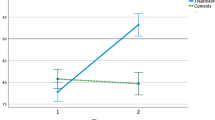
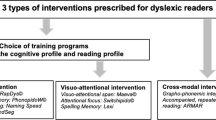
Abstract
In this work, two different studies are examined to evaluate the effectiveness of a novel intervention program for the improvement of reading ability in children with dyslexia, known as repeated reading with vocal music masking (RVM). The proposed remedial approach is inspired by Breznitz’s original work. The studies assess a 5-week program of intensive RVM training in a pre-post-test clinical paradigm, as well as a longitudinal paradigm where it is compared to 8 months of the standard remediation program (SRP). The results of both studies support the efficacy of the newly proposed RVM method. Notably in the longitudinal study, the reading speed of children, as well as related phonological, visuo-attentional, and cognitive skills, and attitudes toward reading, were measured regularly. Significant improvements in reading efficiency and related skills were observed, as well as greater motivation to read after RVM training. A modeling of the data specifically linked executive and processing speed skills to be involved in RVM training, suggesting that RVM may help rebalance the phonological and orthographic coding procedures necessary for efficient reading. The short, intensive, and focused nature of RVM training makes it a viable and attractive intervention for clinical practice. As preliminary results are promising, RVM training may prove to be a valuable tool that clinicians can call upon to effectively treat reading fluency disorders, especially when standard programs do not provide results.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-021-00228-y
Notes
Note: school holidays were included in this time period.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Authors.
Ans, B., Carbonnel, S., & Valdois, S. (1998). A connectionist multiple-trace memory model for polysyllabic word reading. Psychological review, 105(4), 678–723. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.105.4.678-723.
Ardila, A., Ostrosky-Solís, F., & Bernal, B. (2006). Cognitive testing toward the future:The example of semantic verbal fluency (ANIMALS). International Journal of Psychology, 41(5), 324–332.
Baldo, J. V., & Dronkers, N. F. (2006). The role of inferior parietal and inferior frontal cortex in working memory. Neuropsychology, 20(5), 529–538. https://doi.org/10.1037/0894-4105.20.5.529.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society: series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x.
Bertrand, D., Fluss, J., Billard, C., & Ziegler, J. C. (2010). Efficacité, sensibilité, spécificité : Comparaison de différents tests de lecture. L’Année psychologique, 110(2), 299–320. https://doi.org/10.4074/S000350331000206X.
Booth, J. N., Boyle, J. M., & Kelly, S. W. (2010). Do tasks make a difference? Accounting for heterogeneity of performance of children with reading difficulties on tasks of executive function: Findings from a meta-analysis. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 28(1), 133–176. https://doi.org/10.1348/026151009X485432.
Bosse, M. L., Tainturier, M. J., & Valdois, S. (2007). Developmental dyslexia: The visual attention span deficit hypothesis. Cognition, 104(2), 198–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2006.05.009.
Breznitz, Z. (1997). Enhancing the reading of dyslexic children by reading acceleration and auditory masking. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89(1), 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.89.1.103.
Breznitz, Z. (2012). Fluency in reading. Pyschology Pres. Taylor & Francis Group., ISBN-13, 978–0805841442.
Bruck, M. (1992). Persistence of dyslexics’ phonological awareness deficits. Developmental psychology, 28(5), 874–886. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.28.5.874.
Campbell, R., & Coltheart, M. (1984). Gandhi: The nonviolent road to spelling reform? Cognition, 17(3), 185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0277(84)90005-2.
Casalis, S., Leloup, G., & Parriaud, F. B. (2019). Prise en charge des troubles du langage écrit chez l’enfant. Elsevier Health Sciences ISBN 978-2-294-75420-3.
Castles, A., Rastle, K., & Nation, K. (2018). Ending the reading wars: Reading acquisition from novice to expert. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 19, 5–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100618772271.
Cavalli, E., Colé, P., Pattamadilok, C., Badier, J. M., Zielinski, C., Chanoine, V., & Ziegler, J. C. (2017). Spatiotemporal reorganization of the reading network in adult dyslexia. Cortex, 92, 204–221.
Cavalli, E., Colé, P., Leloup, G., Poracchia-George, F., Sprenger-Charolles, L., & El Ahmadi, A. (2018). Screening for dyslexia in French-Speaking University students: An evaluation of the detection accuracy of the alouette test. Journal of learning disabilities, 51(3), 268–282. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219417704637.
