Abstract
Background
Combined Fludarabine and Cyclophosphamide is now standard first-line therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) and the addition of Rituximab improves outcome.
Methods
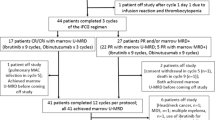
We adopted a modified Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide and Rituximab (FCR) protocol in treating 39 patients (median age 57 years) with progressive or advanced CLL. Depending on CR, treatment was given for four or six cycles.
Result
Twenty-six patients were treatment naïve and 13 were pre-treated. Twelve patients had progressive Binet stage A, 16 stage B and 11 stage C disease. The overall response rate (ORR) was 100%, with 75% achieving CR. Neutropenia was the major toxicity in 71/187 (38%) of the cycles. There were five deaths, two from infection and three from progressive disease. Twenty-six of 31 patients have maintained their post-treatment disease status for a median of 17 months (2–41).
Conclusion
We conclude that FCR is a feasible, well-tolerated and effective treatment for patients with CLL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keating M, Chiorazzi N, Messmer B et al (2003) Biology and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. American Society of Hematology Education Program, pp 153–175
Keating MJ, O’Brien S, Lerner S et al (1998) Long-term follow-up of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving fludarabine regimens as initial therapy. Blood 92(4):1165–1171
Flinn IW, Byrd JC, Morrison C et al (2000) Fludarabine and cyclophosphamide with filgrastim support in patients with previously untreated indolent lymphoid malignancies. Blood 96(1):71–75
Catovsky D, Richards S, Hillmen P (2005) Early results from LRF CLL4: a UK multicenter randomized trial. Blood, vol 106 (Abstract 716)
Almasri NM, Duque RE, Iturraspe J et al (1992) Reduced expression of CD20 antigen as a characteristic marker for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol 40(4):259–263. doi:10.1002/ajh.2830400404
Foran JM, Rohatiner AZ, Cunningham D et al (2000) European phase II study of rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) for patients with newly diagnosed mantle-cell lymphoma and previously treated mantle-cell lymphoma, immunocytoma, and small B-cell lymphocytic lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 18(2):317–324
O’Brien SM, Kantarjian H, Thomas DA et al (2001) Rituximab dose-escalation trial in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 19(8):2165–2170
Manshouri T, Do KA, Wang X et al (2003) Circulating CD20 is detectable in the plasma of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is of prognostic significance. Blood 101(7):2507–2513. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-06-1639
Alas S, Bonavida B (2001) Rituximab inactivates signal transducer and activation of transcription 3 (STAT3) activity in B-non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma through inhibition of the interleukin 10 autocrine/paracrine loop and results in down-regulation of Bcl-2 and sensitization to cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Res 61(13):5137–5144
Keating MJ, Manshouri T, O’Brien S, et al (2002) A high proportion of molecular remission can be obtained with a Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, Rituximab combination (FCR) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Blood, vol 100, p 771a
Byrd JC, Waselenko JK, Maneatis TJ et al (1999) Rituximab therapy in hematologic malignancy patients with circulating blood tumor cells: association with increased infusion-related side effects and rapid blood tumor clearance. J Clin Oncol 17(3):791–795
Keating MJ, O’Brien S, Kantarjian H et al (1993) Long-term follow-up of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with fludarabine as a single agent. Blood 81(11):2878–2884
Hayat A, O’Brien D, O’Rourke P et al (2006) CD38 expression level and pattern of expression remains a reliable and robust marker of progressive disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 47(11):2371–2379. doi:10.1080/10428190600947727
van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M et al (2003) Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 17(12):2257–2317. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2403202
Rawstron AC, Kennedy B, Evans PA et al (2001) Quantitation of minimal disease levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia using a sensitive flow cytometric assay improves the prediction of outcome and can be used to optimize therapy. Blood 98(1):29–35. doi:10.1182/blood.V98.1.29
Binet JL, Auquier A, Dighiero G et al (1981) A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 48(1):198–206. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19810701)48:1<198::AID-CNCR2820480131>3.0.CO;2-V
Clavio M, Miglino M, Spriano M et al (1998) First line Fludarabine treatment of symptomatic chronic lymphoproliferative diseases: clinical results and molecular analysis of minimal residual disease. Eur J Haematol 61(3):197–203
Nguyen DT, Amess JA, Doughty H et al (1999) IDEC-C2B8 anti-CD20 (rituximab) immunotherapy in patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and lymphoproliferative disorders: evaluation of response on 48 patients. Eur J Haematol 62(2):76–82
Di Gaetano N, Xiao Y, Erba E, Bassan R et al (2001) Synergism between fludarabine and rituximab revealed in a follicular lymphoma cell line resistant to the cytotoxic activity of either drug alone. Br J Haematol 114(4):800–809. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.03014.x
Keating MJ, O’Brien S, Albitar M et al (2005) Early results of a chemoimmunotherapy regimen of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as initial therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 23(18):4079–4088. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.12.051
Winkler U, Jensen M, Manzke O et al (1999) Cytokine-release syndrome in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and high lymphocyte counts after treatment with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab, IDEC-C2B8). Blood 94(7):2217–2224
Thornton PD, Bellas C, Santon A et al (2005) Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The possible role of fludarabine and the Epstein-Barr virus in its pathogenesis. Leuk Res 29(4):389–395. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2004.09.008
Voena C, Ladetto M, Astolfi M et al (1997) A novel nested-PCR strategy for the detection of rearranged immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes in B cell tumors. Leukemia 11(10):1793–1798. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2400801
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from Bone Marrow for Leukaemia Trust and Health Research Board of Ireland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayat, A., McGuckin, S., Conneally, E. et al. Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide and Rituximab: an effective chemoimmunotherapy combination with high remission rates for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Ir J Med Sci 178, 441–446 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-009-0358-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-009-0358-9