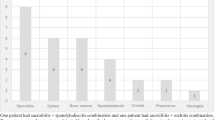
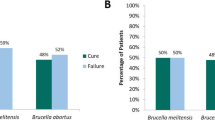
Abstract
Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease that primarily affects the reticuloendothelial system. But, the extent of liver damage in due course of the disease is unclear. This study included 325 brucellosis patients with significant hepatobiliary involvement identified with microbiological analyses from 30 centers between 2000 and 2013. The patients with ≥5 times of the upper limit of normal for aminotransferases, total bilirubin level ≥2 mg/dl or local liver lesions were enrolled. Clinical hepatitis was detected in 284 patients (87.3 %) and cholestasis was detected in 215 (66.1 %) patients. Fatigue (91 %), fever (86 %), sweating (83 %), arthralgia (79 %), and lack of appetite (79 %) were the major symptoms. Laboratory tests showed anemia in 169 (52 %), thrombocytopenia in 117 (36 %), leukopenia in 81 (25 %), pancytopenia in 42 (13 %), and leukocytosis in 20 (6 %) patients. The most commonly used antibiotic combinations were doxycycline plus an aminoglycoside (n = 73), doxycycline plus rifampicin (n = 71), doxycycline plus rifampicin and an aminoglycoside (n = 27). The duration of ALT normalization differed significantly in three treatment groups (p < 0.001). The use of doxycycline and an aminoglycoside in clinical hepatitis showed better results compared to doxycycline and rifampicin or rifampicin, aminoglycoside, doxycycline regimens (p < 0.05). However, the length of hospital stay did not differ significantly between these three combinations (p > 0.05). During the follow-up, treatment failure occurred in four patients (1 %) and relapse was seen in three patients (0.9 %). Mortality was not observed. Hepatobiliary involvement in brucellosis has a benign course with suitable antibiotics and the use of doxycycline and an aminoglycoside regimen seems a better strategy in select patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal
- RBT:
-
Rose Bengal test
- STA:
-
Standard tube agglutination test
- ESR:
-
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- DOXAG:
-
Doxycycline plus an aminoglycoside
- DOXRIF:
-
Doxycycline plus rifampicin
- DOXRIFAG:
-
Doxycycline plus rifampicin and an aminoglycoside
References
Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, Christou L, Tsianos EV (2006) The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis 6(2):91–99
Albayrak A, Albayrak F (2011) Hepatic granulomas associated with brucellosis: Hepatic granulomas and brucellosis. Hepat Mon 11(1):1–2
Buzgan T, Karahocagil MK, Irmak H, Baran AI, Karsen H, Evirgen O, Akdeniz H (2010) Clinical manifestations and complications in 1028 cases of brucellosis: a retrospective evaluation and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis 14(6):e469–e478
Al-Otaibi FE (2010) Acute acalculus cholecystitis and hepatitis caused by Brucella melitensis. J Infect Dev Ctries 4(7):464–467
Erdem I, Cicekler N, Mert D, Yucesoy-Dede B, Ozyurek S, Goktas P (2005) A case report of acute hepatitis due to brucellosis. Int J Infect Dis 9(6):349–350
Gotuzzo E, Carillo C (1998) Brucella. In: Gorbach SL, Bartlett JG, Blacklov NR (eds) Infectious diseases. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 1837–1845
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, Cohen J, Opal SM, Vincent JL, Ramsay G (2003) 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med 31(4):1250–1256
de Benoist B, McLean E, Egli I, Cogswell M (2008) Worldwide prevalence of anaemia 1993-2005. World Health Organization, Geneva
Miller A, Green M, Robinson D (1983) Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 286(6361):266
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2009) EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of cholestatic liver diseases. J Hepatol 51(2):237–267
Kratzer W, Fritz V, Mason RA, Haenle MM, Kaechele V (2003) Factors affecting liver size: a sonographic survey of 2080 subjects. J Ultrasound Med 22(11):1155–1161