Coltheart, M., Curtis, B., Atkins, P., & Haller, M. (1993). Models of reading aloud: Dual-route and parallel-distributed-processing approaches. Psychological review, 100(4), 589–608. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.100.4.589.
Coltheart, M., Rastle, K., Perry, C., Langdon, R., & Ziegler, J. (2001). DRC: a dual route cascaded model of visual word recognition and reading aloud. Psychological review, 108(1), 204–256. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295x.108.1.204.
Crawford, J. R., Garthwaite, P. H., & Porter, S. (2010). Point and interval estimates of effect sizes for the case-controls design in neuropsychology: Rationale, methods, implementations, and proposed reporting standards. Cognitive neuropsychology, 27(3), 245–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2010.513967.
Ecalle, J., Magnan, A., Bouchafa, H., & Gombert, J. E. (2009). Computer-based training with ortho-phonological units in dyslexic children: new investigations. Dyslexia, 15(3), 218–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.373.
Eden, G. F., Jones, K. M., Cappell, K., Gareau, L., Wood, F. B., Zeffiro, T. A., Dietz, N. A. E., Agnew, J. A., & Flowers, D. L. (2004). Neural changes following remediation in adult developmental dyslexia. Neuron, 44(3), 411–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.019.
Ehri, L. C., Nunes, S. R., Willows, D. M., Schuster, B. V., Yaghoub-Zadeh, Z., & Shanahan, T. (2001). Phonemic awareness instruction helps children learn to read: Evidence from the National Reading Panel’s meta-analysis. Reading research quarterly, 36(3), 250–287. https://doi.org/10.1598/RRQ.36.3.2.
Fitz-Gibbon, C. T., & Morris, L. L. (1996). Theory-based evaluation. Evaluation Practice, 17(2), 177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0886-1633(96)90024-0.
Fisk, J. E., & Sharp, C. A. (2004). Age-related impairment in executive functioning: Updating, inhibition, shifting and access. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 26(7), 874–890.
Fraga González, G., Žarić, G., Tijms, J., Bonte, M., Blomert, L., & van der Molen, M. W. (2015). A randomized controlled trial on the beneficial effects of training letter-speech sound integration on reading fluency in children with dyslexia. PloS one, 10(12), e0143914. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143914.
Franceschini, S., Gori, S., Ruffino, M., Viola, S., Molteni, M., & Facoetti, A. (2013). Action video games make dyslexic children read better. Current Biology, 23(6), 462–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.044.
Frith, U., Landerl, K., & Frith, C. (1994). Dyslexia and verbal fluency: More evidence for a phonological deficit. Dyslexia, 1(1), 2–11.
Gabrieli, J. D. (2009). Dyslexia: a new synergy between education and cognitive neuroscience. Science, 325(5938), 280–283. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1171999.
Galuschka, K., Ise, E., Krick, K., & Schulte-Körne, G. (2014). Effectiveness of treatment approaches for children and adolescents with reading disabilities: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PloS one, 9(2), e89900. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089900.
Gathercole, S. E., & Baddeley, A. D. (1993). Essays in cognitive psychology. Working memory and language. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Goswami, U. (2000). Phonological representations, reading development and dyslexia: Towards a cross-linguistic theoretical framework. Dyslexia, 6, 133–151.
Goswami, U., & Bryant, P. (1990). Phonological skills and learning to read. Hove: Erlbaum.
Hachmann, W. M., Bogaerts, L., Szmalec, A., Woumans, E., Duyck, W., & Job, R. (2014). Short-term memory for order but not for item information is impaired in developmental dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 64, 121–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-013-0089-5.
Harm, M. W., & Seidenberg, M. S. (1999). Phonology, reading acquisition, and dyslexia: Insights from connectionist models. Psychological Review, 106(3), 491–528. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.106.3.491.
Hatcher, P. J., Hulme, C., & Ellis, A. W. (1994). Ameliorating early reading failure by integrating the teaching of reading and phonological skills: The phonological linkage hypothesis. Child development, 65(1), 41–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1994.tb00733.
Hatcher, P. J., Hulme, C., & Snowling, M. J. (2004). Explicit phoneme training combined with phonic reading instruction helps young children at risk of reading failure. Journal of child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45(2), 338–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00225.x.
