Abstract
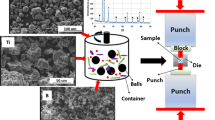
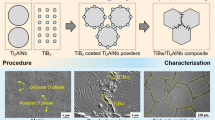
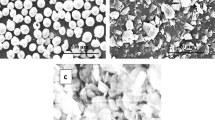
Fe-15Cr-2Mn-1.5Al metal matrix composites (MMCs) reinforced with TiB2 and CrFeB were synthesized from a Fe, Cr, Mn, Al, Ti, and B powder mixture at 1100°C and 50 MPa for 15 min using an in situ spark plasma sintering (SPS) method. A mechanical alloying process was used to improve the activity and uniformity of the composite powder. The reinforced phase and matrix were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The mechanical properties of the steel-based MMCs were also measured by compression and microhardness. The results showed that the in situ synthesized reinforcements of steel-based MMCs were Cr-rich M2B-type boride (CrFeB) and TiB2, and the matrixes were α-Fe. CrFeB addition improved the plastic deformation capacity and weakened the compressive strength as well as the hardness. The plastic deformation capacity of the (15 vol.% M2B + 10 vol.% TiB2)/Fe-15Cr-2Mn-1.5Al composite equaled ~ 14.3%, which was almost double that of the TiB2/Fe-15Cr-2Mn-1.5Al composite (~ 7.5%). The compressive strength and hardness of the TiB2/Fe-15Cr-2Mn-1.5Al composite equaled ~ 2971 MPa and 781 ± 15 HV, respectively, while the compressive strength and hardness of the (15 vol.% M2B + 10 vol.% TiB2)/Fe-15Cr-2Mn-1.5Al composite equaled ~ 2576 MPa and 659 ± 15 HV, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Maria, Incas Bull. 5, 139 (2013).
E.A.M. Shalaby and A.Y. Churyumov, J. Alloys Compd. 727, 540 (2017).
Y.M. Zou, C.L. Tan, Z.G. Tan, W.Y. Tan, M. Kuang, and D.C. Zeng, Addit. Manut. 41, 101971 (2021).
B.H. Li, Y. Liu, H. Cao, L. He, and J. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 3909 (2009).
S.C. Cho, Y.H. Lee, S.M. Ko, H.J. Park, D.H. Lee, S.M. Shin, L. Jo, Y.D. Kim, S.B. Lee, and S.K. Lee, J. Alloys Compd. 817, 152714 (2020).
A. Fedrizzi, M. Pellizzari, M. Zadra, and E. Marin, Mater. Charact. 86, 69 (2013).
D.H. Bacon, L. Edwards, J.E. Moffatt, and M.E. Fitzpatrick, Acta Mater. 59, 3373 (2011).
L. Cha, S. Lartigue-Korinek, M. Walls, and L. Mazerolle, Acta Mater. 60, 6382 (2012).
I. Sulima and G. Boczkal, Micromechanical. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 644, 76 (2015).
S. Iwona, Mater. Charact. 118, 560 (2016).
I. Sulima, R. Kowalik, and P. Hyjek, J. Alloys Compd. 688, 1195 (2016).
S.A.N. Mehrabani, A.T. Tabrizi, H. Aghajani, and H. Pourbagheri, Int. J. Self-propag High 29, 167 (2020).
H. Zhang, H. Springer, R. Aparicio-Fernández, and D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 118, 187 (2016).
R. Aparicio-Fernández, H. Springer, A. Szczepaniak, H. Zhang, and D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 107, 38 (2016).
C. Baron, H. Springer, and D. Raabe, Mater. Des. 111, 185 (2016).
B.H. Li, Y. Liu, J. Li, S.J. Gao, H. Cao, and H. Lin, Mater. Des. 31, 877 (2010).
Z. Xue, J. Kuang, and H. Fu, Mater. Wiss Werkst 39, 557 (2010).
J. Liu, W.P. Chen, L. Chen, Z.B. Xia, H.Q. Xiao, and Z.Q. Fu, J. Alloys Compd. 747, 886 (2018).
Z.F. Huang, J.D. Xing, and C. Guo, Mater. Des. 31, 3084 (2010).