Pozo AL, Godfrey EM, Bowles KM (2009) Splenomegaly: investigation, diagnosis and management. Blood Rev 23(3):105–111
Erdem H, Ulu-Kilic A, Kilic S, Karahocagil M, Shehata G, Eren-Tulek N, Yetkin F, Celen MK, Ceran N, Gul HC, Mert G, Tekin-Koruk S, Dizbay M, Inal AS, Nayman-Alpat S, Bosilkovski M, Inan D, Saltoglu N, Abdel-Baky L, Adeva-Bartolome MT, Ceylan B, Sacar S, Turhan V, Yilmaz E, Elaldi N, Kocak-Tufan Z, Ugurlu K, Dokuzoguz B, Yilmaz H, Gundes S, Guner R, Ozgunes N, Ulcay A, Unal S, Dayan S, Gorenek L, Karakas A, Tasova Y, Usluer G, Bayindir Y, Kurtaran B, Sipahi OR, Leblebicioglu H (2012) Efficacy and tolerability of antibiotic combinations in neurobrucellosis: results of the istanbul study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56(3):1523–1528
Tekin-Koruk S, Erdem H, Koruk I, Erbay A, Tezer-Tekce Y, Erbay AR, Dayan S, Deveci O, Inan A, Engin DO, Guner R, Dikici N, Doyuk-Kartal E, Kurtaran B, Pehlivanoglu F, Sipahi OR, Yalci A, Yemisen M, Alp-Cavus S, Gencer S, Guzel G, Oncul O, Parlak M, Kazak E, Tulek N, Ulcay A, Savasci U (2012) Management of Brucella endocarditis: results of the Gulhane study. Int J Antimicrob Agents 40(2):145–150
Caballeria E, Masso RM, Arago JV, Sanchis A (1992) Ascites as the first manifestation of Brucella granulomatous hepatitis. J Hepatol 15(3):415–416
Mc Cullough NB, Eisele CW (1951) Brucella hepatitis leading to cirrhosis of the liver. AMA Arch Intern Med 88(6):793–802
Debat-Zoguereh D, Badiaga S, Uzan E, Le Treut YP, Lebreuil G, Bourgeade A (1995) Necrotizing hepatic granuloma of brucellosis origin. Apropos of a case. Rev Med Interne 16(1):63–66
Cervantes F, Bruguera M, Carbonell J, Force L, Webb S (1982) Liver disease in brucellosis. A clinical and pathological study of 40 cases. Postgrad Med J 58(680):346–350
Calik S, Gokengin D (2011) Human brucellosis in Turkey: A review of the literature between 1990 and 2009. Turk J Med Sci 41(3):549–555
Bzeizi KI, Benmousa A, Sanai FM (2010) Coincidence of acute brucella hepatitis and dengue fever or serologic cross-reactivity? Saudi J Gastroenterol 16(4):299–301
Hizel K, Guzel O, Dizbay M, Karakus R, Senol E, Arman D, Aktas F, Ulutan F (2007) Age and duration of disease as factors affecting clinical findings and sacroiliitis in brucellosis. Infection 35(6):434–437
Bosilkovski M, Krteva L, Dimzova M, Kondova I (2007) Brucellosis in 418 patients from the Balkan Peninsula: exposure-related differences in clinical manifestations, laboratory test results, and therapy outcome. Int J Infect Dis 11(4):342–347
Bosilkovski M, Krteva L, Dimzova M, Vidinic I, Sopova Z, Spasovska K (2010) Human brucellosis in Macedonia—10 years of clinical experience in endemic region. Croat Med J 51(4):327–336
Hasanjani Roushan MR, Mohrez M, Smailnejad Gangi SM, Soleimani Amiri MJ, Hajiahmadi M (2004) Epidemiological features and clinical manifestations in 469 adult patients with brucellosis in Babol, Northern Iran. Epidemiol Infect 132(6):1109–1114
Ulug M, Celen MK, Ayaz C (2010) An unusual presentation of brucellosis: acute hepatitis. Braz J Infect Dis 14(6):641–642
Franco MP, Mulder M, Gilman RH, Smits HL (2007) Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis 7(12):775–786
Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E (2005) Brucellosis. N Engl J Med 352(22):2325–2336
Erdem H, Kilic S, Sener B, Acikel C, Alp E, Karahocagil M, Yetkin F, Inan A, Kecik-Bosnak V, Gul HC, Tekin-Koruk S, Ceran N, Demirdal T, Yilmaz G, Ulu-Kilic A, Ceylan B, Dogan-Celik A, Nayman-Alpat S, Tekin R, Yalci A, Turhan V, Karaoglan I, Yilmaz H, Mete B, Batirel A, Ulcay A, Dayan S, Seza Inal A, Ahmed SS, Tufan ZK, Karakas A, Teker B, Namiduru M, Savasci U, Pappas G (2013) Diagnosis of chronic brucellar meningitis and meningoencephalitis: the results of the Istanbul-2 study. Clin Microbiol Infect 19(2):E80–86
Erdem H, Inan A, Elaldi N, Tekin R, Gulsun S, Ataman-Hatipoglu C, Beeching N, Deveci O, Yalci A, Bolukcu S, Dagli O (2014) Respiratory system involvement in brucellqosis: rhe results of the Kardelen study. Chest 145(1):87–94
