablation from the perspective of experienced users. Heart, Rhythm. 2018;1556–3871. A review article describing best practices for cryoablation including monitoring for esophageal temperature and phrenic nerve function during cryoablation procedures.
Sanchez-Quintana D, Cabrera JA, Climent V, Farre J, Weiglein A, Ho SY. How close are the phrenic nerves to cardiac structures? Implications for cardiac interventionalists. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16(3):309–13.
Haines DE, Watson DD. Tissue heating during radiofrequency catheter ablation: a thermodynamic model and observations in isolated perfused and superfused canine right ventricular free wall. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1989;12(6):962–76.
Tsong TY, Su ZD. Biological effects of electric shock and heat denaturation and oxidation of molecules, membranes, and cellular functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;888:211–32.
Starmer CF, Biktashev VN, Romashko DN, Stepanov MR, Makarova ON, Krinsky VI. Vulnerability in an excitable medium: analytical and numerical studies of initiating unidirectional propagation. Biophys J. 1993;65(5):1775–87.
Sarabanda AV, Bunch TJ, Johnson SB, Mahapatra S, Milton MA, Leite LR, et al. Efficacy and safety of circumferential pulmonary vein isolation using a novel cryothermal balloon ablation system. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(10):1902–12.
Natale A, Pisano E, Shewchik J, Bash D, Fanelli R, Potenza D, et al. First human experience with pulmonary vein isolation using a through-the-balloon circumferential ultrasound ablation system for recurrent atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2000;102(16):1879–82.
Sacher F, Monahan KH, Thomas SP, Davidson N, Adragao P, Sanders P, et al. Phrenic nerve injury after atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: characterization and outcome in a multicenter study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(12):2498–503.
Andrade JG, Khairy P, Guerra PG, Deyell MW, Rivard L, Macle L, et al. Efficacy and safety of cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation: a systematic review of published studies. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(9):1444–51.
Glenn WW, Phelps ML. Diaphragm pacing by electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerve. Neurosurgery. 1985;17(6):974–84.
•• Parikh V, Kowalski M. Comparison of phrenic nerve injury during atrial fibrillation ablation between different modalities, pathophysiology and management. J Atr Fibrillation. 2015;8(4):1314 This is a review article of different techniques used to monitor phrenic nerve function during ablation for atrial fibrillation.
Andrié RP, Schrickel JW, Nickenig G, Lickfett L. Left phrenic nerve injury during cryoballoon ablation of the left superior pulmonary vein. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012;35(11):e334–e6.
Ghosh J, Sepahpour A, Chan KH, Singarayar S, McGuire MA. Immediate balloon deflation for prevention of persistent phrenic nerve palsy during pulmonary vein isolation by balloon cryoablation. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10(5):646–52.
Robbins IM, Colvin EV, Doyle TP, Kemp WE, Loyd JE, McMahon WS, et al. Pulmonary vein stenosis after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1998;98(17):1769–75.
Taylor GW, Kay GN, Zheng X, Bishop S, Ideker RE. Pathological effects of extensive radiofrequency energy applications in the pulmonary veins in dogs. Circulation. 2000;101(14):1736–42.
Arentz T, Jander N, von Rosenthal J, Blum T, Fürmaier R, Görnandt L, et al. Incidence of pulmonary vein stenosis 2 years after radiofrequency catheter ablation of refractory atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2003;24(10):963–9.
Packer DL, Kowal RC, Wheelan KR, Irwin JM, Champagne J, Guerra PG, et al. Cryoballoon ablation of pulmonary veins for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: first results of the North American Arctic Front (STOP AF) pivotal trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(16):1713–23.
Erin AF, Douglas LP, David RH. Pulmonary vein stenosis after atrial fibrillation ablation. EuroIntervention. 2016;12:X31–X4.
Tse HF, Reek S, Timmermans C, Lee KL, Geller JC, Rodriguez LM, et al. Pulmonary vein isolation using transvenous catheter cryoablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation without risk of pulmonary vein stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(4):752–8.
Tokutake K, Tokuda M, Yamashita S, Sato H, Ikewaki H, Okajima E, et al. Anatomical and procedural factors of severe pulmonary vein stenosis after cryoballoon pulmonary vein ablation. JACC: Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;5(11):1303–15.
Reynolds MA-O, Zheng Q, Doros G. Laser balloon ablation for AF: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29(10):1363–70.
Koruth JS, Kuroki K, Iwasawa J, Viswanathan R, Brose R, Buck ED, et al. Endocardial ventricular pulsed field ablation: a proof-of-concept preclinical evaluation. EP Europace. 2019;22(3):434–9.
Reddy VY, Neuzil P, Koruth JS, Petru J, Funosako M, Cochet H, et al. Pulsed field ablation for pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(3):315–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Nachiket M. Apte declares no conflict of interest. Amit Shrestha declares no conflict of interest. Raghuveer Dendi declares no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Arrhythmia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apte, N.M., Shrestha, A. & Dendi, R. Techniques to Avoid Complications of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. Curr Treat Options Cardio Med 22, 31 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-020-00834-w
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-020-00834-w