Abstract
Purpose of Review
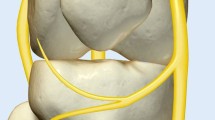
The infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve (IPS) is an under-investigated nerve that can be a source of chronic knee pain. This literature review aims to deliver an up-to-date review of chronic pain transmitted via the IPS along with therapeutic approaches available for pain refractory to conservative measures.
Recent Findings
Knee pain transmitted via the IPS can arise from several etiologies. Damage to the IPS is often iatrogenic and develops following total knee arthroplasty, anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, and other knee surgical procedures. Other causes of IPS-derived pain include entrapment of the nerve, neuromas, Schwannomas, and pain from knee osteoarthritis transmitted through the IPS.This article investigated therapeutic approaches to pain derived from the IPS. Common approaches included radiofrequency ablation, neuroma excisions, Schwannoma excision, nerve blocks, surgical exploration, surgical release of an entrapped nerve, cryoablation, and peripheral nerve stimulation. Pain scores, duration of pain relief, adverse events, and secondary outcomes were all included in this review.
Summary
A subset of the patient population experiences chronic pain deriving from the IPS that is refractory to conservative treatment measures. This review aims to evaluate the etiologies and therapeutic approaches for chronic pain arising from the IPS refractory to conservative treatments.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Change history
02 March 2024
Springer Nature’s version of this paper was updated to remove the educational degree (BS) of the fifth author. 'Kenneth J. Fiala BS' should be corrected to 'Kenneth J. Fiala'
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Yang S-R, Hirschmann MT, Schiffmann A, Kovacs BK, Gehweiler J, Amsler F, et al. Diagnostics of infrapatellar saphenous neuralgia-a reversible cause of chronic anteromedial pain following knee surgery. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2022;32(2):1342–52. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34342695.
Wong TL, Kikuta S, Iwanaga J, Tubbs RS. A multiply split femoral nerve and psoas quartus muscle. Anat Cell Biol [Internet]. 2019;52(2):208–10. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31338239.
House JH, Ahmed K. Entrapment neuropathy of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve. Am J Sports Med [Internet]. 1977;5(5):217–24 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/907036.
Regev GJ, Ben Shabat D, Khashan M, Ofir D, Salame K, Shapira Y, et al. Management of chronic knee pain caused by postsurgical or posttraumatic neuroma of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve. J Orthop Surg Res [Internet]. 2021;16(1):464 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34289862.
Sundaram RO, Ramakrishnan M, Harvey RA, Parkinson RW. Comparison of scars and resulting hypoaesthesia between the medial parapatellar and midline skin incisions in total knee arthroplasty. Knee [Internet]. 2007;14(5):375–8 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17662607.
Ojima T, Yoshimura M, Katsuo S-I, Mizuno K, Yamakado K, Hayashi S, et al. Transverse incision advantages for total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci [Internet]. 2011;16(5):524–30 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21833613.
le Corroller T, Lagier A, Pirro N, Champsaur P. Anatomical study of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve using ultrasonography. Muscle Nerve [Internet]. 2011;44(1):50–4 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21674521.
Uematsu H, Osako S, Hakata S, Kabata D, Shintani A, Kawazoe D, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment of the saphenous nerve for refractory osteoarthritis-associated knee pain. Pain Physician [Internet]. 2021;24(6):E761-9 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34554694.
Grabowski R, Gobbi A, Zabierek S, Domzalski ME. Nonspecific chronic anteromedial knee pain neuroma as a cause of infrapatellar pain syndrome: case study and literature review. Orthop J Sport Med [Internet]. 2018;6(1):2325967117751042 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29404377.
Kachar SM, Williams KM, Finn HA. Neuroma of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve a cause of reversible knee stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty [Internet]. 2008;23(6):927–30 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18722295.
Kim NH, Kang HJ, Hong SH, Park BK, Lee JH, Park JW, et al. A case of subcutaneous neuroma presenting with intractable pain and allodynia over the anteromedial aspect of the knee. Clin J Pain [Internet]. 2012;28(7):635–8 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22699132.
• Darche J-P, Vopat L, Smith D, Zheng A, Vopat BG. Chronic anterior knee pain in a wrestling athlete from a neuroma of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve. Kansas J Med [Internet]. 2020;13:79–80. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32337005. Good discussion of the anatomy.
Tennent TD, Birch NC, Holmes MJ, Birch R, Goddard NJ. Knee pain and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve. J R Soc Med [Internet]. 1998;91(11):573–5 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10325872.
Batistaki C, Saranteas T, Chloros G, Savvidou O. Ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve block for saphenous neuralgia after knee surgery: two case reports and review of literature. Indian J Orthop [Internet]. 2019;53(1):208–12 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30906004.
