Abstract
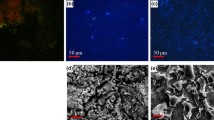
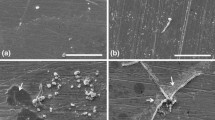
This work focuses on the localized forms of corrosion caused by microbiological activity, which have seldom been considered for long-term alteration processes of copper-based alloys. To reproduce a seldom-documented corrosion morphology found in some archaeological objects, called ‘tentacle like’, a Pseudomonas fluorescens strain was used on analogues of known composition in a solution containing sulfates, carbonates, nitrates and chlorides. The effect of such bacteria has already been assessed in a previous study, and a localized type of corrosion was defined. The results show that, when a biofilm grows on the surface of the samples, pits are observed under the corrosion products, while in the presence of chloride ions, these pits propagate under the metallic surface and into the matrix, forming uncommon morphologies ascribed to the type “tentacle like”.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Scott, Copper and Bronze in Art: Corrosion Colorants Conservation (Los Angeles: Getty Publications, 2002).
R.F. Tylecote, J. Archaeol. Sci. 6, 345 (1979).
M.C. Bernard and S. Joiret, Electrochim. Acta 54, 5199 (2009).
L. Robbiola, J.M. Blengino, and C. Fiaud, Corros. Sci. 40, 2083–2111 (1998).
C. Pearson, eds., Conservation of Marine Archaeological Objects (London: Butterworths, 1987).
D.A. Scott, J. Am. Inst. Conserv 29, 193 (1990).
P. Piccardo B. Mille, and L. Robbiola, in P. Dillmann, G. Beranger, P. Piccardo, and H. Matthiesen (eds) Corrosion of Metallic Heritage Artefacts—Investigation, Conservation and Prediction of Long-Term Behaviour (Woodhead, Cambridge, 2007) p. 239.
J. Redondo-Marugán, J. Piquero-Cilla, M.T. Doménech-Carbó, B. Ramírez-Barat, W. Al Sekhaneh, S. Capelo, and A. Doménech-Carbó, Electrochim. Acta 246, 269 (2017).
M. Bethencourt, T. Fernández-Montblanc, A. Izquierdo, M.M. González-Duarte, and C. Muñoz-Mas, Sci. Total Environm. 613–614, 98 (2018).
M.P. Casaletto, T. De Caro, G.M. Ingo, and C. Riccucci, Appl. Phys. A 83, 611 (2006).
A.M. Pollard, R.G. Thomas, and P.A. Williams, Stud. Conserv. 35, 148 (1990).
D.A. Scott, Stud. Conserv. 45, 39 (2000).
I.D. Macleod, J. Electroan Chme Interf Electrochem. 118, 291 (1981).
R.F. Tylecote, Int. J. Nautical Archaeol. Underwater Explor. 6, 269 (1977).
A. Sanchez del Junco, D.A. Moreno, C. Ranninger, J.J. Ortega-Calvo, and C. Saiz-Jimenez, Int. Biodet. Biodegrad. 29, 367 (1992).
C. Rémazeilles, M. Saheb, D. Neff, E. Guilminot, K. Tran, J.A. Bourdoiseau, R. Sabot, M. Jeannin, H. Matthiesen, P. Dillmann, and P. Refait, J. Raman Spectrosc. 41, 1425 (2010).
M.B. McNeil and B.J. Little, J. Am. Inst. Cons. 38, 186 (1999).
C. Rémazeilles, A. Dheilly, S. Sable, I. Lanneluc, D. Neff, and P. Refait, CEST 45, 388 (2010).
G.M. Ingo, T. de Caro, C. Riccucci, and S. Khosroff, Appl. Phys. A 83, 581 (2006).
P. Piccardo, M. Mödlinger, G. Ghiara, S. Campodonico, and V. Bongiorno, Appl. Phys. A 13, 1039 (2013).
G. Ghiara, C. Grande, S. Ferrando, and P. Piccardo, JOM 70, 81 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2674-2.
L.A. Giannuzzi and F.A. Stevie, eds., Introduction to Focused ion Beams. Instrumentation, Theory, Techniques and Practice (Boston: Springer Science and Business Media Inc., 2005).
L.A. Giannuzzi and F.A. Stevie, Micron 30, 197 (1999).
G. Characklis and K.C. Marshall, Biofilms (New York: Wiley, 1990).
B.J. Little, J.S. Lee, and R.I. Ray, Corrosion (Houston: NACE International, 2006).
X.C. Chen, W.X. Wu, J.Y. Shi, X.H. Xu, H. Wang, and Y.X. Chen, Colloids Surf. B 54, 46 (2001).
F. Ammeloot, C. Fiaud, and E.M.M. Sutter, Electrochim. Acta 44, 2549 (1999).
Acknowledgement
We thank American Journal Experts (AJE) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghiara, G., Repetto, L. & Piccardo, P. The Effect of Pseudomonas fluorescens on the Corrosion Morphology of Archaeological Tin Bronze Analogues. JOM 71, 779–783 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3138-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3138-z