Abstract
Background
Regional distribution of adiposity and lean tissue mass are predictors of health risk that cannot be defined by body mass index but can be attained by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Age and sex-related adult ranges of whole-body and regional adiposity and lean tissue are not available for Irish men and women.
Aims
The aim of this study was to construct a DXA-based body composition profile of Irish adults, focusing on age- and sex-related difference in total and regional adiposity and lean tissue mass.
Methods
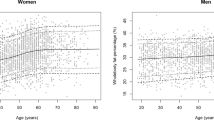
The study population comprised a convenience sample of 1606 participants, aged 18–81 years participating in the University of Limerick Body Composition study. Data were analysed to construct stature-normalised indices of body fat mass (BFMI), site-specific visceral adiposity, lean tissue mass (LTMI) and appendicular lean tissue mass (ALTMI).
Results
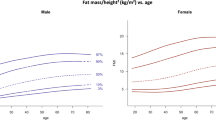
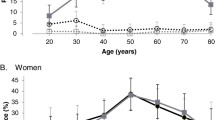
Compared to the young adult (18–29 years), BFMI was higher in women (p < 0.001) but plateaued in men aged >50 years. For men, age-related difference in LTMI was not evident but ALTMI was significantly lower in those >50 years. For women, there was evidence of significantly lower LTMI with advancing age and, similar to men, significantly lower ALTMI in those >50 years.
Conclusions
These data provide an insight into the age-related anthropometric phenotype of Irish adults. Centile data have been constructed that provide informative data of the age and sex-specific range of adiposity and lean tissue mass. These data may assist in identification of those at risk of aberrant, body composition-related disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, Graubard BI (2013) Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 309(1):71–82
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ôunpuu S, Bautista L, Franzosi MG, Commerford P, Lang CC, Rumboldt Z, Onen CL, Lisheng L (2005) Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case–control study. Lancet 366(9497):1640–1649
Rokholm B, Baker JL, Sorensen TI (2010) The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999—a review of evidence and perspectives. Obes Rev 11(12):835–846
McCarthy SN, Harrington KE, Kiely M, Flynn A, Livingstone MBA, Gibney M (2001) Analyses of the anthropometric data from the North/South Ireland Food Consumption Survey. Public Health Nutr 4(5a):1099–1106
Walton J (ed.) on behalf of the Irish Universities Nutrition Alliance (IUNA)(2011) National Adult Nutrition Survey. Summary report on food and nutrient intakes, physical measurements, physical activity patterns and food choice Motives. Dublin, Irish Universities Nutrition Alliance. http://www.iuna.net
Okorodudu DO, Jumean MF, Montori VM, Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Erwin PJ, Lopez-Jimenez F (2010) Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond) 34(5):791–799. doi:10.1038/ijo.2010
Calle EE, Thun M, Petrelli JM, Rodriguez C, Heath CW (1999) Body mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med 341(15):1097–1105
Baumgartner RN, Wayne S, Waters D, Janssen I, Gallagher D, Morley JE (2004) Sarcopenic obesity predicts instrumental activities of daily living disability in the elderly. Obes Res 12(12):1995–2004
Gallagher D, Visser M, De Meersman R, Sepulveda D, Baumgartner RN, Pierson RN, Harris T, Heymsfield SB (1997) Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: effects of age, gender, and ethnicity. J Appl Physiol 83(1):229–239
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinková E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 39(4):412–423
Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ et al (2011) Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc 12:249–256
Gallagher D, Ruts E, Visser M, Heshka S, Baumgartner RN, Wang J, Pierson RN, Pi-Sunyer FX, Heymsfield SB (2000) Weight stability masks sarcopenia in elderly men and women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279(2):E366–E375
Hangartner TN, Warner S, Braillon P, Jankowski L, Shepherd J (2013) The Official Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry: acquisition of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition and considerations regarding analysis and repeatability of measures. J Clin Densitom 16(4):520–536. doi:10.1016/j.jocd.2013.08.007
