Abstract
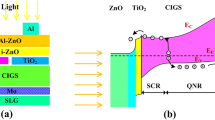
Copper indium gallium sulfur (CIGS) solar cells show good efficiency; however, the buffer/absorber and absorber/back contact interfaces are the most critical factors affecting that efficiency. We have investigated CIGS-based solar cells with two different buffer layers, ZnO1−xSx and SnS2, a non-toxic alternative to CdS using a solar cell capacitance simulator. First, we propose a cell structure with a ZnO1−xSx/CIGS interface for different sulfur content in ZnO1−xSx. The band gap of ZnO1−xSx and the conduction band offset (∆Ec) at the ZnO1−xSx /CIGS interface can be tuned by the sulfur content, enabling high efficiency. We found that the ZnO1−xSx buffer layer with a sulfur composition S/(O + S) ratio of 0.85 leads to enhanced performance of CIGS solar cells up to 23.94%. Above 0.85, the performance of the solar cells is affected, depending on its thickness and the carrier concentration of both absorber and buffer layers. The CIGS solar cell performance was evaluated using SnS2 as a buffer layer. The results show that the efficiency of CIGS-based solar cells with Zn(O0.30S0.79) and with SnS2 is slightly different, at 23.54% and 23.44%, respectively. In addition, there is a difference in the open-circuit voltage (Voc) and short-circuit current density (Jsc) due to the reduction in the interface recombination and band structure at the buffer/CIGS interface.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All the data is included in the manuscript. Further data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
A. Bouich, J. Marí-Guaita, F. Baig, Y.H. Khattak, B.M. Soucase, and P. Palacios, Nanomaterials 12(17), 3027 https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173027 (2022).
Pv-magazine, “Hanergy’s Solibro Achieves 18.72% CIGS Module Efficiency Record”, https://www.pv-magazine.com/2018/02/02/hanergys-solibro-achieves-18-72-cigs-module-efficiency-record. Accessed 1 Jun 2023.
M. Nakamura, K. Yamaguchi, Y. Kimoto, Y. Yasaki, T. Kato, and H. Sugimoto, IEEE J. Photovolt. 9, 1863 (2019).
T. Feurer, P. Reinhard, E. Avancini, B. Bissig, J. Löckinger, P. Fuchs, R. Carron, T.P. Weiss, J. Perrenoud, S. Stutterheim, S. Buecheler, and A.N. Tiwari, Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 25, 645 (2017).
A. Bouich, J. Marí-Guaita, B.M. Soucase, and P. Palacios, Nanomaterials 12(17), 2901 (2022).
J. Marí-Guaita, A. Bouich, and B. Marí, JOM 74, 1 (2022).
V. Achard, M. Balestrieri, S. Bechu, M. Jubault, M. Bouttemy, L. Lombez, T. Hildebrandt, N. Naghavib, A. Etcheberry, D. Lincot, and F. Donsanti, Thin Solid Films 669, 494 (2019).
M.A. Shafi, A. Bouich, K. Fradi, J.M. Guaita, L. Khan, et al., Optik 258, 168854 (2022).
J.Y. Park, R.B.V. Chalapathy, A.C. Lokhande, C.W. Hong, and J.H. Kim, J. Alloys Compd. 695, 2652 (2017).
C. Zhang, K. Alberi, C. Honsberg, and K. Park, Appl. Surf. Sci. 549, 149245 (2021).
Z. Zhao, Y. Cao, J. Yi, X. He, C. Ma, and J. Qiu, ChemPhysChem 13, 1551 (2012).
X. Gu, W. Cui, H. Li, Z. Wu, Z. Zeng, S.T. Lee, H. Zhang, and B. Sun, Adv. Energy Mater. 3, 1262 (2013).
T. Ericson, J.J. Scragg, A. Hultqvist, J.T. Wätjen, P. Szaniawski, T. Törndahl, and C. Platzer-Björkman, IEEE J. Photovolt. 4, 465 (2013).
S. Polivtseva, N. Spalatu, A. Abdalla, O. Volobujeva, J. Hiie, and S. Bereznev, ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 6505 (2018).
D. Hironiwa, N. Matsuo, J. Chantana, N. Sakai, T. Kato, H. Sugimoto, and T. Minemoto, Phys. Status Solidi 212, 2766 (2015).
K. Sun, C. Yan, F. Liu, J. Huang, F. Zhou, J.A. Stride, M. Green, and X. Hao, Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1600046 (2016).
S.M. Alqahtani, A.A. Baloch, S.S. Ahmed, and F.H. Alharbi, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67, 1666 (2020).
M. Burgelman, P. Nollet, and S. Degrave, Thin Solid Films 361–362, 527 (2000).
J. Verschraegen and M. Burgelman, Thin Solid Films 515, 6276 (2007).
R.R. Thankalekshmi and A.C. Rastogi, J. Appl. Phys. 112, 063708 (2012).
D.H. Cho, W.J. Lee, B. Shin, and Y.D. Chung, Appl. Surf. Sci. 486, 555 (2019).
D.-H. Cho, W.-J. Lee, M.E. Kim, K. Kim, J.H. Yun, and Y.-D. Chung, J. Alloys Compd. 842, 155986 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155986 (2020).
C. Persson, C. Platzer-Björkman, J. Malmström, T. Törndahl, and M. Edoff, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 146403 (2006).
C. Platzer-Björkman, T. Törndahl, D. Abou-Ras, J. Malmström, J. Kessler, and L. Stolt, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 044506 (2006).
A. Bouich, J. Marí-Guaita, B. Sahraoui, P. Palacios, and B. Marí, Energy Res. 10, 840817 (2022).
A.O. Pudov, A. Kanevce, H.A. Al-Thani, J.R. Sites, and F.S. Hasoon, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 064901 (2005).
A. Kumar, Superlattices Microstruct. 153, 106872 (2021).
J. Marí-Guaita, A. Bouich, and B. Marí, Eng. Proc. 12(1), 1 (2021).
A. Bouich, J. Marí-Guaita, A. Bouich, I.G. Pradas, and B. Marí, Eng. Proc. 12(1), 81 (2022).
S. Bouazizi, W. Tlili, A. Bouich, B.M. Soucase, and A. Omri, Mater. Res. Express 9(9), 096402 (2022).
A. Bouich, B. Mari, L. Atourki, S. Ullah, and M.E. Touhami, JOM 73(2), 551 (2021).
A. Bouich, Study and Characterization of Hybrid Perovskites and Copper-Indium-Gallium Selenide Thin Films for Tandem Solar Cells. (Doctoral dissertation, Universitat Politècnica de València) (2021).
Funding
The author Amal Bouich postdoctoral researcher acknowledges Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (Spain) (MCIN) for funding support through Margarita Salas Fellowship (MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033). Author N’Guessan Armel Ignace acknowledges his Erasmus + KA 107 grant. Author Amal Bouich acknowledged the post-doctoral contract supported by the RRHH, the Postdoctoral contract the Margarita Salas financed with Union European Next Generation EU. This research has been funded by Grant PID2019-107137RB-C22 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by “ERDF A way of making Europe”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have participated in (a) conception and design or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and (c) approval of the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
N’guessan, A.I., Bouich, A., Touré, A. et al. Influence of Sulfur Content in Zn(O,S) Buffer Layer onto Copper Indium Gallium Sulfur-Based Solar Cells Through Surface Engineering at ZnO1−xSx/CIGS Interface. JOM 75, 4332–4340 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06018-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06018-8