Hindson, B., Byrne, B., Fielding-Barnsley, R., Newman, C., Hine, D. W., & Shankweiler, D. (2005). Assessment and early instruction of preschool children at risk for reading disability. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97(4), 687–704. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.97.4.687.
Hoover, W. A., & Gough, P. B. (1990). The simple view of reading. Reading and writing, 2(2), 127–160.
Hutzler, F., Ziegler, J. C., Perry, C., Wimmer, H., & Zorzi, M. (2004). Do current connectionist learning models account for reading development in different languages? Cognition, 91(3), 273–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2003.09.006.
Kudo, M. F., Lussier, C. M., & Swanson, H. L. (2015). Reading disabilities in children: a selective meta-analysis of the cognitive literature. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 40, 51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2015.01.002.
Landerl, K., & Wimmer, H. (2008). Development of word reading fluency and spelling in a consistent orthography: An 8-year follow-up. Journal of educational psychology, 100(1), 150–161. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.100.1.150.
Lefavrais, P. (1967). Test de l’Alouette. Paris: Editions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée.
Lefavrais, P. (2005). Test de l’Alouette Révisé. Paris: Editions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée.
Lété, B., Sprenger-Charolles, L., & Colé, P. (2004). MANULEX: A grade-level lexical database from French elementary school readers. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 36(1), 156–166. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03195560.
Livingston, E. M., Siegel, L. S., & Ribary, U. (2018). Developmental dyslexia: Emotional impact and consequences. Australian Journal of Learning Difficulties, 23(2), 107–135. https://doi.org/10.1080/19404158.2018.1479975.
Lorusso, M. L., Facoetti, A., Toraldo, A., & Molteni, M. (2005). Tachistoscopic treatment of dyslexia changes the distribution of visual–spatial attention. Brain and Cognition, 57(2), 135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2004.08.057.
Lovett, M. W., Steinbach, K. A., & Frijters, J. C. (2000). Remediating the core deficits of developmental reading disability: A double-deficit perspective. Journal of learning disabilities, 33(4), 334–358. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221940003300406.
Lyon, G. R., Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2003). A definition of dyslexia. Annals of dyslexia, 53(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-003-0001-9.
Majerus, S., & Boukebza, C. (2013). Short-term memory for serial order supports vocabulary development: new evidence from a novel word learning paradigm. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 116(4), 811–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2013.07.014.
Majerus, S., & Cowan, N. (2016). The nature of verbal short-term impairment in dyslexia: the importance of serial order. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, Article 1522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01522.
Mammarella, I. C., Ghisi, M., Bomba, M., Bottesi, G., Caviola, S., Broggi, F., & Nacinovich, R. (2016). Anxiety and depression in children with nonverbal learning disabilities, reading disabilities, or typical development. Journal of learning disabilities, 49(2), 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219414529336.
Martin, J., Colé, P., Leuwers, C., Casalis, S., Zorman, M., & Sprenger-Charolles, L. (2010). Reading in French-speaking adults with dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 60(2), 238–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-010-0043-8.
McArthur, G., Castles, A., Kohnen, S., Larsen, L., Jones, K., Anandakumar, T., & Banales, E. (2015). Sight word and phonics training in children with dyslexia. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 48(4), 391–407. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219413504996.
Mehringer, H., Fraga-González, G., Pleisch, G., Röthlisberger, M., Aepli, F., Keller, V., Karipidis, I. I., & Brem, S. (2020). (Swiss) GraphoLearn: An app-based tool to support beginning readers. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 15(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-020-0125-0.
Melby-Lervåg, M., Lyster, S. A. H., & Hulme, C. (2012). Phonological skills and their role in learning to read: A meta-analytic review. Psychological bulletin, 138(2), 322–352. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026744.
Menghini, D., Finzi, A., Benassi, M., Bolzani, R., Facoetti, A., Giovagnoli, S., Ruffino, M., & Vicari, S. (2010). Different underlying neurocognitive deficits in developmental dyslexia: A comparative study. Neuropsychologia, 48(4), 863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.11.003.
Meyer, M. S., & Felton, R. H. (1999). Repeated reading to enhance fluency: Old approaches and new directions. Annals of dyslexia, 49(1), 283–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-999-0027-8.