Sonika U, Kar P (2012) Tuberculosis and liver disease: management issues. Trop Gastroenterol 33(2):102–106
Uygur-Bayramicli O, Dabak G, Dabak R (2003) A clinical dilemma: abdominal tuberculosis. World J Gastroenterol 9(5):1098–1101
Tan KK, Chen K, Sim R (2009) The spectrum of abdominal tuberculosis in a developed country: a single institution’s experience over 7 years. J Gastrointest Surg 13(1):142–147
Malik M, Kurban L, Murray GI, Alkari B (2011) Isolated tuberculosis of the liver: a diagnostic challenge. BMJ Case Rep 2011;pii: bcr1220103654
Perez Fernandez T, Lopez Serrano P, Tomas E, Gutierrez ML, Lledo JL, Cacho G, Santander C, Fernandez Rodriguez CM (2004) Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to cholestatic liver disease. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 96(1):60–73
Colmenero JD, Reguera JM, Martos F, Sanchez-De-Mora D, Delgado M, Causse M, Martin-Farfan A, Juarez C (1996) Complications associated with Brucella melitensis infection: a study of 530 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 75(4):195–211
Ko J, Splitter GA (2003) Molecular host-pathogen interaction in brucellosis: current understanding and future approaches to vaccine development for mice and humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 16(1):65–78
Dornand J, Gross A, Lafont V, Liautard J, Oliaro J, Liautard JP (2002) The innate immune response against Brucella in humans. Vet Microbiol 90(1–4):383–394
Rodriguez-Zapata M, Alvarez-Mon M, Salmeron I, Prieto A, Manzano L, Salmeron OJ, Carballido J (1996) Diminished T lymphocyte proliferative response to polyclonal mitogens in acute brucellosis patients. Infection 24(2):115–120
Rodriguez-Zapata M, Salmeron I, Manzano L, Salmeron OJ, Prieto A, Alvarez-Mon M (1996) Defective interferon-gamma production by T-lymphocytes from patients with acute brucellosis. Eur J Clin Invest 26(2):136–140
Ugalde RA (1999) Intracellular lifestyle of Brucella spp. Common genes with other animal pathogens, plant pathogens, and endosymbionts. Microbes Infect 1(14):1211–1219
Hashemi SH, Gachkar L, Keramat F, Mamani M, Hajilooi M, Janbakhsh A, Majzoobi MM, Mahjub H (2012) Comparison of doxycycline-streptomycin, doxycycline-rifampin, and ofloxacin-rifampin in the treatment of brucellosis: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Infect Dis 16(4):e247–e251
Solera J, Espinosa A, Geijo P, Martinez-Alfaro E, Saez L, Sepulveda MA, Ruiz-Ribo MD (1996) Treatment of human brucellosis with netilmicin and doxycycline. Clin Infect Dis 22(3):441–445
Garcia S, del Pozo J, Solera J (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials in the treatment of human brucellosis. PLoS One 7(2):e32090
Corbel MJ (2006) Brucellosis in humans and animals. WHO Press, World Health Organization, Geneva
Kursun E, Turunc T, Demiroglu Y, Arslan H (2013) Evaluation of four hundred and forty seven brucellosis cases. Intern Med 52(7):745–750
Solera J, Martinez-Alfaro E, Saez L (1994) Meta-analysis of the efficacy of the combination of + rifampicin and doxycycline in the treatment of human brucellosis. Med Clin (Barc) 102(19):731–738
Skalsky K, Yahav D, Bishara J, Pitlik S, Leibovici L, Paul M (2008) Treatment of human brucellosis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 336(7646):701–704
Baciewicz AM, Sokos DR, Cowan RI (2003) Aminoglycoside-associated nephrotoxicity in the elderly. Ann Pharmacother 37(2):182–186
Conflict of interest
We have no competing interests to declare.
Financial support
We did not receive any kind of financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk-Engin, D., Erdem, H., Gencer, S. et al. Liver involvement in patients with brucellosis: results of the Marmara study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 33, 1253–1262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2064-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2064-4