Y. Liu, B. H. Li, J. Li, L. He, S.J. Lin, and T. G. Nieh, Mater. Lett. 64, 1299 (2010).
Z.F. Huang, J.D. Xing, and L.L. Lv, Mater. Charact. 75, 63 (2013).
H.G. Fu, Q. Xiao, J.C. Kuang, Z.Q. Jiang, and J.D. Xing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 466, 160 (2007).
S.Q. Ma, J.D. Xing, G.F. Liu, D.W. Yi, H.G. Fu, J.J. Zhang, and Y.F. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 6800 (2010).
Z.B. Sun, A. Du, X.M. Cao, and M. Wen, Metal Hotwork. Technol. 36, 9 ((in Chinese)) (2007).
Y.X. Jian, Z.F. Huang, J.D. Xing, and B.Y. Wang, Mater. Charact. 110, 138 (2015).
C.T. Zhou, J.D. Xing, B. Xiao, J. Feng, X.J. Xie, and Y.H. Chen, Comput. Mater. Sci. 44(4), 1056 (2009).
Y.X. Jian, Z.F. Huang, J.D. Xing, X.Z. Guo, Y. Wang, and Z. Lv, Tribol. Int. 103, 243 (2016).
Y.X. Jian, Z.F. Huang, X.T. Liu, J.L. Sun, and J.D. Xing, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 57, 174 (2020).
J. Liu, and W. Chen, J. Alloys Compd. 741, 348–359 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.132 (2018).
J. Liu, and W.P. Chen, Vacuum 150, 49 (2018).
X.G. Zeng, Powder Metall. 58, 193 (2015).
A.A. Sorour, R.R. Chromik, and M. Brochu, Powder Metall. 58, 20 (2015).
H.X. Khoa, N.Q. Tuan, Y.H. Lee, B.H. Lee, and J.S. Kim, J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst. 20, 221 (2013).
Z. Yu, H. Fu, Y. Jiang, Q. Cen, Y. Lei, R. Zhou, and H. Guo, Mater. Wiss Werkst 43, 12 (2012).
Z. Lv, H.G. Fu, J.D. Xing, S.Q. Ma, and Y. Hu, J. Alloys Compd. 662, 54 (2016).
M. Ziemnicka-Sylwester, L. Gai, and S. Miura, Mater Design 69, 1 (2015).
Y. Wang, Z.Q. Zhang, H.Y. Wang, B.X. Ma, and Q.C. Jiang, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 422(1–2), 339–345 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.012 (2006).
GB/T 7314-2017, Metallic materials-compression testing at ambient temperature, (National Standard of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing, China, 2017). http://c.gb688.cn/bzgk/gb/showGb?type=online&hcno=8216FA25DB28F50FD47096AB26198632
J. Liu, M. Wu, J. Chen, Z.B. Ye, and C. Du, Materials 14, 2346 (2021).
J. Liu, M. Wu, J. Chen, Z.B. Ye, C. Lin, W. Xu, and W.P. Chen, Trans. India Inst. Mater. 75, 161 (2021).
I. Goldfarb, W.D. Kaplan, S. Ariely, and M. Bamberger, Philos. Mag. A 72, 963 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1080/01418619508239947
A. Röttger, J. Lentz, and W. Theisen, Mater. Des. 88, 420 (2015).
B. Basu, G.B. Raju, and A.K. Suri, Int. Mater. Rev. 51, 352 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Planning Projects of Guangzhou (202102080110), the Science and Technology Planning Projects of Guangzhou (201905010007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51805104), the Science and Technology Planning Projects of Guangzhou, China (201803030041), Guangdong education department project (2017GCZX003) and (2020A1515111194), Youth Project of 2020 Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Guangdong and Dongguan) Joint Foundation(2020A1515111194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author (Jian Liu) states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wu, M., Wang, B. et al. In Situ Spark Plasma Sintering, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-15Cr-2Mn-1.5Al Matrix Composites Reinforced with TiB2 and CrFeB. JOM 75, 886–894 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05683-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05683-5