Abstract
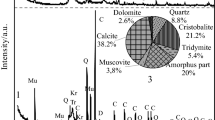
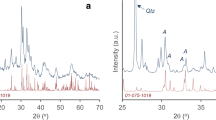
The lunar regolith can be utilized as raw materials for constructing lunar bases through the fabrication of lunar cement. However, the low CaO content in lunar regolith presents a challenge for producing silicate cement. This study explores enriching CaO in NEU-1 lunar soil simulant by calciothermic reduction. Non-isothermal differential scanning calorimetry analysis indicated that calcium reacted with Fe2O3, SiO2, and Al2O3 at approximately 808°C, 816°C, and 826°C, respectively. The reaction ratios were 1.1, 1.6, and 0.8, with apparent activation energies of 941.6 kJ/mol, 965.17 kJ/mol, and 547.28 kJ/mol. The products obtained from the calciothermic reduction of lunar soil simulant were CaO, Ca2Si, and AlFe, as analyzed by X-ray diffraction. Increasing the temperature was found to be beneficial to the reaction process, and a suitable reaction temperature of 850°C was determined. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis showed that the reduction percentages of SiO2 and Al2O3 were 93.01% and 91.04%, respectively, at 850°C for 30 min. The CaO content in the product obtained by calciothermic reduction was 50.65%, which could be further increased to 81.16% after crude purification, and the CaO yield was 82.57%. These results demonstrated that the process has a significant CaO enrichment effect.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Benaroya and L. Bernold, Acta Astronaut. 62, 277 (2008).
L. Wang, D. Guo, Z. Zhang, Z. Lyu, M. Zhao, and Y. Liu, Spacecr. Recovery Remote Sens. 41, 1 (in Chinese) (2020).
F. Xu and J. Ou, Acta Astronaut. 203, 341 (2023).
I. Casanova, Exploration of lunar resources for in-situ utilisation, in Paper presented at Proceedings of The Fourth International Conference on Exploration of The Moon, vol 462 (2000), p. 239.
T. Zhang, Y. Li, Y. Chen, X. Feng, X. Zhu, Z. Chen, J. Yao, Y. Zheng, J. Cai, H. Song, and S. Sun, Appl. Energy 292, 116896 (2021).
C. Schwandt, J.A. Hamilton, D.J. Fray, and I.A. Crawford, Planet. Space Sci. 74, 49 (2012).
Y. Lu, D. Mantha, and R.G. Reddy, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41, 1321 (2010).
R.J. Gustafson, E.E. Rice, and B.C. White, AIP Conf. Proc. 746, 1224 (2005).
Y. Zhao and F. Shadman, AIChE J. 36, 1433 (1990).
A. Liu, Z. Shi, X. Hu, B. Gao, and Z. Wang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, H126 (2017).
A. Liu, Z. Shi, X. Hu, B. Kubikova, M. Boca, B. Gao, and Z. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 718, 279 (2017).
B.A. Lomax, M. Conti, N. Khan, N.S. Bennett, A.Y. Ganin, and M.D. Symes, Planet. Space Sci. 180, 104748 (2020).
L. Sibille, D. Sadoway, A. Sirk, P. Tripathy, O. Melendez, E. Standish, J. Dominguez, D. Stefanescu, P. Curreri, and S. Poizeau, Recent advances in scale-up development of molten regolith electrolysis for oxygen production in support of a lunar base, in Paper Presented at 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, Florida, 5–8 Jan 2009.
K. Xie, Z. Shi, J. Xu, X. Hu, B. Gao, and Z. Wang, JOM 69, 1963 (2017).
A. Liu, Z. Shi, J. Xu, X. Hu, B. Gao, and Z. Wang, JOM 68, 1518 (2016).
A. Khitab, W. Anwar, I. Mehmood, S.M.S. Kazmi, and M.J. Munir, Astron. Rep. 60, 306 (2016).
Y.C. Toklu and P. Akpinar, Adv. Space Res. 70, 762 (2022).
S. Wilhelm and M. Curbach, Struct. Concr. 15, 419 (2014).
H.A. Toutanji, S. Evans, and R.N. Grugel, Constr. Build. Mater. 29, 444 (2012).
R.N. Grugel, Adv. Space Res. 50, 1294 (2012).
R.N. Grugel and H. Toutanji, Adv. Space Res. 41, 103 (2008).
T. Chen, B.J. Chow, M. Wang, Y. Shi, C. Zhao, and Y. Qiao, J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 28, 06015013 (2016).
T. Chen, B.J. Chow, M. Wang, Y. Zhong, and Y. Qiao, J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 29, 06017013 (2017).
T. Sik Lee, J. Lee, and K. Yong Ann, Acta Astronaut. 114, 60 (2015).
W. Kaituo, P.N. Lemougna, T. Qing, L. Wei, and C. Xuemin, Gondwana Res. 44, 1 (2017).
S. Lee and A.V. Riessen, Materials 15, 4516 (2022).
K. Wang, Q. Tang, X. Cui, Y. He, and L. Liu, Sci. Rep. 6, 29659 (2016).
N. Su and Y. Peng, Cem. Concr. Res. 31, 609 (2001).
I. Casanova and V. Aulesa, Construction materials from in-situ resources on the Moon and Mars, in Paper Presented at Seventh International Conference and Exposition on Engineering, Construction, Operations, and Business in Space, Albuquerque, New Mexico, 27 Feb–2 Mar 2000.
C. Li, K. Xie, A. Liu, and Z. Shi, JOM 71, 1471 (2019).
B.M. Willman, W.W. Boles, D.S. McKay, and C.C. Allen, J. Aerosp. Eng. 8, 77 (1995).
Y. Zheng, S. Wang, Z. Ouyang, Y. Zou, J. Liu, C. Li, X. Li, and J. Feng, Adv. Space Res. 43, 448 (2009).
C. Li, H. Hu, M. Yang, Z. Pei, Q. Zhou, X. Ren, B. Liu, D. Liu, X. Zeng, G. Zhang, H. Zhang, J. Liu, Q. Wang, X. Deng, C. Xiao, Y. Yao, D. Xue, W. Zuo, Y. Su, W. Wen, and Z. Ouyang, Natl. Sci. Rev. 9, nwab188 (2022).
A. Jerez, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 26, 315 (1983).
E.S. Freeman and B. Carroll, J. Phys. Chem. 62, 394 (1958).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52074084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Li, D., Zhang, Y. et al. Concentrating CaO from Lunar Simulant by Calciothermic Reduction Process. JOM 76, 2403–2413 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-024-06488-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-024-06488-4