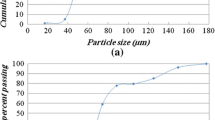
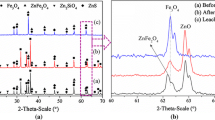
Abstract
Hydrometallurgy is a flexible and efficient process for recovering heavy and valuable metals from industrial residues. In this study, various parameters of cobalt reductive leaching were investigated using the Taguchi experiment design (DOE) method to determine the best conditions for dissolving cobalt from zinc plant residue. The experiment parameters included: initial sulfuric acid concentration (0.1 M, 0.316 M and 1 M), reaction temperature (70, 80 and 90°C), reaction time (15, 30 and 60 min), and solid/liquid ratio (1:5, 1:6 and 1:7 g/L). The iron sulfate was used as a reducing agent, and the sulfuric acid was used as the solvent. The experiment results showed that the optimal conditions for dissolving cobalt were initial sulfuric acid concentration 1 M, temperature 90°C, time 60 min, and solid/liquid ratio 1:7. Under these conditions, there was good agreement between predicted (97.5%) and experimental results (97.2%) in terms of cobalt dissolution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Kongolo, M.D. Mwema, A.N. Banza, and E. Gock, Miner. Eng 16, 1371 (2003).
M. Liwen, N. Xiaoli, X. Zuoren, and H. Xin’gang, Hydrometallurgy 136, 1 (2013).
Z. Xiu-jing, L. Nai-jun, Z. Xu, F. Yan, and J. Lan, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 21, 2117 (2011).
L. Boisvert, K. Turgeon, J.F. Boulanger, C. Bazin, and G. Houlachi, Metals 10, 1553 (2020).
M.K. Jha, V. Kumar, and R. Singh, Resources, Conserv. Recycl. 33, 1 (2001).
B. Kasongo, and H.M. Mwanat, South African J. Sci. 117(5-6), 1–8 (2021).
Y. Zhang, Q. Liu, and C. Sun, Miner. Eng. 14(5), 525–537 (2001).
M. Tanaka, K. Koyama, H. Nartia, and T. Oihi, Recycling valuable metals via hydrometallurgical routes (Design for innovative value towards a sustainable society, Springer, 2012), pp 507–512.
M. Minakshi, N. Sharma, D. Ralph, D. Appadoo, and K. Nallathamby, Solid-state lett. 14, 86 (2011).
C.C. Yong, B.R. Keith, Z. Wensheng, Z. Zhaowu, P. Yoko, and J. Chin, Eng 24, 237 (2016).
C. Fan, X. Zhai, Y. Fu, Y. Chang, B. Li, and Z. Ting-an, Hydrometallurgy 105(1-2), 191–194 (2010).
R. Ewa, B. Lidia, and G. Wanda, Miner. Eng 22, 88 (2009).
S. Shaole, S. Wei, W. Li, L. Runqing, H. Haisheng, H. Yuehua, Y. Yue, and J. Environ, Chem. Eng 7, 102777 (2019).
G. Bina, D. Akash, and S. Virendra, Hydrometallurgy 70, 121 (2003).
J.M. Kumar, K. Anjan, J.A. Kumari, K. Vinay, H. Jhumki, and D.P. Banshi, Waste Manage 33, 1890 (2013).
S. Palanivel, and S. Natarajan, Met 2, 24 (2012).
Z. Yunran, T. Jia, L. Shijun, H. Fang, L. Mei, J. Wei, and H. Jiugang, Sep. Purif. Technol 101, 240 (2020).
C.C. Yong, U. Mark, D. Michael, P. Yoko, and Z. Zhaowu, Miner. Eng 77, 17 (2015).
A. ZhangL, B. NieZ, C. XiX, and D. MaL, Sep. Purif. Technol 195, 244 (2018).
R.K. Mishra, P.C. Rout, K. Sarangi, and K.C. Nathsarma, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26, 301 (2016).
L. Guang-hui, R. Ming-jun, L. Qian, P. Zhi-wei, and J. Tao, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 20, 1517 (2010).
P. Rafighi, M.R. Yaftian, and N. Noshiranzadeh, Sep. Purif. Technol 75, 32 (2010).
X. Peng, W. Cheng-yan, X. Sheng-ming, and J. Zhong-jun, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23, 517 (2013).
F. Farahmand, D. Moradkhani, M.S. Safarzadeh, and F. Rashchi, Hydrometallurgy 95(3-4), 316–324 (2009).
A. Fattahi, F. Rashchi, and E. Abkhoshk, Hydrometallurgy 161, 185–192 (2016).
M.S. Safarzadeh, D. Nikhil, B. Mustafa, and D. Moradkhani, Hydrometallurgy 106, 51 (2011).
R. Ahmadi, and H.R. Madaah Hosseini, Mater. Sci-Poland 31, 253 (2013).
A. Babaei-Dehkordi, J. Moghaddam, and A. Mostafaei, Mater. Res. Bull 48, 4235 (2013).
G. Taguchi, E.A. Elsayed, and T.C. Hsiang, Quality engineering in production systems (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989), pp 12–23.
B. Behnajady, and J. Moghaddam, Chem. Eng. Res. Des 117, 564 (2017).
R. Golmohammadzadeh, F. Rashchi, and E. Vahidi, Waste Manage 64, 244 (2017).
M. Kavand, P. Eslami, and L. Razeh, J. Water Process. Eng 34, 101151 (2020).
K. Ozgul, Hydrometallurgy 95, 333 (2009).
S. Karimi, F. Rashchi, and J. Moghaddam, Int. J. Miner. Process 162, 58 (2017).
M. Deniz Turan, H. Soner Altundogan, and F. Tumen, Hydrometallurgy 75, 169 (2004).
S. Basudev, J. Jinki, L. Jae-chun, L. Gae-Ho, and S. Jeong-Soo, J. Power Sources 167, 536 (2007).
D. Moradkhani, B. Sedaghat, M. Khodakarami, and I. Ataei, Miner. Process. 50(2), 735–746 (2014).
S.B. Kanungo, and R.P. Das, Hydrometallurgy. 21, 41–58 (1988).
D.W. Fuerstenau, and K.N. Han, Miner. Process. Technol. Rev. 1, 1–83 (1983).
J.C. Agarwal, N. Beecher, D.S. Davis, G.L. Hubred, V.K. Kakaria, and R.N. Kust, J. Metals. 28, 24–31 (1976).
J.M. Richardson, L.G. Stevens, and M.C. Kuhn, The recovery of metal values from nickel-bearingllaterite ores by reductive roast/ammonia leach technology (Process and fundamental considerations of selected hydrometallurgical systems, New York, 1981), pp 17–34.
Acknowledgement
The authors appreciate the support of Zanjan Zinc KhalesSazan Industries Company (ZZKICO) to provide samples and analysis used in present investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodaei, M., Moghaddam, J. & Ahmadi, R. Optimization of Cobalt Reductive Leaching from Zinc Plant Residue (ZPR) Using Taguchi Experimental Design Method. JOM 74, 3030–3038 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05370-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05370-5