Abstract
Purpose of review
In patients with type 1 diabetes with extreme glycemic variability, the restoration of pancreas endocrine function is potentially and completely achieved with islets of Langerhans (tissue derived from whole organ) or pancreas (whole organ) transplantation. The aim of our review is to report on the latest studies and to highlight the benefits and risks of the two procedures, providing clearer, more selective, evidence-based clinical indications that also consider the impact on the degenerative complications of diabetes as a potential benefit.
Recent findings
Clinical experience in this field has been dynamic over the last three decades, and has been characterized by the development of more standardized protocols and a clearer definition of clinical outcome. On the contrary, the recommendations thus far are not well delineated and tend to overlap, and the past ADA position statement for pancreas transplant alone has also been applied to islet transplant alone, without differentiation.
Summary
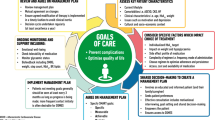
Both outcome-driven and non-outcome-driven criteria are considered in the conclusions, in an attempt to streamline indications for islet-alone or pancreas-alone transplantation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Lind M, Svensson AM, Kosiborod M, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Pivodic A, Wedel H, et al. Glycemic control and excess mortality in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(21):1972–82. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1408214.
• The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular outcomes in type 1 diabetes: the DCCT/EDIC study 30-year follow-up. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(5):686–93. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-1990. This paper is important because it reports data from one of the largest and most rigorous epidemiological studies performed in a cohort of patients with type 1 diabetes, highlighting the relevance of glycemic control in cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death for these patients.
Hammes HP, Kerner W, Hofer S, Kordonouri O, Raile K, Holl RW, et al. Diabetic retinopathy in type 1 diabetes - a contemporary analysis of 8,784 patients. Diabetologia. 2011;54(8):1977–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2198-1.
Pop-Busui R, Boulton AJ, Feldman EL, Bril V, Freeman R, Malik RA, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):136–54. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-2042.
Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(25):2643–53.
• Kandaswamy R, Stock PG, Gustafson SK, Skeans MA, Curry MA, Prentice MA, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2016 annual data report: pancreas. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(Suppl 1):114–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14558. This is an up-to-date account of pancreas transplantation activity in the USA, which includes all numbers of pancreas transplants centers. The knowledge of waiting list trends, donor characteristics, patient survival, graft function, and immunosuppressive protocols are benchmarks for every center with a commitment to this field.
Barton FB, Rickels MR, Alejandro R, Hering BJ, Wease S, Naziruddin B, et al. Improvement in outcomes of clinical islet transplantation: 1999–2010. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(7):1436–45. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-0063.
American Diabetes Association. Pancreas transplantation for patients with type I diabetes (Position Statement). Diabetes Care. 2000;23:117.
Largiadèr F, Kolb E, Binswanger U. A long-term functioning human pancreatic islet allotransplant. Transplantation. 1980;29(1):76–7.
Alejandro R, Mintz DH, Noel J, Latif Z, Koh N, Russell E, et al. Islet cell transplantation in type I diabetes mellitus. Transplant Proc. 1987;19(1 Pt 3):2359–61.
Ricordi C, Lacy PE, Finke EH, Olack BJ, Scharp DW. Automated method for isolation of human pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1988;37(4):413–20.
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(4):230–8.
Collaborative Islet Transplant Registry, 10th Annual Report, www.citregistry.org. Accessed Aug 2018.
Hering BJ, Clarke WR, Bridges ND, Eggerman TL, Alejandro R, Bellin MD, et al. Clinical islet transplantation consortium. Phase 3 trial of transplantation of human islets in type 1 diabetes complicated by severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(7):1230–40. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-1988.
Bellin MD, Kandaswamy R, Parkey J, Zhang HJ, Liu B, Ihm SH, et al. Prolonged insulin independence after islet allotransplants in recipients with type 1 diabetes. Am J Transplant. 2008;8(11):2463–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02404.
Vantyghem MC, Kerr-Conte J, Arnalsteen L, Sergent G, Defrance F, Gmyr V, et al. Primary graft function, metabolic control, and graft survival after islet transplantation. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(8):1473–8. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-1685.
Lablanche S, Vantyghem MC, Kessler L, Wojtusciszyn A, Borot S, Thivolet C, et al.; TRIMECO trial investigators. Islet transplantation versus insulin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes with severe hypoglycaemia or poorly controlled glycaemia after kidney transplantation (TRIMECO): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(7):527–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30078-0.
Venturini M, Angeli E, Maffi P, Fiorina P, Bertuzzi F, Salvioni M, et al. Technique complications and therapeutic efficacy of percutaneous transplantation of human pancreatic islet cells in type 1 diabetes: the role of US. Radiology. 2005;234(2):617–24.
Kawahara T, Kin T, Kashkoush S, Gala-Lopez B, Bigam DL, Kneteman NM, et al. Portal vein thrombosis is a potentially preventable complication in clinical islet transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(12):2700–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03717.
Kelly WD, Lillehei RC, Merkel FK, Idezuki Y, Goetz FC. Allotransplantation of the pancreas and duodenum along with the kidney in diabetic nephropathy. Surgery. 1967;61(6):827–37.
Gruessner AC, Gruessner RW. Long-term outcome after pancreas transplantation: a registry analysis. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2016;21(4):377–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOT.0000000000000331.
Definition of pancreas graft failure OPTN policy notices: OPTN; 2015 [updated 7/2015]. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/media/1572/policynotice_20150701_pancreas.pdf [Accessed 10 May 2016].
