Abstract
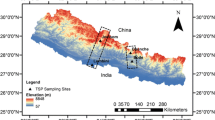
Based on more than 300 atmospheric TSP and PM2.5 samples collected at five sites over China in 2007 and 2008, characteristics, sources, and interactions of the major water-soluble species were investigated for a better understanding of their role in urban air quality and offshore eco-environment. From the dust source regions in Northwestern China to an offshore isle over the East China Sea, concentration levels and fine/coarse particle distributions of five representative water-soluble components were well elucidated, reflecting the distinct differences of geo-history, location, and present economic situation among the target areas. NO3−/SO42− mass ratios reflected significant divergence of motorization among the studied regions. Specifically, a case study during the World Car-Free Day proved that traffic restriction measures could indeed help mitigate the aerosol species formed from vehicle emissions. Investigation on the molar concentration stoichiometry and mass percentage variations of particulate NO3−, SO42−, and NH4+ revealed that NH3 was a driving factor in the formation of major secondary water-soluble ions in atmospheric fine particles over urban areas. Based on the prevailing wind analysis, observation over an offshore isle clearly indicated the influence of the relative strength of anthropogenic sources and ocean-related natural sources on the formation and size distribution of MSA (methanesulfonic acid), a major water-soluble organic component in aerosol. Annual dry deposition flux of particulate NO3− and NH4+ over the East China Sea was estimated based on the strength of an improved calculation formula. Reductive nitrogen was found to be the major form of the deposited atmospheric inorganic nitrogen, accounting for ~ 69% of the total nitrogen depositions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard CL, Tanenbaum SJ (2003) Differences between weekday and weekend air pollutant levels in South California. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 53:816–828
Chang YH, Zhou Z, Deng CR, Huang K, Collett JL, Lin J, Zhuang GS (2016) The importance of vehicle emissions as a source of atmospheric ammonia in the megacity of Shanghai. Atmos Chem Phys 16:3577–3594
Chen G, Davis DD, Kasibhatla P, Bandy AR, Thornton DC, Huebert BJ, Clarke AD, Blomquist BW (2000) A study of DMS oxidation in the tropics: comparison of Christmas Island field observations of DMS, SO2, and DMSO with model simulations. J Atmos Chem 37:137–160
Chen YL, Chen HY (2003) Nitrate-based new production and its relationship to primary production and chemical hydrography in spring and fall in the East China Sea. Deep Sea Res PT II 50:1249–1264
Chinkin LR, Coe DL, Funk TH, Hafner HR, Roberts PT, Ryan PA, Lawson DR (2003) Weekday versus weekend activity patterns for ozone precursor emissions in California’s South Coast Air Basin. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 53:829–843
Cornell S, Rendell A, Jickells T (1995) Atmospheric inputs of dissolved organic nitrogen to the oceans. Nature 376:243–246
Dong YQ, Chen CH, Huang C, Wang HL, Li L, Dai P, Jia JH (2009) Anthropogenic emissions and distribution of ammonia over the Yangtze River Delta. Acta Scien Circum 29:1611–1617 (Chinese)
EPA (2003) National air Quality and emissions trends report. Office of air Quality Planning and Standards, Research Triangle Park, NC
Fraser MP, Cass GR (1998) Detection of excess ammonia emissions from in-use vehicles and the implications for fine particle control. Environ Sci Technol 32:1053–1057
Galloway JN (1995) Acid deposition: perspectives in time and space. Water Air Soil Poll 85:15–24
Galloway JN, Howarth RW, Michaels AF, Nixon SW, Prospero JM, Dentener FJ (1996) Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets of the North Atlantic Ocean and its watershed. Biogeochemistry 35:3–25
Gao Y, Arimoto R, Zhou MY, Merrill JT, Duce RA (1992) Relationships between the dust concentrations over eastern Asia and the remote North Pacific. J Geophys Res 97:9867–9872
Gao Y, Arimoto R, Duce RA, Chen LQ, Zhou MY, Gu DY (1996) Atmospheric non-sea-salt sulfate, nitrate and methanesulfonate over the China Sea. J Geophys Res 101:12601–12611
Goebes MD, Strader R, Davidson C (2003) An ammonia emission inventory for fertilizer application in the United States. Atmos Environ 37:2539–2550
Huang K, Zhuang GS, Li J, Wang QZ, Sun YL, Lin YF (2010) Mixing of Asian dust with pollution aerosol and the transformation of aerosol components during the dust storm over China in spring 2007. J Geophys Res 115:1307–1314
