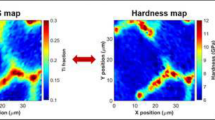
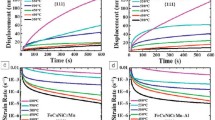
Abstract
Development of structural materials for service under extreme conditions is slowed by the lack of high-throughput test protocols. Here, a method that integrates high-throughput nanoindentation mapping with precise temperature control under a vacuum atmosphere is demonstrated. High-entropy alloys (HEAs) may possess the strength and stability required of high-temperature structural materials in next-generation nuclear applications. These alloys, including the compositional variation AlxFeCrNiMn (x = 0, 0.3, 1) presented in this work, have distinct microstructural morphologies, and nanoindentation mapping reveals the mechanical behavior of the distinct phases as a function of temperature up to 400°C. FeCrNiMn (Al = 0) consists of a face-centered cubic (FCC) matrix with body-centered cubic (BCC) precipitates and exhibits significant softening in both phases at elevated temperature. In contrast, both the FCC phase and FCC–BCC phases present in Al0.3FeCrNiMn show approximately 90% retention of the room temperature hardness at 400°C, and AlFeCrNiMn with BCC and B2 structures shows a similar 85% retention of hardness.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Cantor, I. Chang, P. Knight, and A. Vincent, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375, 213 (2004).
C. Lu, L. Niu, N. Chen, K. Jin, T. Yang, P. Xiu, Y. Zhang, F. Gao, H. Bei, and S. Shi, Nat. Commun. 7, 13564 (2016).
Y. Guérin, G.S. Was, and S.J. Zinkle, MRS Bull. 34, 10 (2009).
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299 (2004).
M. Laurent-Brocq, A. Akhatova, L. Perrière, S. Chebini, X. Sauvage, E. Leroy, and Y. Champion, Acta Mater. 88, 355 (2015).
Z. Li, K.G. Pradeep, Y. Deng, D. Raabe, and C.C. Tasan, Nature 534, 227 (2016).
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, and R.O. Ritchie, Science 345, 1153 (2014).
M.A. Hemphill, T. Yuan, G. Wang, J. Yeh, C. Tsai, A. Chuang, and P. Liaw, Acta Mater. 60, 5723 (2012).
D.B. Miracle and O.N. Senkov, Acta Mater. 122, 448 (2017).
Y. Zhang, G.M. Stocks, K. Jin, C. Lu, H. Bei, B.C. Sales, L. Wang, L.K. Béland, R.E. Stoller, and G.D. Samolyuk, Nat. Commun. 6, 8736 (2015).
F. Granberg, K. Nordlund, M.W. Ullah, K. Jin, C. Lu, H. Bei, L. Wang, F. Djurabekova, W. Weber, and Y. Zhang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 135504 (2016).
B. Kombaiah, K. Jin, H. Bei, P.D. Edmondson, and Y. Zhang, Mater. Des. 160, 1208 (2018).
O. El-Atwani, N. Li, M. Li, A. Devaraj, J. Baldwin, M. Schneider, D. Sobieraj, J. Wróbel, D. Nguyen-Manh, and S. Maloy, Sci. Adv. 5, eaav2002 (2019).
F. Otto, Y. Yang, H. Bei, and E.P. George, Acta Mater. 61, 2628 (2013).
O. Senkov, J. Miller, D. Miracle, and C. Woodward, Nat. Commun. 6, 6529 (2015).
Y.-F. Kao, T.-J. Chen, S.-K. Chen, and J.-W. Yeh, J. Alloys Compd. 488, 57 (2009).
N. Stepanov, D. Shaysultanov, R. Chernichenko, M. Tikhonovsky, and S. Zherebtsov, J. Alloys Compd. 770, 194 (2019).
O. Senkov, S. Senkova, and C. Woodward, Acta Mater. 68, 214 (2014).
F. Wang, Y. Zhang, and G. Chen, J. Alloys Compd. 478, 321 (2009).
T. Yang, S. Xia, S. Liu, C. Wang, S. Liu, Y. Fang, Y. Zhang, J. Xue, S. Yan, and Y. Wang, Sci. Rep. 6, 32146 (2016).
G.S. Was, Fundamentals of Radiation Materials Science: Metals and Alloys (Berlin: Springer, 2016).
W. Wen, L. Capolungo, A. Patra, and C. Tomé, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 48, 2603 (2017).
S.-T. Chen, W.-Y. Tang, Y.-F. Kuo, S.-Y. Chen, C.-H. Tsau, T.-T. Shun, and J.-W. Yeh, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 5818 (2010).
A. Munitz, L. Meshi, and M. Kaufman, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 689, 384 (2017).
E.D. Hintsala, U. Hangen, and D.D. Stauffer, JOM 70, 494 (2018).
U.D. Hangen, D.D. Stauffer, and S.S. Asif, Nanomechanical Analysis of High Performance Materials, Vol. 85 (Berlin: Springer, 2014).
K. Johnson, Contact Mechanics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1985).
K.P. Murphy, Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective (Cambridge: MIT Press, 2012).
F. Pedregosa, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, V. Michel, B. Thirion, O. Grisel, M. Blondel, P. Prettenhofer, R. Weiss, and V. Dubourg, J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825 (2011).
N.K. Kumar, C. Li, K. Leonard, H. Bei, and S. Zinkle, Acta Mater. 113, 230 (2016).
S.J. Zinkle and L.L. Snead, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 44, 241 (2014).
F. Otto, A. Dlouhý, C. Somsen, H. Bei, G. Eggeler, and E.P. George, Acta Mater. 61, 5743 (2013).
W.-R. Wang, W.-L. Wang, and J.-W. Yeh, J. Alloys Compd. 589, 143 (2014).
C.-Y. Hsu, C.-C. Juan, W.-R. Wang, T.-S. Sheu, J.-W. Yeh, and S.-K. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 3581 (2011).
C. Elkan. in Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03). 147.
Acknowledgements
NAM and Y. Chen gratefully acknowledge financial support from Bruker Nano Surfaces. This work was performed, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, an Office of Science User Facility operated for the US Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science. Los Alamos National Laboratory, an affirmative action equal opportunity employer, is managed by Triad National Security, LLC, for the US Department of Energy’s NNSA, under Contract 89233218CNA000001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Hintsala, E., Li, N. et al. High-Throughput Nanomechanical Screening of Phase-Specific and Temperature-Dependent Hardness in AlxFeCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 71, 3368–3377 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03714-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03714-2