Abstract
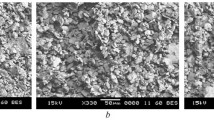
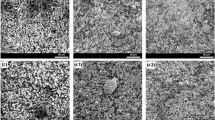
Fe-6.5 wt.% Si nanocrystalline alloys with good magnetic softness were prepared by mechanical alloying at various milling times (0–12 h) via a high-energy ball mill. Elemental iron and silicon powders were used as raw materials. Structural evolution, particle size distribution, and magnetic properties were investigated for as-milled Fe-Si alloy powders. During the alloying process, Si atoms dissolve substitutionally into α-Fe lattice, causing a decrease of lattice parameter with the milling time. A single α-(Fe,Si) solid-solution phase with grain size of ~ 10 nm is obtained, and no ordered phases (B2 or DO3) are observed. Ball-milling effectively reduces particle size of the alloy powders from 64 μm to 30 μm, and exhibits a controlled distribution of the particle size. A transition in the dominant factor and a deviation from the sixth power law on grain size are confirmed in the coercivity of these Fe-Si alloy powders. Good magnetic softness, with a saturation magnetization of ~ 198 Am2/kg and coercivity of ~ 20 A/m, has been achieved. This study validates that mechanical alloying is an effective way to produce single-phase BCC Fe-6.5 wt.% Si alloy powders for applications with magnetic powder cores.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Krings, A. Boglietti, A. Cavagnino, and S. Sprague, IEEE Trans. Ind. Elctron. 64, 2405 https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2613844 (2017).
J.M. Silveyra, E. Ferrara, D.L. Huber, and T.C. Monson, Science 362, 6413 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0195 (2018).
O. Gutfleisch, M.A. Willard, E. Brück, C.H. Chen, S.G. Sankar, and J.P. Liu, Adv. Mater. 23, 821 https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201002180 (2011).
A.S. Inoue and N. Nishiyama, MRS Bull. 32, 651 https://doi.org/10.1557/MRS2007.128 (2007).
O.A. Tretiakov, D.R. Clarke, G. Chern, Y.B. Bazaliy, and O. Tchernyshyov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 127204 https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.127204 (2008).
R.C. Ohandley, Modern Magnetic Materials: Principles and Applications (Wiley, New York, 2000), pp338–347.
M.A. Willard, M. Daniil, and K.E. Kniping, Scr. Mater. 67, 554 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCRIPTAMAT.2011.12.043 (2012).
G.D. Herzer, Acta Mater. 61, 718 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.10.040 (2013).
H. Fu, Y. Mo, Z. Zhang, and J. Xie, Mater. Sci. Eng. 656, 90 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2016.01.036 (2016).
M.F. Littmann, IEEE Trans. Magn. 7, 48 https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.1971.1066998 (1971).
W.J. Yuan, R. Li, Q. Shen, and L. Zhang, Mater Charact 58, 376 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHAR.2006.06.003 (2007).
Y. Yoshizawa, S. Oguma, and K. Yamauchi, J. Appl. Phys. 64, 6044 https://doi.org/10.1063/1.342149 (1988).
G. Ouyang, X. Chen, Y. Liang, C.R. Macziewski, and J. Cui, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 481, 234 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMMM.2019.02.089 (2019).
P.R. Swann, L. Granas, and B. Lehtinen, Metal Sci. 9, 90 https://doi.org/10.1179/030634575790445279 (1975).
Z. Bensebaa, B. Bouzabata, and A. Otmani, J. Alloys Compd. 469, 24 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2008.01.151 (2009).
C.C. Lima, M.C.A. da Silva, M.D.C. Sobral, R.E. Coelho, and C. Bolfarini, J. Alloys Compd. 586, S314 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2012.09.074 (2014).
P. Arató, I. Bóc, and T. Gróf, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 41, 53 https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(84)90135-5 (1984).
B. Viala, J. Degauque, M. Fagot, M. Baricco, E. Ferrara, and F. Fiorillo, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 212, 62 https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(96)10188-X (1996).
S. Cui, G. Ouyang, T. Ma, C.R. Macziewski, V.I. Levitas, L. Zhou, M.J. Kramer, and J. Cui, J. Alloys Compd. 771, 643 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2018.08.293 (2019).
J.S. Shin, J.S. Bae, H.J. Kim, H.M. Lee, T.D. Lee, E.J. Lavernia, and Z.H. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 407, 282 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2005.07.012 (2005).
H. Yu, W. Yu, and X. Bi, J. Alloys Compd. 634, 83 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2015.01.156 (2015).
M. Li, R. Birringer, W.L. Johnson, and R.D. Shull, Nanostruct. Mater. 3, 407 https://doi.org/10.1016/0965-9773(93)90106-L (1993).
C. Stanciu, F. Popa, I. Chicinas, and O. Isnard, Adv Electron Forum. 13, 109 https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AEF.13.109 (2015).
T. Clark and S.N. Mathaudhu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 484, 350 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMMM.2019.03.070 (2019).
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9 (2001).
W. Shen, F. Wang, D. Boroyevich, and C.W. Tipton, IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23, 475 https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2007.911881 (2007).
M. Abdellaoui, T. Barradi, and E. Gaffet, J. Alloys Compd. 198, 155 https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8388(93)90159-K (1993).
H. Shokrollahi and K. Janghorban, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 189, 1 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.02.034 (2007).
Origin®. https://www.origin.com/hkg/en-us/. Accessed June 9th 2023
C. Groschner, S. Lan, A. Wiase, A. Leary, M.S. Lucas, C. Park, D.E. Laughlin, M. Diaz-Michelena, and M.E. McHenry, IEEE Trans. Magn. 49, 4273 https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2250928 (2013).
U. Holzwarth and N. Gibson, Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 534 https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.145 (2011).
J.B. Nelson and D.P. Riley, Proc. Phys. Soc. 57, 160 https://doi.org/10.1088/0959-5309/57/3/302 (1945).
J.B. Nelson and D.P. Riley, Proc. Phys. Soc. 57, 477 https://doi.org/10.1088/0959-5309/57/6/303 (1945).
G.K. Williamson and W.H. Hall, Acta Metall. 1, 22 https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(53)90006-6 (1953).
F. González and Y. Houbaert, Rev. Metal. 49, 178 https://doi.org/10.3989/revmetalm.1223 (2013).
R.M. Bozorth, Ferromagnetism (D. Van Nostrand, New Jersey, 1951), pp74–75.
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley, Massachusetts, 1956), p395.
G.D. Herzer, IEEE Trans. Magn. 26, 1397 https://doi.org/10.1109/20.104389 (1990).
B. Dong, J. Healy, S. Lan, M. Daniil, and M.A. Willard, AIP Adv. 8, 056124 https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5007248 (2018).
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission [Grant Number KJQN202000738]; the Graduate Research and Innovation Project of Chongqing Jiaotong University [Grant Number 2022S0058]; and the Students Venture Fund of Chongqing Jiaotong University [Grant Number CY202139].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Chen, Y., Lan, C. et al. Microstructure, Particle Size, and Magnetic Property of Fe-6.5 wt.% Si Nanocrystalline Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. JOM 76, 1066–1075 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06300-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06300-9