Huebert BJ, Zhuang L, Howell S, Noone K, Noone B (1996) Sulfate, nitrate, methanesulfonate, chloride, ammonium, and sodium measurements from ship, island, and aircraft during the Atlantic stratocumulus transition, experiment/marine aerosol gas exchange. J Geophys Res 101:4413–4423
Jassby AD, Reuter JE, Axler RP, Goldman CR, Hackley SH (1994) Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in the annual nutrient load of Lake Tahoe (California-Nevada). Water Resour Res 30:2207–2216
Jiang YL, Zhuang GS, Wang QZ, Liu TN, Huang K, Fu JS, Li J, Lin YF, Zhang R, Deng CR (2014) Aerosol oxalate and its implication to haze pollution in Shanghai, China. Chin Sci Bull 59:227–238
Jickells TD (2002) Emissions from the oceans to the atmosphere, deposition from the atmosphere to the oceans and the interactions between them. In: Steffen W, Jager J, Carson DA, Bradshaw C (eds) Challenges of a changing earth. Springer, Berlin, pp 93–96
Jung J, Lee H, Kim YJ, Liu X, Zhang Y, Gu J, Fan S (2009) Aerosol chemistry and the effect of aerosol water content on visibility impairment and radiative forcing in Guangzhou during the 2006 Pearl River Delta campaign. J Environ Manag 90:3231–3244
Kang CM, Lee HS, Kang BW, Lee SK, Sunwoo Y (2004) Chemical characteristics of acidic gas pollutants and PM2.5 species during hazy episodes in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos Environ 38:4749–4760
Kean AJ, Littlejohn D, Ban-Weiss GA, Harley RA, Kirchstetter TW, Lunden MM (2009) Trends in on-road vehicle emissions of ammonia. Atmos Environ 43:1565–1570
Legrand M, Sciare J, Jourdian B, Genthon C (2001) Subdaily variations of atmospheric dimethylsulfide, dimethylsulfoxide, methanesulfonate, and non- sea-salt sulfate aerosols in the atmospheric boundary layer at Dumont d’Urvile (coastal Antarctica) during summer. J Geophys Res 106:14409–14422
Li J (2009) Characteristics, source, long-range transport of dust aerosol over the central Asia and its potential effect on global change. Fudan University (Chinese), Dissertation
Mackey KRM, Hunter D, Fischer EV, Jiang YL, Allen B, Chen Y, Liston A, Reuter J, Schladow G, Paytan A (2013) Aerosol-nutrient-induced picoplankton growth in Lake Tahoe. J Geophys Res 118:1054–1067
Moeckli MA, Fierz M, Sigrist MW (1996) Emission factors for ethene and ammonia from a tunnel study with a photoacoustic trace gas detection system. Environ Sci Technol 30:2864–2867
Nakamura T, Matsumoto K, Uematsu M (2005) Chemical characteristics of aerosols transported from Asia to the East China Sea: an evaluation of anthropogenic combined nitrogen deposition in autumn. Atmos Environ 39:1749–1758
Paerl HW (1995) Coastal eutrophication in relation to atmospheric nitrogen deposition—current perspectives. Ophelia 41:237–259
Paerl HW, Whittal DR (1999) Anthropogenically-derived atmospheric nitrogen deposition, marine eutrophication and harmful algal bloom expansion: is there a link? Ambio 28:307–311
Pakkanen TA, Kerminen VM, Korhonen CH, Hillamo RE, Aarnio P, Koskentalo T, Maenhaut W (2001) Urban and rural ultrafine (PM0.1) particles in the Helsinki area. Atmos Environ 35:4593–4607
Park SJ, Yoon TI, Bae JH, Seo HJ, Park HJ (2001) Biological treatment of waste-water containing dimethyl sulphoxide from the semiconductor industry. Process Biochem 36:579–589
Prospero JM, Barrett K, Church T, Dentener F, Duce RA, Galloway JN, Levy H, Moody J, Quinn P (1996) Atmospheric deposition of nutrients to the North Atlantic. Biogeochemistry 35:27–73
Saltzman ES, Savoie DL, Zika RG, Prospero JM (1983) Methane sulfonic acid in the marine atmosphere. J Geophys Res 88:10897–10902
Savioe DL, Prospero JM, Arimoto M, Duce RA (1994) Non-sea-salt sulfate and methanesulfonate at American Samoa. J Geophys Res 99:3587–3596
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (2006) Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change. Wiley-Interscience, San Francisco
Shon ZH, Kim KH, Song SK (2011) Long-term trend in NO2 and NOx levels and their emission ratio in relation to road traffic activities in East Asia. Atmos Environ 45:3120–3131
Spokes LJ, Jickells TD (2005) Is the atmosphere really an important source of reactive nitrogen to coastal waters? Cont Shelf Res 25:2022–2035
Stevens RK, King F, Bell J, Whitfield J (1988) Measurement of the chemical species that contribute to urban haze. 81st Annual Meeting of Air Pollution Control Association. Dallas, Texas
Sun J, Liu T (2006) The age of the Taklimakan Desert. Science 312:1621
