Abstract
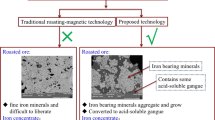
Efficient separation of boron and iron from ludwigite ore has been achieved by developing a process consisting of low-temperature microwave reductive roasting, milling and leaching, and magnetic separation. To facilitate the separation, microwave reductive roasting was performed based on the design of core–shell composite pellets composed of ludwigite ore, renewable biomass-redrived biochar, and sodium carbonate, which took advantage of their differences in the microwave penetration depth and microwave reflection loss according to the rule of impedance matching. Under the optimal conditions of roasting temperature of 700°C and dwell time of 20 min, the metallized pellets with iron metallization degree of 89.8% were obtained for simultaneous milling and leaching, which produced a boron-rich leachate with boron leaching percentage of 83.9% and a direct reduced iron powder with total iron content of 90.1 wt.%, iron metallization degree of 94.2%, and iron recovery of 85.9% after magnetic separation of the leaching residue.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
R. Orhan, E. Aydoğmuş, S. Topuz, and H. Arslanoğlu, J. Build. Eng. 42, 103051 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103051 (2021).
Z. Balta and E.B. Simsek, J. Alloy. Compd. 898, 162897 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162897 (2021).
M. Zhu, X. Zhou, H. Zhang, L. Wang, and H. Sun, Resour. Policy 82, 103542 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103542 (2023).
Boron Statistics and Information. https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center/boron-statistics-and-information. Accessed 2 May 2023
R. Liu, X. Xue, X. Liu, D. Wang, F. Zha, and D. Huang, Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 25, 102 https://doi.org/10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2006.06.025 (2006).
G. Wang, Q. Xue, and J. Wang, Thermochim. Acta 621, 90 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2015.10.013 (2015).
J. An and X. Xue, J. Clean. Prod. 66, 121 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.10.020 (2014).
S. Liu, C. Cui, and X. Zhang, ISIJ Int. 38(10), 1077 https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.38.1077 (1998).
Z. Yang, S. Liu, Z. Li, and X. Xue, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 14(6), 32 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(07)60086-7 (2007).
G. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Ding, S. Ma, and Q. Xue, ISIJ Int. 52(1), 45 https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.52.45 (2012).
G. Li, B. Liang, M. Rao, Y. Zhang, and T. Jiang, Miner. Eng. 56, 57 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2013.10.030 (2014).
X. Zhu, C. Liu, Y. Wang, F. Wang, J. Gao, and L. Zhang, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 18, 882 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.03.024 (2022).
L. Ye, Z. Peng, R. Tian, H. Tang, J. Zhang, M. Rao, and G. Li, Powder Technol. 410, 117848 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117848 (2022).
The Paris Agreement, https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/what-is-the-paris-agreement. Accessed 1 May 2023
E. Singh, R. Mishra, A. Kumar, S.K. Shukla, S.L. Lo, and S. Kumar, Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 163, 585 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.05.056 (2022).
L. Ye, Z. Peng, L. Wang, A. Anzulevich, I. Bychkov, D. Kalganov, H. Tang, M. Rao, G. Li, and T. Jiang, JOM 71, 3931 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03766-4 (2019).
M. Ahmad, A.U. Rajapaksha, J.E. Lim, M. Zhang, N. Bolan, D. Mohan, M. Vithanage, S.S. Lee, and Y.S. Ok, Chemosphere 99, 19 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.071 (2014).
L. Wang, Q. Quan, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, P. Lin, S. Pan, and Z. Zhong, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 449, 385 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.10.067 (2018).
Z. Peng and J.Y. Hwang, Int. Mater. Rev. 60(1), 30 https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280414y.0000000042 (2015).
S.H. Jung and J.S. Kim, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 107, 116 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.02.011 (2014).
L. Ye, Z. Peng, L. Wang, A. Anzulevich, I. Bychkov, H. Tang, M. Rao, Y. Zhang, G. Li, and T. Jiang, Powder Technol. 338, 365 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.07.037 (2018).
T. Jiang, Iron ore Agglomeration, Central South University Press, Changsha, China (2016).
Z. Peng, J.Y. Hwang, J. Mouris, R. Hutcheon, and X. Huang, ISIJ Int. 50(11), 1590 https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.50.1590 (2010).
P. Singh, V.K. Babbar, A. Razdan, R.K. Puri, and T.C. Goel, J. Appl. Phys. 87(9), 4362 https://doi.org/10.1063/1.373079 (2000).
S.C. Khattoi and G.G. Roy, Trans. Indian Inst. Metals 68, 683 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-014-0498-0 (2015).
S. Mishra and G.G. Roy, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 2347 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0666-1 (2016).
X. Ye, S. Guo, W. Qu, L. Yang, T. Hu, S. Xu, L. Zhang, B. Liu, and Z. Zhang, J. Hazard. Mater. 366, 432 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.024 (2009).
M. Wang, Y. Duan, S. Liu, X. Li, and Z. Ji, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3442 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.06.040 (2009).
Y. He, R. Gong, and H. He, Funct. Mater. 35, 782 https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2004.06.042 (2004).
M.M. Breda and D.C.J.I. Parreiras, ISIJ Int. 41, 27https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.41.Suppl_S27 (2001).
Z. Su, J. Wang, S. Liu, Y. Zhang, and T. Jiang, Powder Technol. 407, 117694 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117694 (2022).
Y. Li, J. Qu, G. Wei, and T. Qi, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23(2), 103 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30020-6 (2016).
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, A.C. Ferrari, and J. Robertson, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A. 362(1824), 2477 https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2004.1452 (2004).
G. Wang, Q. Xue, and J. Wang, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(1), 282 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64116-X (2016).
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2020YFC1909800, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 72088101, and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Hunan Province, China, under Grant 2019RS2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, L., Tian, R., Tang, H. et al. Microwave-Intensified Separation of Boron and Iron from Ludwigite Ore Based on Impedance Matching. JOM 75, 5149–5159 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06137-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06137-2