Abstract
Aim
Brucellosis is a zoonotic infection that can affect almost every organ. A mild elevation of aminotransferase levels is usually observed in liver involvement. However, the development of clinical hepatitis is rare. In this study, we aimed to present the hospitalized cases with brucellosis hepatitis in our clinic in a 13-year period.
Methods
A hundred and three patients with significant hepatobiliary involvement, diagnosed by microbiological analysis, were included in the study. For the presence of hepatitis, it was required that the aminotransferases must be ≥ 5 times more than the upper limit and/or the total bilirubin level must be ≥ 2 mg/dl and/or the local hepatic lesion must be demonstrated.
Results
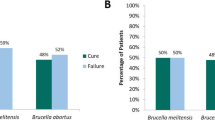
Of the cases, 35.9%, 17.5%, and 46.6% had clinical hepatitis, cholestatic hepatitis, and both clinical and cholestatic hepatitis, respectively. The most frequent symptom was fever (85.4%) while the most preferred treatment options were combinations containing aminoglycosides. It was observed that the mean time-interval to decrease to normal values of ALT, AST, and bilirubin values was 15.2 ± 7.8 days while the patients having their treatment regimens. In our study, which focused on liver involvement, it was found that a chronic liver disease did not develop in any of the cases.
Conclusion
Our study showed that, even in the presence of hepatitis, clinical response and laboratory improvement were high with appropriate treatment. It was observed that the improvement in aminotransferases and total bilirubin values delayed in the cases with blood culture positivity, secondary organ involvement, and alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase > 1.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Hull NC, Schumaker BA (2018) Comparisons of brucellosis between human and veterinary medicine. Infect Ecol Epidemiol 8(1):1500846. https://doi.org/10.1080/20008686.2018.1500846
Giambartolomei GH, Delpino MV (2019) Immunopathogenesis of hepatic brucellosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 9:423. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00423
Kokoglu OF, Hosoglu S, Geyik MF et al (2006) Clinical and laboratory features of brucellosis in two university hospitals in Southeast Turkey. Trop Doct 36(1):49–51. https://doi.org/10.1258/004947506775598752
Akritidis N, Tzivras M, Delladetsima I et al (2007) The liver in brucellosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(9):1109–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2006.08.010
Gül HC, Erdem H (2020) Brucellozis (Brucella Species). Principles and practice of ınfectious diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier 2753–8
Buzgan T, Karahocagil MK, Irmak H et al (2010) Clinical manifestations and complications in 1028 cases of brucellosis: a retrospective evaluation and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis 14(6):e469–e478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2009.06.031
Ozturk-Engin D, Erdem H, Gencer S et al (2014) Liver involvement in patients with brucellosis: results of the Marmara study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 33(7):1253–1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2064-4
Karahocagil MK (2012) Klinik. Turkiye Klinikleri J Inf Dis-Special Topics 5(1):24–33
Aygen B, Doğanay M, Sümerkan B et al (2002) Clinical manifestations, complications and treatment of brucellosis: a retrospective evaluation of 480 patients. Medecine et maladies infectieuses 32(9):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0399-077x(02)00403-1
Demiroğlu YZ, Turunç T, Çalışkan H et al (2007) Brucellosis: retrospective evaluation of the clinical, laboratory and epidemiological features in 151 cases. Mikrobiyol Bul 41:517–527 (PMID: 18173070)
Gonen I, Sozen H, Kaya O et al (2014) Brucellosis: evaluation of 201 cases in an endemic area of Mediterranean Basin. Acta Medica Mediterranea 30:121–126
Spink WW, Hoffbauer FW, Walker WW et al (1949) Histopathology of the liver in human brucellosis. J Lab Clin Med 34:40–58 (PMID: 18106408)
Young EJ, Hasanjani Roushan MR, Shafae S et al (2014) Liver histology of acute brucellosis caused by Brucella melitensis. Hum Pathol 45(10):2023–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2014.07.007
Guerra H, Deter RL, Williams RP (1973) Infection at the subcellular level IIDistribution and fate of intravenously injected brucellae with in phagocytic cells of guinea pigs. Infect Immun 8:694–699. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.8.5.694-699.1973
Geyik MF, Gür A, Nas K et al (2002) Musculoskeletal involvement in brucellosis in different age groups: a study of 195 cases. Swiss medical weekly. 23;132(7–8):98–105. https://doi.org/10.57187/smw.2002.09900
Al-Otaibi FE (2010) Acute acalculus cholecystitis and hepatitis caused by Brucella melitensis. J Infect Dev Ctries 4(7):464–467. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.618
Denk A, Ozden M (2015) A case of brucellosis presenting with acute hepatitis and bicytopenia. Infez Med 23(2):178–181 (PMID: 26110300)
Erdem I, Cicekler N, Mert D et al (2005) A case report of acute hepatitis due to brucellosis. Int J Infect Dis 9(6):349–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2004.12.002
Fernandez Fernandez MA, de Paso G, Mora M, Mateos Checa R et al (2010) Brucellosis infection presenting with cholestasis. Int J Infect Dis 14(Suppl 3):e322–e324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2010.04.001
Garcia Casallas JC, Villalobos Monsalve W, Arias Villate SC et al. (2018) Acute liver failure complication of brucellosis infection: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 9;12(1):62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1576-4
Ulug M, Celen MK, Ayaz C (2010) An unusual presentation of brucellosis: acute hepatitis. Braz J Infect Dis 14(6):641–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1413-8670(10)70127-6
Débat-Zoguéreh D et al (1995) Necrotizing hepatic granuloma of brucellosis origin. Apropos of a case. La Revue de Medecine Interne.16(1):63–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/0248-8663(96)80666-7
Pons J, Teyssau H, Bureau M et al (1981) Hepatic calcifications in isolated necrotizing, granulomatous hepatitis due to Brucella. A case report and review of the literature (author's transl). Journal de radiologie. 62(10):521–5. PMID: 22087106
Aygen B, Sümerkan B, Doğanay M et al (1998) Prostatitis and hepatitis due to Brucella melitensis: a case report. J Infect 36(1):111–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-4453(98)93486-7
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the whole medical microbiology laboratory team of our hospital that contributed to the collections and interpretation of serological and culture tests for the diagnosis of brucellosis, and all the doctors, nurses, and staff of our clinic who played a role in the diagnosis and treatment of patients. This study was derived from the thesis of medical specialty “Brucellosis-associated acute hepatitis: Our 13-year experience”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YA and AIB designed the study and directed the study design. YA, AIB, and MC reviewed the literature and evaluated appropriate datasets. YA and MC performed statistical analysis. YA and AIB wrote the draft of the article. All authors contributed to discussion of results, interpretation and writing of the article and jointly approved the final article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of ınterest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arslan, Y., Baran, A.İ. & Çelik, M. Brucellosis-associated hepatitis. Ir J Med Sci 193, 149–156 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-023-03382-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-023-03382-x