Karthik K, Aarthi S, Gordon-Dixon A. Schwannoma presenting with anteromedial knee pain and bone defect. J Knee Surg [Internet]. 2023;26(Suppl 1):S30-3 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23288730.
Rao Y, Hou F, Huang H, Xiao X. The combined treatment of entrapped infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve after ACL reconstruction: ultrasound-guided perineural injection and acupotomy. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil [Internet]. 2022;35(3):479–83. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34744070.
Abd-Elsayed A, Strand N, Gritsenko K, Martens J, Chakravarthy K, Sayed D, Deer T. Radiofrequency ablation for the knee joint: a survey by the American Society of Pain and Neuroscience. J Pain Res. 2022;27(15):1247–55.
Orhurhu V, Urits I, Grandhi R, Abd-Elsayed A. Systematic review of radiofrequency ablation for management of knee pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(8):55.
Carpenedo R, Al-Wardat M, Vizzolo L, Germani G, Chinè E, Ridolfo S, et al. Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency of the saphenous nerve for knee osteoarthritis pain: a pilot randomized trial. Pain Manag [Internet]. 2022;12(2):181–93. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34431329.
Jin H, Zuo H, Xu R, Ji Y, Wang Z. A case report of ultrasound-guided knee nerve pulse radiofrequency combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;100(51):e27878 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34941033.
Shimizu S, Iwashita N, Fukui S, Kitagawa H. Ultrasound imaging with an electric stimulant was useful in pulsed radiofrequency for chronic knee pain in the medial region. JA Clin reports [Internet]. 2022;8(1):92. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36459261.
Ikeuchi M, Ushida T, Izumi M, Tani T. Percutaneous radiofrequency treatment for refractory anteromedial pain of osteoarthritic knees. Pain Med [Internet]. 2011;12(4):546–51. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21463469.
Clendenen S, Greengrass R, Whalen J, O’Connor MI. Infrapatellar saphenous neuralgia after TKA can be improved with ultrasound-guided local treatments. Clin Orthop Relat Res [Internet]. 2015;473(1):119–25 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25062704.
van Dijk W, van Eerten P, Scheltinga M. Infrapatellar nerve damage : a neglected cause of severe localized leg pain. Unfallchirurg [Internet]. 2020;123(Suppl 1):25–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31960086.
Tan J, Wang X, Xiong F, Qian J, Ying Q, Mi J. Case report: a case of injury to the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve caused by medial approach in knee arthroscopy. Front Neurol [Internet]. 2023;14:1083871 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36937537.
Hasoon J, Chitneni A, Urits I, Viswanath O, Kaye AD. Peripheral stimulation of the saphenous and superior lateral genicular nerves for chronic knee pain. Cureus [Internet]. 2021;13(4):e14753. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34084679.
•• Abd-Elsayed A, Moghim R. Efficacy of peripheral nerve stimulation with a high frequency electromagnetic coupled (HF-EMC) powered implanted receiver in treating different pain targets/neuralgias. J Pain Res. 2023;16:589–96. Good study that included about the use of peripheral nerve stimulation for treating chronic knee pain.
Busch C, Smith O, Weaver T, Vallabh J, Abd-Elsayed A. Peripheral nerve stimulation for lower extremity pain. Biomedicines. 2022;10(7):1666.
Abd-Elsayed A, D’Souza RS. Peripheral nerve stimulation: the evolution in pain medicine. Biomedicines. 2021;10(1):18.
Poehling GG, Pollock FE, Koman LA. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy of the knee after sensory nerve injury. Arthroscopy [Internet]. 1988;4(1):31–5. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3355636.
Dasa V, Lensing G, Parsons M, Harris J, Volaufova J, Bliss R. Percutaneous freezing of sensory nerves prior to total knee arthroplasty. Knee [Internet]. 2016;23(3):523–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26875052.
•• McLean BC, Nguyen CD, Newman DP. Cryoablation of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve identified by non-invasive peripheral nerve stimulator for the treatment of non-surgical anterior knee pain: a case series and review of the literature. Cureus [Internet]. 2020;12(6):e8747. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32714685. Relevant and complimentary article.
Trescot AM, Brown MN, Karl HW. Infrapatellar saphenous neuralgia - diagnosis and treatment. Pain Physician [Internet]. 2013;16(3):E315-24. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23703431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AA developed methodology and concept. AA, LH, BS, PY, and KF participated in the literature search, drafting, and writing the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abd-Elsayed, A., Henjum, L.J., Shiferaw, B.T. et al. Infrapatellar Branch of the Saphenous Nerve: Therapeutic Approaches to Chronic Knee Pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep 28, 279–294 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-024-01217-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-024-01217-7