Gruessner AC, Gruessner RWG. Pancreas transplantation for patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United States: a registry report. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2018;47(2):417–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2018.01.009.
Gruessner RW, Sutherland DE, Gruessner AC. Mortality assessment for pancreas transplants. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(12):2018–26.
Kandaswamy R, Stock PG, Gustafson SK, Skeans MA, Curry MA, Prentice MA, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2016 annual data report: pancreas. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(Suppl 1):114–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.1455.
Niederhaus SV, Leverson GE, Lorentzen DF, Robillard DJ, Sollinger HW, Pirsch JD, et al. Acute cellular and antibody-mediated rejection of the pancreas allograft: incidence, risk factors and outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(11):2945–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12443.
Finger EB, Radosevich DM, Dunn TB, Chinnakotla S, Sutherland DE, Matas AJ, et al. A composite risk model for predicting technical failure in pancreas transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(7):1840–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12269.
La Rocca E, Fiorina P, Di Carlo V, Astorri E, Rossetti C, Lucignani G, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes after kidney-pancreas and kidney-alone transplantation. Kidney Int. 2001;60(5):1964–71.
Fiorina P, Venturini M, Folli F, Losio C, Maffi P, Placidi C, et al. Natural history of kidney graft survival, hypertrophy, and vascular function in end-stage renal disease type 1 diabetic kidney-transplanted patients: beneficial impact of pancreas and successful islet cotransplantation. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(6):1303–10.
Fiorina P, Folli F, Bertuzzi F, Maffi P, Finzi G, Venturini M, et al. Long-term beneficial effect of islet transplantation on diabetic macro-/microangiopathy in type 1 diabetic kidney-transplanted patients. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(4):1129–36.
Kennedy WR, Navarro X, Goetz FC, Sutherland DE, Najaran JS. Effect of pancreatic transplantation on diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322(15):1031–7.
Del Carro U, Fiorina P, Amadio S, De Toni Franceschini L, Petrelli A, Menini S, et al. Evaluation of polyneuropathy markers in type 1 diabetic kidney transplant patients and effects of islet transplantation: neurophysiological and skin biopsy longitudinal analysis. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(12):3063–9.
Fiorina P, Vezzulli P, Bassi R, Gremizzi C, Falautano M, D'Addio F, et al. Near normalization of metabolic and functional features of the central nervous system in type 1 diabetic patients with end-stage renal disease after kidney-pancreas transplantation. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(2):367–74. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1697.
Boggi U, Vistoli F, Amorese G, Giannarelli R, Coppelli A, Mariotti R, et al. Long-term (5 years) efficacy and safety of pancreas transplantation alone in type 1 diabetic patients. Transplantation. 2012;93(8):842–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e318247a782.
Occhipinti M, Rondinini L, Mariotti R, Vistoli F, Baronti W, Barsotti M, et al. Amelioration of cardiac morphology and function in type 1 diabetic patients with sustained success of pancreas transplant alone. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(8):e171–2. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-0061.
Giannarelli R, Coppelli A, Sartini MS, Del Chiaro M, Vistoli F, Rizzo G, et al. Pancreas transplant alone has beneficial effects on retinopathy in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2006;49(12):2977–82.
Venturini M, Fiorina P, Maffi P, Losio C, Vergani A, Secchi A, et al. Early increase of retinal arterial and venous blood flow velocities at color Doppler imaging in brittle type 1 diabetes after islet transplant alone. Transplantation. 2006;81(9):1274–7.
D'Addio F, Maffi P, Vezzulli P, Vergani A, Mello A, Bassi R, et al. Islet transplantation stabilizes hemostatic abnormalities and cerebral metabolism in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(1):267–76. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-1663.
Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Sutherland DE, Goetz FC, Mauer M. Reversal of lesions of diabetic nephropathy after pancreas transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(2):69–75.
Boggi U, Vistoli F, Amorese G, Giannarelli R, Coppelli A, Mariotti R, et al. Results of pancreas transplantation alone with special attention to native kidney function and proteinuria in type 1 diabetes patients. Rev Diabet Stud. 2011;8(2):259–67. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2011.8.259.
Jenssen T, Hartmann A, Birkeland K. Long-term diabetes complications after pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017;22(4):382–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOT.0000000000000436.
Maffi P, Bertuzzi F, De Taddeo F, Magistretti P, Nano R, Fiorina P, et al. Kidney function after islet transplant alone in type 1 diabetes: impact of immunosuppressive therapy on progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(5):1150–5.
Leitão CB, Cure P, Messinger S, Pileggi A, Lenz O, Froud T, et al. Stable renal function after islet transplantation: importance of patient selection and aggressive clinical management. Transplantation. 2009;87(5):681–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31819279a8.
Thompson DM, Meloche M, Ao Z, Paty B, Keown P, Shapiro RJ, et al. Reduced progression of diabetic microvascular complications with islet cell transplantation compared with intensive medical therapy. Transplantation. 2011;91(3):373–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31820437f3.
•• Shapiro AM, Pokrywczynska M, Ricordi C. Clinical pancreatic islet transplantation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(5):268–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.178. This review outlines the key points in the development of islet transplantation, giving a clear picture of the state of the art in this field, and enables one to carefully consider the option of islet transplantation for the potential cure of type 1 diabetes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Paola Maffi and Antonio Secchi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Immunology, Transplantation, and Regenerative Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maffi, P., Secchi, A. Islet Transplantation Alone Versus Solitary Pancreas Transplantation: an Outcome-Driven Choice?. Curr Diab Rep 19, 26 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1145-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1145-2