Abstract
Background
Although radiofrequency thermocoagulation is considered as a primary treatment for most patients with trigeminal neuralgia, neuronavigator-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation has been rarely reported. The object of this study was to assess the clinical value of neuronavigator-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
Methods
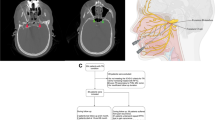
The radiofrequency thermocoagulation was performed in 100 cases of trigeminal neuralgia. The patients were positioned supine or sitting, under Hartel’s technique (reported by Sweet and Wepsic J Neurosurg 40:143–156, 1974), by anterior lateral facial approaches. The Gasserian ganglions were acupunctured, assisted by intraoperative CT scanning (3-digital reconstruction) and electrophysiology in order to accurately locate target.
Results
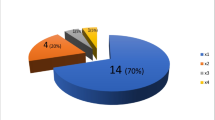
The needles located in oval foramen at the first puncture, the direction and position could be defined according to the electrophysiology examination. The pain alleviated immediately after operation. There occurred no serious complication and other nerve injury in all patients despite face numbness only.
Conclusions
3D-CT and electrophysiology Gasser’s ganglion locations can raise the success rate of puncture, enhance the safety and reduce the incidence of complication, showing high academic value and its promising future.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sweet WH, Wepsic JG (1974) Controlled thermocoagulation of trigeminal ganglion and rootlets for differential destruction of pain fibers. 1. Trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 40(2):143–156
Cheng-yuan Wu, Fan-gang Meng, Shu-jun Xu, Yu-guang Liu, Hong-wei Wang (2004) Selective percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: report on 1860 cases. Chinese Med J 117(3):467–470
Shu-jun Xu, Wen-hua Zhang, Teng Chen, Cheng-yuan Wu, Mao-de Zhou (2006) Neuronavigator-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of intractable trigeminal neuralgia. Chinese Med J 119(18):1528–1535
Kanpolat Y, Savas A, Bekar A et al (2001) Percutaneous controlled radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: 25-year experience with 1,600 patients. Neurosurgery 48:524–532
Burchiel KJ, Baumann TK (2004) Pathophysiology of trigeminal neuralgia: new evidence from a trigeminal ganglion intraoperative microneurographic recording. Case report. J Neurosurg 101:872–873
Lopez BC, Hamlyn PJ, Zakrzewska JM (2004) Systematic review of ablative neurosurgical techniques for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 54:973–982
Taha JM, JR Tew JM, Buncher CR (1995) A prospective 15-year follow up of 154 consecutive patients with trigeminal neuralgia treated by percutaneous stereotactic radiofrequency thermal rhizotomy. J Neurosurg 83(6):989–993
Tronnier VM, Rasche D, Hamer J et al (2001) Treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia:comparison of long-term outcome after radiofrequency rhizotomy and microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 48:1261–1268
Egan RA, Pless M, Shults WT (2001) Monocular blindness as a complication of trigeminal radiofrequency rhizotomy. Am J Ophthalmol 131:237–240
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W.C., Zhong, W.X., Li, S.T. et al. Neuronavigator-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Ir J Med Sci 181, 7–13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-011-0770-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-011-0770-9