Monzalvo, K., Fluss, J., Billard, C., Dehaene, S., & Dehaene-Lambertz, G. (2012). Cortical networks for vision and language in dyslexic and normal children of variable socio-economic status. Neuroimage, 61(1), 258–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.035.
Nation, K., & Snowling, M. J. (1998). Individual differences in contextual facilitation: Evidence from dyslexia and poor reading comprehension. Child development, 69(4), 996–1011. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1998.tb06157.x.
Norton, E. S., Beach, S. D., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2014). Neurobiology of dyslexia. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 30, 73e78.
Norton, E. S., & Wolf, M. (2012). Rapid automatized naming (RAN) and reading fluency: Implications for understanding and treatment of reading disabilities. Annual review of psychology, 63, 427–452. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100431.
Pacton, S., Sobaco, A., Fayol, M., & Treiman, R. (2013). How does graphotactic knowledge influence children’s learning of new spellings? Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 701. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00701.
Paizi, D., Zoccolotti, P., & Burani, C. (2010). Lexical reading in Italian developmental dyslexic readers. Reading and dyslexia in different orthographies, 181–198. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203858462.
Pennington, B. F. (2006). From single to multiple deficit models of developmental disorders. Cognition, 101(2), 385–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2006.04.008.
Perfetti, C. M. A., Goloman, S. M. A., & Hogaboam, T.-W. (1979). Reading skill and the identification of words in discourse context. Memory and Cognition, 7, 273–282.
Perry, C., Ziegler, J. C., & Zorzi, M. (2007). Nested incremental modeling in the development of computational theories: The CDP+ model of reading aloud. Psychological Review, 114(2), 273–315. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.114.2.273.
Perry, C., Zorzi, M., & Ziegler, J. C. (2019). Understanding dyslexia through personalized large-scale computational models. Psychological Science, 30, 386–395.
Plaut, D. C., McClelland, J. L., Seidenberg, M. S., & Patterson, K. (1996). Understanding normal and impaired word reading: computational principles in quasi-regular domains. Psychological review, 103(1), 56–115. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295x.103.1.56.
Rack, J. P., Snowling, M. J., & Olson, R. K. (1992). The nonword reading deficit in developmental dyslexia: A review. Reading Research Quarterly, 27, 29–53. https://doi.org/10.2307/747832.
Ramus, F., & Ahissar, M. (2012). Developmental dyslexia: The difficulties of interpreting poor performance, and the importance of normal performance. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 29(1-2), 104–122.
Ramus, F., Rosen, S., Dakin, S. C., Day, B. L., Castellote, J. M., White, S., & Frith, U. (2003). Theories of developmental dyslexia: insights from a multiple case study of dyslexic adults. Brain, 126(4), 841–865. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awg076.
Romani, C., Tsouknida, E., & Olson, A. (2015). Encoding order and developmental dyslexia: a family of skills predicting different orthographic components. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 68, 99–128. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2014.938666.
Sackett, D. L., Rosenberg, W. C., Muir Gray, J. A., Haynes, R. B., & Richardson, W. S. (1996). Evidence based medicine: What it is and what it isn’t. BMJ, 312, 71–72.
Saine, N. L., Lerkkanen, M. K., Ahonen, T., Tolvanen, A., & Lyytinen, H. (2011). Computer-assisted remedial reading intervention for school beginners at risk for reading disability. Child development, 82(3), 1013–1028. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2011.01580.x.
Saksida, A., Iannuzzi, S., Bogliotti, C., Chaix, Y., Démonet, J. F., Bricout, L., et al. (2016). Phonological skills, visual attention span, and visual stress in developmental dyslexia. Developmental psychology, 52(10), 1503–1516. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000184.
Salamé, P., & Baddeley, A. (1987). Noise, unattended speech and short-term memory. Ergonomics, 30(8), 1185–1194.
Salame, P., & Baddeley, A. (1989). Effects of background music on phonological short-term memory. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 41(1), 107–122.
Samuels, S. J. (1979). The method of repeated readings. The reading teacher, 32(4), 403–408.
Seguin, C. (2018). Rééducation cognitive chez l’enfant: Apport des neurosciences, méthodologie et pratiques. De Boeck Superieur ISBN 978-2-35327-440-6.
Seidenberg, M. S., & McClelland, J. L. (1989). A distributed, developmental model of word recognition and naming. Psychological review, 96(4), 523–568. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.96.4.523.