Ergun DL, Rothney MP, Oates MK, Xia Y, Wacker WK, Binkley NC (2013) Visceral adipose tissue quantification using Lunar Prodigy. J Clin Densitom 16(1):75–78
Rothney MP, Xia Y, Wacker WK, Martin F-P, Beaumont M, Rezzi S, Giusti V, Ergun DL (2013) Precision of a new tool to measure visceral adipose tissue (VAT) using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Obesity 21:E134–E136
Pan H, Cole TJ (2004) A comparison of goodness of fit tests for age-related reference ranges. Stat Med 23(11):1749–1765
Kuk JL, Saunders TJ, Davidson LE, Ross R (2009) Age-related changes in total and regional fat distribution. Ageing Res Rev 8(4):339–348
Bigaard J, Frederiksen K, Tjonneland A, Thomsen B, Overvad K, Heitmann BL, Sorensen TI (2004) Body fat and fat-free mass and all-cause mortality. Obes Res 12:1042–1049
Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Sierra-Johnson J, Korenfeld Y, Boarin S, Korinek J, Jensen MD, Parati G, Lopez-Jimenez F (2010) Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. Eur Heart J 31(6):737–746
Bazzocchi A, Diano D, Ponti F, Andreone A, Sassi C, Albisinni U, Marchesini G, Battista G (2013) Health and ageing: a cross-sectional study of body composition. Clin Nutr 32(4):569–578. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2012.10.004
Sayer AA, Robinson SM, Patel HP, Shavlakadze T, Cooper C, Grounds MD (2013) New horizons in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of sarcopenia. Age Ageing 42(2):145–150
Coin A, Sergi G, Minicuci N, Giannini S, Barbiero E, Manzato E, Pedrazzoni M, Minisola S, Rossini M, Del Puente A, Zamboni M, Inelmen EM, Enzi G (2008) Fat-free mass and fat mass reference values by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) in a 20–80 year-old Italian population. Clin Nutr 27(1):87–94
Shepherd JA, Baim S, Bilezikian JP, Schousboe JT (2013) Executive summary of the 2013 international society for clinical densitometry position development conference on body composition. J Clin Densitom 16(4):489–495
Goodpastor B, Krishnaswami S, Harris T, Katsiaras A, Kritchevsky SB, Simonsick E, Nevitt M, Holvoet P, Newman AB (2005) Obesity, regional body fat distribution, and the metabolic syndrome in older men and women. Arch Intern Med 165:777–783
Chang SH, Beason TS, Hunleth JM, Colditz GA (2012) A systematic review of body fat distribution and mortality in older people. Maturitas 72(3):175–191
Rothney MP, Catapano AL, Xia J, Wacker WK, Tidone C, Grigore L, Xia Y, Ergun DL (2013) Abdominal visceral fat measurement using dual-energy X-ray: association with cardiometabolic risk factors. Obesity 21(9):1798–1802
Kaul S, Rothney MP, Peters DM, Wacker WK, Davis CE, Shapiro MD, Ergun DL (2012) Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for quantification of visceral fat. Obesity 20(6):1313–1318
Leahy S, O’Neill C, Sohun R, Toomey C, Jakeman P (2013) Generalised equations for the prediction of percentage body fat by anthropometry in adult men and women aged 18–81 years. Br J Nutr 109(4):678–685
Leahy S, O’Neill C, Sohun R, Jakeman P (2012) A comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and bioelectrical impedance analysis to measure total and segmental body composition in healthy young adults. Eur J App Physiol 112(2):589–595
Leahy S, Toomey C, McCreesh K, O’Neill C, Jakeman P (2012) Ultrasound measurement of subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness accurately predicts total and segmental body fat of young adults. Ultrasound Med Biol 38(1):28–34
Toomey CM, Cremona A, Hughes K, Norton C, Jakeman P (2015) A review of body composition measurement in the assessment of health. Top Clin Nutr 30:16–32
Petak S, Barbu CG, Yu EW, Fielding R, Mulligan K, Sabowitz B, Wu CH, Shephard JA (2013) The Official Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry: body composition analysis reporting. J Clin Densitom 16(4):508–519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toomey, C., Leahy, S., McCreesh, K. et al. The body composition phenotype of Irish adults aged 18–81 years. Ir J Med Sci 185, 537–544 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1338-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1338-x