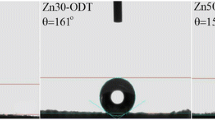
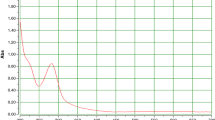
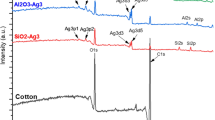
Abstract
Hospital fabrics are commonly exposed to multiple patients and contaminated surfaces between washing/sterilization cycles. Consequently, these textiles act as vectors for the spread of diseases, especially bacterial pathogens. Many modification schemes have been proposed to mitigate the growth and spread of bacteria on fabrics, including use of antimicrobial metal oxide nanoparticles. The aim of this study is to examine the effectiveness of conformal nanoscale ZnO coatings applied to cotton fabrics via atomic layer deposition to control bacterial spread. We find that, at low ZnO loading fractions, bacteria metabolize Zn2+ ions and reproduce more rapidly. However, as the ZnO loading is increased, the higher concentrations of Zn2+ overwhelm the bacteria and the nanocoatings become effective antibacterial treatments, killing all bacteria present. These results map out an important design space for implementing ZnO coatings as a potential antimicrobial treatment for textiles and other surfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mitchell, M. Spencer, and C. Edmiston Jr., J. Hosp. Infect. 90, 285 (2015).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Types of Healthcare-Associated Infections (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014, March 26). https://www.cdc.gov/hai/infectiontypes.html. Accessed 15 June 2018.
I. Perelshtein, A. Lipovsky, N. Perkas, T. Tzanov, M. Arguirova, M. Leseva, and A. Gedanken, Ultrason. Sonochem. 25, 82 (2015).
K.N. Kelly and J.R. Monson, Surg. (Oxf.) 30, 640 (2012).
L.S. Munoz-Price, K.L. Arheart, J.P. Mills, T. Cleary, D. DePascale, A. Jimenez, Y. Fajardo-Aquino, G. Coro, D.J. Birnbach, and D.A. Lubarsky, Am. J. Infect. Control 40, 245 (2012).
J.M. Nordstrom, K.A. Reynolds, and C.P. Gerba, Am. J. Infect. Control 40, 539 (2012).
G. Suleyman, G. Alangaden, and A.C. Bardossy, Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 20, 1 (2018).
J. Sawai, J. Microbiol. Methods 54, 177 (2003).
P.J.P. Espitia, N.F.F. Soares, J.S.R. Coimbra, N.J. de Andrade, R.S. Cruz, and E.A.A. Medeiros, Food Bioprocess Technol. 5, 1447 (2012).
P. Chandrangsu, C. Rensing, and J.D. Helmann, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15, 338 (2017).
A.A. Navarrete, E.V. Mellis, A. Escalas, L.N. Lemos, J.L. Junior, J.A. Quaggio, J. Zhou, and S.M. Tsai, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 236, 187 (2017).
M. Li, L. Zhu, and D. Lin, Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 1977 (2011).
K.M. Reddy, K. Feris, J. Bell, D.G. Wingett, C. Hanley, and A. Punnoose, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 213902 (2007).
W.A. Daoud and J.H. Xin, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 87, 953 (2004).
H. Zhang and G. Chen, Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 2905 (2009).
B. Mahltig, H. Haufe, and H. Böttcher, J. Mater. Chem. 15, 4385 (2005).
A. Yadav, V. Prasad, A.A. Kathe, S. Raj, D. Yadav, C. Sundaramoorthy, and N. Vigneshwaran, Bull. Mater. Sci. 29, 641 (2006).
B.A. Holt, S.A. Gregory, T. Sulchek, S. Yee, and M.D. Losego, A.C.S. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 7709 (2018).
M. Vasanthi, K. Ravichandran, N.J. Begum, G. Muruganantham, S. Snega, A. Panneerselvam, and P. Kavitha, Superlattices Microstruct. 55, 180 (2013).
A. Arunachalam, S. Dhanapandian, C. Manoharan, and G. Sivakumar, Spectrochim. Acta Part A 138, 105 (2015).
A.G. Cuevas, K. Balangcod, T. Balangcod, and A. Jasmin, Procedia Eng. 68, 537 (2013).
Y.Y. Xi, B.Q. Huang, A.B. Djurišić, C.M. Chan, F.C. Leung, W.K. Chan, and D.T. Au, Thin Solid Films 517, 6527 (2009).
