Abstract
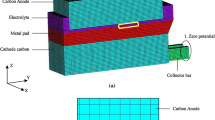
This study reports on an assessment of an anodic large bubble on the horizontal current in the metal pad of an aluminum electrolytic cell using a numerical model. The effects of bubble position and coverage on the horizontal current were investigated. The predicted results show that large bubbles have a significant impact on the horizontal current: The horizontal current with a bubble located at the right part of carbon anode (cell side) will provide coverage of 33.3% up to 30,174 A m−2 compared with 13,001 A m−2 without bubble at the upper surface of metal pad; For a fixed bubble position, the maximum horizontal current increases and the location of the maximum horizontal current density shifts from the anode center to the cell center with increasing the bubble coverage; The bubble position (for a fixed bubble coverage) significantly influences horizontal current. When the bubble varies from the cell center to the cell side, the maximum horizontal current density will increase and the location of the maximum horizontal current density shifts from the cell center to the cell side. When the whole anode is covered with a large bubble, a large inward horizontal current appears on the cell side and the maximum inward horizontal current can reach up to 35,575 A m−2.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.A. Davidson and R.I. Lindsay, J. Fluid Mech. 362, 327 (1998).
A. Furman, Light Metals 1978, ed. J.J. Miller (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1978), pp. 87–106.
H. Wintter and K. Lauer, U.S. patent, 3787311 (1974).
N.X. Feng, China patent, CN201110385777.0 (2012). (In Chinese)
W.J. Tao, T.F. Li, Z.W. Wang, B.L. Gao, Z.N. Shi, X.W. Hu, and J.Z. Cui, JOM 67, 929 (2015).
Y. Song, N.X. Feng, J.P. Peng, B.K. Li, and Q. Wang, Light Metals 2015, ed. M. Hyland (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2015), pp. 827–830.
T. Hudson, J. Huni, V. Potocnik, and D. MacMillan, U.S. patent, 4194959 (1980).
W.J. Tao, L. Wang, Z.W. Wang, B.L. Gao, Z.N. Shi, X.W. Hu, and J.Z. Cui, JOM 67, 322 (2015).
J. McGeer, U.S. patent, 4592820 (1986).
M. Gagnon, P. Goulet, R. Beeler, D. Ziegler, and M. Fafard, Light Metals 2013, ed. B. Sadler (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2013), pp. 621–626.
D. Townsend, U.S. patent 4795540 (1989).
A. Shenyang, Al and Mg Eng. Res. Inst., China Patent CN102453927A (2012) (in Chinese).
M. Blais, M. Desilets, and M. Lacroix, Appl. Therm. Eng. 58, 439 (2013).
K.J. Fraser, D. Billinghurst, K.L.Chen, and J.T. Keniry, Light Metals 1989, ed. P.G. Gampbell (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1989) pp. 219–226.
M.F. El-Demerdash, E.E. Khali, H.A. Ahmed, and S. Reda, Light Metals 1993, ed. S.K. Das (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1993) pp. 369–374.
X.Q. Qi, N.X. Feng, and J.Z. Cui, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 15, 931 (2005).
Y. Arita and H. Ikeuchi, Light Metals 1981, eds. C.J. McMinn, E.M. Adkins, and J.E. Andersen (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1981), pp. 357–371.
R.F. Robl, Light Metals 1983, ed. E.M. Adkins (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1983), pp. 449–456.
W.J. Tao, Z.W. Wang, B.L. Gao, Z.N. Shi, X.W. Hu, and J.Z. Cui, Metalurgija 53, 311 (2014).
M.A. Cooksey, M.P. Taylor, and J.J.J. Chen, JOM 51–57 (2008).
W. Haupin and H. Kvande, Light Metals 2000, ed. R.D. Peterson (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2000), pp. 379–384.
K. Qian and J.J.J. Chen, J. Appl. Electrochem. 27, 434 (1997).
K. Qian, Z.D. Chen, and J.J.J. Chen, J. Appl. Electrochem. 28, 1141 (1998).
K.Y. Zhang, Y.Q. Feng, P. Witt, W. Yang, M. Cooksey, Z.W. Wang, and M. Phil Schwarz, J. Appl. Electrochem. 44, 1081 (2014).
S. Fortin, M. Gerhardt and A.J. Gesing, Light Metals 1984, ed. J.P. McGeer (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1984), pp. 721–741.
B.L. Gao, X.W. Hu, J.L. Xu, Z.N. Shi, Z.W. Wang, and Z.X. Qiu, Light Metals 2006, ed. T.J. Galloway (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2006), pp. 467–470.
K.Y. Zhang, Y.Q. Feng, P. Schwarz, Z.W. Wang, and M. Cooksey, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 11378 (2013).
Y. Liu, Y.D. Li, T.A. Zhang, and N.X. Feng, JOM 66, 1202 (2014).
J.L. Xue and H.A. Oye, Light Metals 1995, ed. J.W. Evans (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1995), pp. 265–271.
M.A. Cooksey and W. Yang, Light Metals 2006, ed. T.J. Galloway (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2006), pp. 359–365.
K.Y. Zhang, Y. Q. Feng, P. Schwarz, M. Cooksey, and Z.W. Wang, Light Metals 2012, ed. C.E. Suarez (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2012), pp. 881–886.
Y.Q. Feng, M.A. Cooksey, and P. Schwarz, Light Metals 2007, ed. M. Sorlie (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2007), pp. 339–344.
R.J. Aaberg, V. Ranum, K. Williamson, and B.J. Welch, Light Metals 1997, ed. R. Huglen (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1997), pp. 341–346.
W.E. Haupin, Journal of Metals 23, 46 (1971).
E. Dewing, Can. Met. Quart. 30, 265 (1991).
Z.B. Zhao, Z.W. Wang, B.L. Gao, Y.Q. Feng, Z.N. Shi, and X.W. Hu, Light Metals 2015, ed. M. Hyland (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2015), pp. 801–806.
J. Zoric and A. Solheim, J. Appl. Electrochem. 30, 787 (2000).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude for the financial support by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2012BAE08B01), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51322406, 51434005, 51474060, 51574070, 51529401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, W., Li, T., Wang, Z. et al. A Numerical Assessment of Anodic Large Bubble on Horizontal Current in Metal Pad of Aluminum Electrolytic Cells. JOM 68, 600–609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1713-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1713-0