Serniclaes, W., Collet, G., & Sprenger-Charolles, L. (2015). Review of neural rehabilitation programs for dyslexia: how can an allophonic system be changed into a phonemic one? Frontiers in psychology, 6, 190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00190.
Sesma, H. W., Mahone, E. M., Levine, T., Eason, S. H., & Cutting, L. E. (2009). The contribution of executive skills to reading comprehension. Child Neuropsychology, 15(3), 232–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297040802220029.
Share, D. L. (1995). Phonological recoding and self-teaching: Sine qua non of reading acquisition. Cognition, 55(2), 151–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0277(94)00645-2.
Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2005). Dyslexia (specific reading disability). Biological psychiatry, 57(11), 1301–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.01.043.
Snowling, M. J. (2000). Dyslexia (2nd ed.). Blackwell Publishing.
Snowling, M., & Hulme, C. (1989). A longitudinal case study of developmental phonological dyslexia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 6(4), 379–401. https://doi.org/10.1080/02643298908253289.
Sonuga-Barke, E. J. (2003). The dual pathway model of AD/HD: An elaboration of neuro-developmental characteristics. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 27(7), 593–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.08.005.
Sprenger-Charolles, L., Colé, P., Piquard-Kipffer, A., & Leloup, G. (2010). EVALEC Enfant une batterie d’évaluation diagnostique des troubles spécifiques d’apprentissage de la lecture (ou dyslexie) (Ortho-Edition.).
Sprenger-Charolles, L., Siegel, L. S., Jiménez, J. E., & Ziegler, J. C. (2011). Prevalence and reliability of phonological, surface, and mixed profiles in dyslexia: A review of studies conducted in languages varying in orthographic depth. Scientific Studies of Reading, 15(6), 498–521. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2010.524463.
Sprenger-Charolles, L. (2019). Developmental dyslexia in French. In Verhoeven, C. Perfetti &K. Pugh, Developmental dyslexia across languages and writing systems, Connecticut pp-50-72. Cambridge University Press., ISBN-13, 978–1108428774.
Sprenger-Charolles, L., Colé, P., Béchennec, D., & Kipffer-Piquard, A. (2005). French normative data on reading and related skills from EVALEC, a new computerized battery of tests (end Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3, and Grade 4). Revue Européenne de Psychologie Appliquée, 55, 157–186.
Stanovich, K. E. (1984). The interactive-compensatory model of reading: A confluence of developmental, experimental, and educational psychology. RASE: Remedial & Special Education, 5(3), 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/074193258400500306.
Strickland, W. D., Boon, R. T., & Spencer, V. G. (2013). The effects of repeated reading on the fluency and comprehension skills of elementary-age students with learning disabilities (LD), 2001-2011: A review of research and practice. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 11(1), 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219416638028.
Suggate, S. P. (2016). A meta-analysis of the long-term effects of phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, and reading comprehension interventions. Journal of learning disabilities, 49(1), 77–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219414528540.
Swanson, H. L., & Alexander, J. E. (1997). Cognitive processes as predictors of word recognition and reading comprehension in learning-disabled and skilled readers: Revisiting the specificity hypothesis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89(1), 128–158.
Swanson, H. L., & Ashbaker, M. H. (2000). Working memory, short-term memory, speech rate, word recognition and reading comprehension in learning disabled readers: Does the executive system have a role? Intelligence, 28(1), 1–30.
Swanson, H. L., & Jerman, O. (2007). The influence of working memory on reading growth in subgroups of children with reading disabilities. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 96, 249–283.
Tan, A., & Nicholson, T. (1997). Flashcards revisited: Training poor readers to read words faster improves their comprehension of text. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89(2), 276–288. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.89.2.276.
Therrien, W. J. (2004). Fluency and comprehension gains as a result of repeated reading: A meta-analysis. Remedial and special education, 25(4), 252–261. https://doi.org/10.1177/07419325040250040801.
Torgesen, J. K. (1997). Preventive and remedial interventions for children with severe reading disabilities. Learning Disabilities: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 8(1), 51–61 ISSN: ISSN-1046-6819.