G.J. Chi, S.W. Yao, J. Fan, W.G. Zhang, and H.Z. Wang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 157, 162 (2002).
N.A. Aal, F. Al-Hazmi, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, F. El-Tantawy, and F. Yakuphanoglu, Spectrochim. Acta Part A 135, 871 (2015).
K.H. Tam, A.B. Djurišić, C.M.N. Chan, Y.Y. Xi, C.W. Tse, Y.H. Leung, W.K. Chan, F.C.C. Leung, and D.W.T. Au, Thin Solid Films 516, 6167 (2008).
G.K. Hyde, K.J. Park, S.M. Stewart, J.P. Hinestroza, and G.N. Parsons, Langmuir 23, 9844 (2007).
G.K. Hyde, G. Scarel, J.C. Spagnola, Q. Peng, K. Lee, B. Gong, K.G. Roberts, K.M. Roth, C.A. Hanson, C.K. Devine, and S.M. Stewart, Langmuir 26, 2550 (2010).
K. Lee, J.S. Jur, D.H. Kim, and G.N. Parsons, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 30, 01A163 (2012).
S.M. George, Chem. Rev. 110, 111 (2010).
R.L. Puurunen, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 9 (2005).
B.D. Piercy and M.D. Losego, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 33, 043201 (2015).
E. Guziewicz, I.A. Kowalik, M. Godlewski, K. Kopalko, V. Osinniy, A. Wójcik, S. Yatsunenko, E. Łusakowska, W. Paszkowicz, and M. Guziewicz, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 033515 (2008).
S.K. Kim, C.S. Hwang, S.-H.K. Park, and S.J. Yun, Thin Solid Films 478, 103 (2005).
D. Price, A. Horrocks, M. Akalin, and A. Faroq, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 40, 511 (1997).
M. Yatagai and S.H. Zeronian, Cellulose 1, 205 (1994).
A.E. Shafei and A. Abou-Okeil, Carbohydr. Polym. 83, 920 (2011).
AATCC, TM100:2004 Assessment of Antibacterial Finishes on Textile Materials, Developed from American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (2004).
J. Jur, W.J. Sweet, C.J. Oldham, and G.N. Parsons, Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 1993 (2011).
D. Hojo, G. K. Hyde, J. Spagnola, and G. N. Parsons, MRS Online Proceedings Library, 1054 (2007).
S. Selvam, R. Rajiv Gandhi, J. Suresh, S. Gowri, S. Ravikumar, and M. Sundrarajan, Int. J. Pharm. 434, 366 (2012).
K. Hantke, Zinc Biochemistry, Physiology, and Homeostasis (Dordrecht: Springer, 2001), pp. 53–63.
N. Padmavathy and R. Vijayaraghavan, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9, 035004 (2008).
M.G. Palmgren, S. Clemens, L.E. Williams, U. Krämer, S. Borg, J.K. Schjørring, and D. Sanders, Trends Plant Sci. 13, 464 (2008).
B.A. Holt, M.C. Bellavia, D. Potter, D. White, S.R. Stowell, and T. Sulchek, Biomater. Sci. 5, 463 (2017).
M.L. Kääriäinen, C.K. Weiss, S. Ritz, S. Pütz, D.C. Cameron, V. Mailänder, and K. Landfester, Appl. Surf. Sci. 287, 375 (2013).
Acknowledgements
Funding for this project came from the Georgia Tech President’s Undergraduate Research Award (PURA), the Petit Bioengineering Undergraduate Research Fellowship, and the Roxanne D. Westendorf Undergraduate Research Fund. Additionally, this material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program under Grant No. DGE-1650044. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. Part of this research was conducted in Georgia Tech’s Materials Innovation & Learning Laboratory (The MILL), an uncommon “make and measure” space committed to elevating undergraduate research in materials science. This work was also performed in part at the Georgia Tech Institute for Electronics and Nanotechnology, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure, which is supported by the National Science Foundation (Grant No. ECCS-1542174). Finally, the authors thank Brandon D. Piercy for performing x-ray diffraction for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puvvada, R.U., Wooding, J.P., Bellavia, M.C. et al. Bacterial Growth and Death on Cotton Fabrics Conformally Coated with ZnO Thin Films of Varying Thicknesses via Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD). JOM 71, 178–184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3154-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3154-z