Sun YL, Zhuang GS, Wang Y, Han LH, Guo JH, Dan M, Zhang WJ, Wang ZF (2004) The air-borne particulate pollution at Beijing-concentrations, composition, distribution, and sources of Beijing aerosol. Atmos Environ 38:5991–6004
Sun YL, Zhuang GS, Tang AH, Wang Y, An ZS (2006) Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 in haze-fog episodes in Beijing. Environ Sci Technol 41:3148–3155
Wang QZ, Zhuang GS, Li J, Huang K, Zhang R, Jiang YL, Lin YF, Fu JS (2011) Mixing of dust with pollution on the transport path of Asian dust—revealed from the aerosol over Yulin, the north edge of loess plateau. Sci Total Environ 409:573–581
Wang SL, Chai FH, Zhang YH, Zhou LD, Wang QL (2004) Analysis on the sources and characters of particles in Chengdu. Sci Geogr Sin 24:488–492
Wang QZ, Zhuang GS, Huang K, Liu TN, Deng CR, Xu J, Lin YF, Guo ZG, Chen Y, Fu QY, Fu JS, Chen JK (2015) Probing the severe haze pollution in three typical regions of China: characteristics, sources and regional impacts. Atmos Environ 120:76–88
Wang QZ, Zhuang GS, Huang K, Liu TN, Lin YF, Deng CR, Fu QY, Fu JS, Chen JK, Zhang WJ, Yiming M (2016) Evolution of particulate sulfate and nitrate along the Asian dust pathway: secondary transformation and primary pollutants via long-range transport. Atmos Res 169:86–95
Warneck P (1999) Chemistry of the natural atmosphere. Academic Press, London
Xiao HY, Liu CQ (2004) Chemical characteristics of water-soluble components in TSP over Guiyang, SW China, 2003. Atmos Environ 38:6297–6306
Xu J, Wang Q, Deng C, McNeill VF, Fankhauser A, Wang F, Zheng X, Shen J, Huang K, Zhuang G (2018) Insights into the characteristics and sources of primary and secondary organic carbon: high time resolution observation in urban Shanghai. Environ Pollut 233:1177–1187
Xu L, Zhou J, Guo Y, Wu T, Chen T, Zhong Q, Yuan D, Chen P, Ou C (2017) Spatiotemporal pattern of air quality index and its associated factors in 31 Chinese provincial capital cities. Air Qual Atmos Health 10(5):601–609
Yan Y, He Q, Song Q, Guo L, He Q, Wang X (2017) Exposure to hazardous air pollutants in underground car parks in Guangzhou, China. Air Qual Atmos Health 10(5):555–563
Yao J, Wang G, Lin J, Fan X, Geng Y, Wei N, Shan J, Li Y, Lu W (2010) Relationships between atmospheric particles and visibility in Shanghai. J Meteor Environ 26:17–21 (Chinese)
Yao XH, Chan CK, Fang M, Cadle S, Chan T, Mulawa P, He KB, Ye BM (2002) The water-soluble ionic composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai and Beijng, China. Atmos Environ 36:4223–4234
Yin F, Grosjean D, Flagan RC, Seinfeld JH (1990a) Photooxidation of dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide. II: mechanism evaluation. J Atmos Chem 11:365–399
Yin F, Grosjean D, Seinfeld JH (1990b) Photooxidation of dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide. I: mechanism development. J Atmos Chem 11:309–364
Yuan H, Wang Y, Zhuang GS (2004) MSA in Beijing aerosol. Chin Sci Bull 49:1020–1025
Zhang Y, Yu Q, Ma WC, Chen LM (2010) Atmospheric deposition of inorganic nitrogen to the eastern China seas and its implications to marine biogeochemistry. J Geophys Res 115:D00K10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD012814
Zhao B, Wang SX, Liu H, Xu JY, Fu K, Klimont Z, Hao JM, He KB, Cofala J, Amann M (2013) NOx emissions in China: historical trends and future perspective. Atmos Chem Phys 13:9869–9897
Zhu L, Chen Y, Guo L, Wang FJ (2013) Estimate of dry deposition fluxes of nutrients over the East China Sea: the implication of aerosol ammonium to non-sea-salt sulfate ratio to nutrient deposition of coastal oceans. Atmos Environ 69:131–138
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41429501 (fund for collaboration with overseas scholars), 91644105, and 41405115). Y.L.J., M.L., and Z.Z. would like to acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21607056) and Natural Fund of Guangdong Province (2015A030313339). C.X. is sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (15ZR1434900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.J., K.H., and C.D. conceived the study. Y.J., K.H., G.Z., and G.Y. conducted the data analysis and wrote the paper. All authors contributed to interpreting the results and writing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Zhuang, G., Wang, Q. et al. Impact of mixed anthropogenic and natural emissions on air quality and eco-environment—the major water-soluble components in aerosols from northwest to offshore isle . Air Qual Atmos Health 11, 521–534 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0557-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0557-5