Torgesen, J. K., Alexander, A. W., Wagner, R. K., Rashotte, C. A., Voeller, K. K., & Conway, T. (2001). Intensive remedial instruction for children with severe reading disabilities: Immediate and long-term outcomes from two instructional approaches. Journal of learning disabilities, 34(1), 33–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221940103400104.
Torgesen, J. K., Morgan, S. T., & Davis, C. (1992). Effects of two types of phonological awareness training on word learning in kindergarten children. Journal of Educational psychology, 84(3), 364–370. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.84.3.364.
Troyer, A. K., Moscovitch, M., & Winocur, G. (1997). Clustering and switching as two components verbal fluency: Evidence from younger and older healthy adults. Neuropsychology, 11, 138–146.
Valdois, S., Guinet, E., & Embs, J. L. (2014). EVADYS: outils diagnostic des troubles de l’empan VA. Happy Neuron.
Varvara, P., Varuzza, C., Sorrentino, A. C. P., Vicari, S., & Menghini, D. (2014). Executive functions in developmental dyslexia. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, Article 120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00120.
Vellutino, F. R., Scanlon, D. M., Sipay, E. R., Small, S. G., Pratt, A., Chen, R., & Denckla, M. B. (1996). Cognitive profiles of difficult-to-remediate and readily remediated poor readers: Early intervention as a vehicle for distinguishing between cognitive and experiential deficits as basic causes of specific reading disability. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88(4), 601–638. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.88.4.601.
Wechsler, D. (2014). Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children–Fifth Edition technical and interpretive manual. San Antonio, TX: NCS Pearson.
Weckerly, J., Wulfeck, B., & Reilly, J. (2001). Verbal fluency deficits in children with specific language impairment: slow rapid naming or slow to name? Child Neuropsychology, 7(3), 142–152. https://doi.org/10.1076/chin.7.3.142.8741.
Wexler, J., Vaughn, S., Edmonds, M., & Reutebuch, C. K. (2008). A synthesis of fluency interventions for secondary struggling readers. Reading and Writing, 21(4), 317–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-007-9085-7.
White, S., Milne, E., Rosen, S., Hansen, P. C., Swettenham, J., Frith, U., et al. (2006). The role of sensorimotor impairments in dyslexia: A multiple case study of dyslexic children. Developmental Science, 9(3), 237–255.
Willcutt, E. G., & Pennington, B. F. (2000). Psychiatric comorbidity in children and adolescents with reading disability. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 41(8), 1039–1048. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00691.
Ziegler, J. C., & Goswami, U. (2005). Reading acquisition, developmental dyslexia, and skilled reading across languages: a psycholinguistic grain size theory. Psychological bulletin, 131(1), 3–29. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.131.1.3.
Ziegler, J., Perry, C., & Zorzi, M. (2019). Modeling the variability of developmental dyslexia. In L. Verhoeven, C. Perfetti, & K. Pugh (Eds.), Developmental dyslexia across languages and writing systems (pp. 350–371). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108553377.016.
Ziegler, J. C., PerrY, C., & Zorzi, M. (2014). Modelling reading development through phonological decoding and self-teaching: Implications for dyslexia. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 369(1634), 20120397.
Ziegler, J. C., Pech-Georgel, C., Dufau, S., & Grainger, J. (2010). Rapid processing of letters, digits, and symbols: What purely visual-attentional deficit in developmental dyslexia? Developmental Science, 13, F8–F14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2010.00983.x.
Zoubrinetzky, R., Bielle, F., & Valdois, S. (2014). New insights on developmental dyslexia subtypes: heterogeneity of mixed reading profiles. PloS one, 9(6), e99337. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099337.
Zoubrinetzky, R., Collet, G., Nguyen-Morel, M. A., Valdois, S., & Serniclaes, W. (2019). Remediation of allophonic perception and visual attention span in developmental dyslexia : A joint assay. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01502.
Acknowledgements
This work was performed within the framework of the LABEX CORTEX (ANR-11-LABX-0042) of Université de Lyon, within the program “Investissements d’Avenir” (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR). The authors gratefully acknowledge all the children who participated in this study. Special thanks are due to the speech therapists who are involved in the remedial intervention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leloup, G., Anders, R., Charlet, V. et al. Improving reading skills in children with dyslexia: efficacy studies on a newly proposed remedial intervention—repeated reading with vocal music masking (RVM). Ann. of Dyslexia 71, 60–83 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-021-00222-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-021-00222-4