Abstract
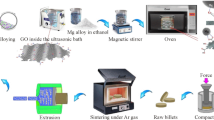
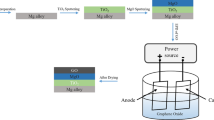
The problem of the degradation rate being too slow is a key technical bottleneck to clinical applications for pure iron (Fe), a promising candidate biodegradable metal. This work used powders of pure Fe and graphene oxide (GO) to prepare Fe-xGO composites (x = 0.4 wt.%, 0.8 wt.%, 1.2 wt.%, and 1.6 wt.%) via selective laser melting (SLM), aiming to obtain a higher degradation rate. The microstructure, hardness, biodegradation and cytocompatibility were investigated. The degradation rate of the SLMed Fe-xGO composites was faster than that of SLMed Fe, due to incorporating GO into Fe. The GO content had a significant effect on the microstructure, hardness and degradation rate. The SLMed Fe-0.8 GO composite presented the finest, relatively uniform grains, had the maximum degradation rate, density and hardness, and had good cytocompatibility. The mechanisms were also clarified.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.Q. Xie, H. Takada, and H. Kanetaka, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 671, 48 (2016).
S.G. Wang, Y.C. Xu, J. Zhou, H.Y. Li, J. Chang, and Z.G. Huan, Bioact. Mater. 2, 10 (2017).
S. Johnston, Z. Shi, J. Venezuela, C. Wen, M.S. Dargusch, and A. Atrens, JOM 71, 1406 (2019).
J. Cheng and Y.F. Zheng, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 101B, 485 (2013).
M. Peuster, P. Wohlsein, M. Brugmann, M. Ehlerding, K. Seidler, C. Fink, H. Brauer, A. Fischer, and G. Hausdorf, Heart 86, 563 (2001).
M. Peuster, C. Hesse, T. Schloo, C. Fink, P. Beerbaum, and C. von Schna-Kenburg, Biomaterials 27, 4955 (2006).
M. Schinhammer, A.C. Hanzi, J.F. Loffler, and P.J. Uggowitzer, Acta Biomater. 6, 1705 (2010).
X.D. Yan, P. Wan, L. Tan, M. Zhao, C. Shuai, and Y. Ke, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 105 (2018).
B. Liu and Y.F. Zheng, Acta Biomater. 7, 1407 (2011).
Z.Y. Zhao, R.G. Guan, X.H. Guan, Z.X. Feng, X. Zhen, H. Chen, and Y. Chen, Adv. Eng. Mater. 17, 663 (2015).
P.S. Bharadiya, M.K. Singh, and S. Mishra, JOM 71, 838 (2019).
H. Zhang, X.H. Wang, Y.P. Li, C.S. Guo, and C.M. Zhang, JOM 71, 541 (2019).
H. Kwon, J. Mondal, K.A. AlOgab, V. Sammelselg, M. Takamichi, and A. Kawaski, J. Alloys Compd. 698, 807 (2017).
S. Ding, T. Xiang, C. Li, S. Zheng, J. Wang, M. Zhang, C. Dong, and W. Chan, Mater. Design 117, 280 (2017).
B. Yilbas, A. Ibrahim, H. Ali, M. Khaled, and T. Laoui, Appl. Surf. Sci. 442, 213 (2018).
R. Karthik and S. Thambidurai, J. Alloys Compd. 715, 254 (2017).
R. Xu, M. Zhao, Y. Zhao, L. Liu, C. Liu, C. Gao, C. Shuai, and A. Atrens, Mater. Lett. 237, 253 (2019).
A. Macpherson, X.P. Li, P. McCormick, L. Ren, K. Yang, and T.B. Sercombe, JOM 69, 2719 (2017).
C. Liu, M.C. Zhao, Y.C. Zhao, L. Zhang, D.F. Yin, Y. Tian, Y.Y. Shan, K. Yang, and A. Atrens, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 755, 50 (2019).
C. Liu, Q.Q. Shi, W. Yan, C.G. Shen, K. Yang, Y. Shan, and M. Zhao, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 266 (2019).
C. Liu, M. Zhao, T. Unenbayar, Y.C. Zhao, B. Xie, Y. Tian, Y.Y. Shan, and K. Yang, Acta Metall. Sin. (English Lett.) 32, 825 (2019).
M. Moravej, F. Prima, M. Fiset, and D. Mantovani, Acta Biomater. 6, 1726 (2010).
C. Shuai, H. Sun, C. Gao, P. Feng, W. Guo, Y. Yang, M. Zhao, S. Yang, F. Yuan, and S. Peng, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 75, 423 (2017).
Y. Zhao, Y. Tang, M. Zhao, L. Liu, C. Gao, C. Shuai, R. Zeng, A. Atrens, and Y. Lin, Adv. Eng. Mater. 21, 1900314 (2019).
Y. Zhao, M. Zhao, R. Xu, L. Liu, J.X. Tao, C. Gao, C. Shuai, and A. Atrens, J. Alloys Compd. 770, 549 (2019).
M.C. Zhao, M. Liu, G. Song, and A. Atrens, Corros. Sci. 50, 1939 (2008).
H. Kato, Y. Todaka, M. Umemoto, M. Haga, and E. Sentoku, Wear 336–337, 58 (2015).
W. Zhang, L.L. Tan, D.R. Li, J.X. Chen, Y.C. Zhao, L. Liu, C.J. Shuai, K. Yang, A. Atrens, and M.C. Zhao, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 777 (2019).
M. Zhao, Y. Deng, and X. Zhang, Scr. Mater. 58, 560 (2008).
K.V. Zakharchenko, M.I. Katsnelson, and A. Fasolino, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 046808 (2009).
M. Rashad, F. Pan, J. Zhang, and M. Asif, J. Alloys Compd. 646, 223 (2015).
X. Yan, M. Zhao, Y. Yang, L. Tan, Y. Zhao, D. Yin, K. Yang, and A. Atrens, Corros. Sci. 156, 125 (2019).
M.C. Zhao, Y.C. Zhao, D.F. Yin, S. Wang, Y. Shangguan, C. Liu, L. Tan, and C. Shuai, Acta Metall. Sin. (English Lett.) 32, 1195 (2019).
H. Hermawan, A. Purnama, D. Dube, J. Couet, and D. Mantovani, Acta Biomater. 6, 1852 (2010).
A. Yamamoto, R. Honma, and M. Sumita, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 39, 331 (1998).
X. Gu, Y. Zheng, Y. Cheng, S. Zhong, and T. Xi, Biomaterials 30, 484 (2009).
K.A. Duck and J.R. Connor, Biometals 29, 573 (2016).
S. Zhu, N. Huang, L. Xu, Y. Zhang, H. Liu, H. Sun, and Y. Leng, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29, 1589 (2009).
Acknowledgements
Financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51874368).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, YC., Tang, Y., Zhao, MC. et al. Study on Fe-xGO Composites Prepared by Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure, Hardness, Biodegradation and Cytocompatibility. JOM 72, 1163–1174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03814-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03814-z